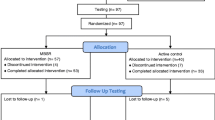
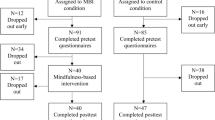
Abstract
To determine if mindfulness meditation (MM) in older adults improves cognition and, secondarily, if MM improves mental health and physiology, 134 at least mildly stressed 50–85-year olds were randomized to a 6-week MM intervention or a waitlist control. Outcome measures were assessed at baseline and 2 months later at visit 2. The primary outcome measure was an executive function/attentional measure (flanker task). Other outcome measures included additional cognitive assessments, salivary cortisol, respiratory rate, heart rate variability, Positive and Negative Affect Schedule (PANAS), Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression (CESD), Perceived Stress Scale (PSS), Neuroticism-Extraversion-Openness (NEO) personality traits, and SF-36 health-related quality of life. One hundred twenty-eight participants completed the study though visit 2 assessments. There was no significant change in the primary or other cognitive outcome measures. Even after statistical adjustment for multiple outcomes, self-rated measures related to negative affect and stress were all significantly improved in the MM intervention compared to waitlist group (PANAS-negative, CESD, PSS, and SF-36 health-related quality of life Vitality and Mental Health Component). The SF-36 Mental Health Component score improved more than the minimum clinically important difference. There were also significant changes in personality traits such as Neuroticism. Changes in positive affect were not observed. There were no group differences in salivary cortisol or heart rate variability. These moderate-sized improvements in self-rated measures were not paralleled by improvements in cognitive function or physiological measures. Potential explanations for this discrepancy in stress-related outcomes are discussed to help improve future studies.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott, R. A., Whear, R., Rodgers, L. R., Bethel, A., Thompson Coon, J., Kuyken, W.,…Dickens, C. (2014). Effectiveness of mindfulness-based stress reduction and mindfulness based cognitive therapy in vascular disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 76(5), 341–351. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2014.02.012
Astin, J. A. (1997). Stress reduction through mindfulness meditation. Effects on psychological symptomatology, sense of control, and spiritual experiences. Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics, 66(2), 97–106. doi:10.1159/000289116.
Baer, R. A., Smith, G. T., & Allen, K. B. (2004). Assessment of mindfulness by self-report: the Kentucky Inventory of mindfulness skills. Assessment, 11(3), 191–206.
Baer, R. A., Smith, G. T., Hopkins, J., Krietmeyer, J., & Toney, L. (2006). Using self-report assessment methods to explore facets of mindfulness. Assessment, 13, 27–45. doi:10.1177/1073191105283504.
Barlow, D. H., Ellard, K. K., Sauer-Zavala, S., Bullis, J. R., & Carl, J. R. (2014). The origins of neuroticism. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 9(5), 481–496. doi:10.1177/1745691614544528.
Benjamini, Y., & Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological), 57(289–300).
Benton, A. L., & Hamsher, K. D. S. (1989). Multilingual aphasia examination. Iowa City: AJA Associates.
Brookmeyer, R., Gray, S., & Kawas, C. (1998). Projections of Alzheimer’s disease in the United States and the public health impact of delaying disease onset. American Journal of Public Health, 88(9), 1337–1342.
Brown, K. W., & Ryan, R. M. (2003). The benefits of being present: mindfulness and its role in psychological well-being. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 84, 822–848.
Buysse, D. J., Reynolds, C. F., Monk, T. H., Berman, S. R., & Kupfer, D. J. (1989). The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: a new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatric Research, 28(2), 192–213. doi:10.1016/0165-1781(89)90047-4.
Caspi, A., Hariri, A. R., Holmes, A., Uher, R., & Moffitt, T. E. (2010). Genetic sensitivity to the environment: the case of the serotonin transporter gene and its implications for studying complex diseases and traits. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 167(5), 509–527. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2010.09101452.
Cherkin, D., Deyo, R. A., & Berg, A. O. (1991). Evaluation of a physician intervention to improve primary care for low-back pain: II. Impact on patients. Spine, 16, 1173–1178.
Chiesa, A., & Serretti, A. (2010). A systematic review of neurobiological and clinical features of mindfulness meditations. Psychological Medicine, 40, 1239–1252. doi:10.1017/S0033291709991747.
Chiesa, A., Calati, R., & Serretti, A. (2011). Does mindfulness training improve cognitive abilities? A systematic review of neuropsychological findings. Clinical Psychology Review, 31(3), 449–464. doi:10.1016/j.cpr.2010.11.003.
Cohen, S., Karmarck, T., & Mermelstein, R. (1983). A global measure of perceived stress. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 24, 385–396.
Costa, P. T., & McCrae, R. R. (2010). NEO inventories: professional manual. Lutz: Psychological Assessment Resources, Inc.
Coteur, G., Feagan, B., Keininger, D. L., & Kosinski, M. (2009). Evaluation of the meaningfulness of health-related quality of life improvements as assessed by the SF-36 and the EQ-5D VAS in patients with active Crohn’s disease. Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 29(9), 1032–1041. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2009.03966.x.
Davidson, R. J., & McEwen, B. S. (2012). Social influences on neuroplasticity: stress and interventions to promote well-being. Nature Neuroscience, 15(5), 689–695. doi:10.1038/nn.3093.
Daviglus, M.L., Bell, C.C., Berrettini, W., Bowen, P.E., Connolly, E.S., Cox, N.J.,…Trevisan, M. (2010). NIH state-of-the-science conference statement: preventing Alzheimer’s disease and cognitive decline. NIH Consensus State of the Science Statements, 27(4), 1–30.
DeRubeis, R. J., Siegle, G. J., & Hollon, S. D. (2008). Cognitive therapy versus medication for depression: treatment outcomes and neural mechanisms. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 9(10), 788–796. doi:10.1038/nrn2345.
Devilly, G. J., & Borkovec, T. D. (2000). Psychometric properties of the credibility/expectancy questionnaire. Journal of Behavioral Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 31, 73–86. doi:10.1016/S0005-7916(00)00012-4.
Esch, T., Stefano, G. B., Fricchione, G. L., & Benson, H. (2002). The role of stress in neurodegenerative diseases and mental disorders. Neuroendocrinology Letters, 23(3), 199–208.
Evans, G. W., & Schamberg, M. A. (2009). Childhood poverty, chronic stress, and adult working memory. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 106, 6545–6549. doi:10.1073/pnas.0811910106.
Gard, T., Holzel, B. K., & Lazar, S. W. (2014). The potential effects of meditation on age-related cognitive decline: a systematic review. The Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1307, 89–103. doi:10.1111/nyas.12348.
Golden, C. J. (2002). Stroop color and word test manual. Wood Dale: Stoelting Co.
Goyal, M., Singh, S., Sibinga, E. M., Gould, N. F., Rowland-Seymour, A., Sharma, R.,…Haythornthwaite, J. A. (2014a). Meditation programs for psychological stress and well-being: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Internal Medicine. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.13018
Goyal, M., Singh, S., Sibinga, E. M., Gould, N. F., Rowland-Seymour, A., Sharma, R.,…Haythornthwaite, J. A. (2014b). Meditation programs for psychological stress and well-being: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Internal Medicine, 174(3), 357–368. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.13018
Grossman, P., Niemann, L., Schmidt, S., & Walach, H. (2004). Mindfulness-based stress reduction and health benefits: a meta-analysis. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 57(1), 35–43. doi:10.1016/S0022-3999(03)00573-7.
Hasenkamp, W., Wilson-Mendenhall, C. D., Duncan, E., & Barsalou, L. W. (2012). Mind wandering and attention during focused meditation: a fine-grained temporal analysis of fluctuating cognitive states. NeuroImage, 59(1), 750–760. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.07.008.
Hrobjartsson, A., & Gotzsche, P. C. (2001). Is the placebo powerless? An analysis of clinical trials comparing placebo with no treatment. The New England Journal of Medicine, 344(21), 1594–1620. doi:10.1056/NEJM200105243442106.
Hruschka, D. J., Kohrt, B. A., & Worthman, C. M. (2005). Estimating between- and within-individual variation in cortisol levels using multilevel models. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 30(7), 698–714. doi:10.1016/j.psyneuen.2005.03.002.
Hurd, M. D., Martorell, P., Delavande, A., Mullen, K. J., & Langa, K. M. (2013). Monetary costs of dementia in the United States. The New England Journal of Medicine, 368(14), 1326–1334. doi:10.1056/NEJMsa1204629.
Institute of Medicine (U.S.). Committee on the public health dimensions of cognitive aging, Blazer, Dan G., Yaffe, Kristine, & Liverman, Catharyn T. (2015). Cognitive aging: progress in understanding and opportunities for action. National Academies Press.
Jacobs, T. L., Epel, E. S., Lin, J., Blackburn, E. H., Wolkowitz, O. M., Bridwell, D. A.,…Saron, C. D. (2011). Intensive meditation training, immune cell telomerase activity, and psychological mediators. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 36(5), 664–681. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2010.09.010
Jha, A. P., Krompinger, J., & Baime, M. J. (2007). Mindfulness training modifies subsystems of attention. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 7(2), 109–119. doi:10.3758/CABN.7.2.109.
Jha, A. P., Stanley, E. A., Kiyonaga, A., Wong, L., & Gelfand, L. (2010). Examining the protective effects of mindfulness training on working memory capacity and affective experience. Emotion, 10(1), 54–64. doi:10.1037/a0018438.
Juster, R. P., McEwen, B. S., & Lupien, S. J. (2009). Allostatic load biomarkers of chronic stress and impact on health and cognition. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews. doi:10.1016/neubiorev.2009.10.002.
Kabat-Zinn, J. (1982). An outpatient program in behavioral medicine for chronic pain patients based on the practice of mindfulness meditation: theoretical considerations and preliminary results. General Hospital Psychiatry, 4(1), 33–47. doi:10.1016/0163-8343(82)90026-3.
Kabat-Zinn, J., Massion, A. O., Kristeller, J., Peterson, L. G., Fletcher, K. E., Pbert, L.,…Santorelli, S. F. (1992). Effectiveness of a meditation-based stress reduction program in the treatment of anxiety disorders. Am J Psychiatry, 149(7), 936–943.
Kaul, P., Passafiume, J., Sargent, C. R., & O’Hara, B. F. (2010). Meditation acutely improves psychomotor vigilance, and may decrease sleep need. Behavioral and Brain Functions, 6, 47. doi:10.1186/1744-9081-6-47.
Khoury, B., Lecomte, T., Fortin, G., Masse, M., Therien, P., Bouchard, V.,…Hofmann, S. G. (2013). Mindfulness-based therapy: a comprehensive meta-analysis. Clinical Psychology Review, 33(6), 763–771. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2013.05.005
Kirsch, I. (2010). The emperor’s new drugs: exploding the antidepressant myth. New York: Basic Books.
Knopman, D. S., Roberts, R. O., Geda, Y. E., Pankratz, V. S., Christianson, T. J., Petersen, R. C., & Rocca, W. A. (2010). Validation of the telephone interview for cognitive status-modified in subjects with normal cognition, mild cognitive impairment, or dementia. Neuroepidemiology, 34(1), 34–42. doi:10.1159/000255464.
Kraemer, H. C., Giese-Davis, J., Yutsis, M., O’Hara, R., Neri, E., Gallagher-Thompson, D.,…Spiegel, D. (2006). Design decisions to optimize reliability of daytime cortisol slopes in an older population. The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 14(4), 325–333. doi: 10.1097/01.JGP.0000201816.26786.5b
Kremen, W. S., Lachman, M. E., Pruessner, J. C., Sliwinski, M., & Wilson, R. S. (2012). Mechanisms of age-related cognitive change and targets for intervention: social interactions and stress. Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, 67(7), 760–765. doi:10.1093/gerona/gls125.
Lahey, B. B. (2009). Public health significance of neuroticism. The American Psychologist, 64(4), 241–256. doi:10.1037/a0015309.
Lupien, S. J., Nair, N. P. V., Briere, S., Maheu, F., Tu, M. T., Lemay, M.,…Meaney, M. J. (1999). Increased cortisol levels and impaired cognition in human aging: implication for depression and dementia later in life. Reviews in the Neurosciences, 10(2), 117–139. doi: 10.1515/REVNEURO.1999.10.2.117
Lupien, S. J., McEwen, B. S., Gunnar, M. R., & Heim, C. (2009). Effects of stress throughout the lifespan on the brain, behaviour and cognition. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 10(6), 434–445. doi:10.1038/nrn2639.
McEwen, B. S. (1998). Protective and damaging effects of stress mediators. The New England Journal of Medicine, 338(3), 171–179. doi:10.1056/NEJM199801153380307.
Mobus, G.E., & Kalton, M.C. (2015). Principles of systems science. New York: Springer.
Moore, A., Gruber, T., Derose, J., & Malinowski, P. (2012). Regular, brief mindfulness meditation practice improves electrophysiological markers of attentional control. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 6, 18. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2012.00018.
Morris, J., Heyman, A., Mohs, R., & Hughes, M. (1989). The Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer’s Disease (CERAD) part 1. Clinical and neuropsychological assessment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology, 39, 1159–1165. doi:10.1212/WNL.39.9.1159.
Moynihan, J. A., Chapman, B. P., Klorman, R., Krasner, M. S., Duberstein, P. R., Brown, K. W., & Talbot, N. L. (2013). Mindfulness-based stress reduction for older adults: effects on executive function, frontal alpha asymmetry and immune function. Neuropsychobiology, 68(1), 34–43. doi:10.1159/000350949.
Mukherjee, S., Yadav, R., Yung, I., Zajdel, D., & Oken, B. S. (2011). Sensitivity to mental effort and test-retest reliability of heart rate variability measures in healthy seniors. Clinical Neurophysiology, 122, 2059–2066. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2011.02.032.
Neuendorf, R., Wahbeh, H., Chaime, I., Yu, J., Hutshison, K., & Oken, B. S. (2015a). The effects of mind-body interventions on sleep quality: a systematic review. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. doi:10.1155/2015/902708.
Neuendorf, R., Wahbeh, H., Chamine, I., Yu, J., Hutchison, K., & Oken, B. S. (2015b). The effects of mind-body interventions on sleep quality: a systematic review. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2015, 902708. doi:10.1155/2015/902708.
NPR, Foundation, Robert Wood Johnson, & Health, Harvard School of Public. (2014). The Burden of Stress in America. http://www.rwjf.org/content/dam/farm/reports/surveys_and_polls/2014/rwjf414295
Oken, B. S. (2008). Placebo effects: clinical aspects and neurobiology. Brain, 131, 2812–2823. doi:10.1093/brain/awn116.
Oken, B.S., Kishiyama, S., Zajdel, D, Bourdette, D., Carlsen, J., Haas, M.,…Mass, M. (2004). Randomized controlled trial of yoga and exercise in multiple sclerosis. Neurology, 62(11), 2058–2064. doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000129534.88602.5C
Oken, B.S., Zajdel, D., Kishiyama, S., Flegal, K., Dehen, C., Haas, M.,…Leyva, J. (2006). Randomized controlled 6-month trial of yoga in healthy seniors. Alternative Therapies in Health and Medicine, 12(1), 40–47.
Oken, B. S., Flegal, K., Zajdel, D., Kishiyama, S., Haas, M., & Peters, D. (2008). Expectancy effect: impact of pill administration on cognitive performance in healthy seniors. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 30, 7–17. doi:10.1080/13803390701775428.
Oken, B. S., Fonareva, I., Haas, M., Wahbeh, H., Lane, J. B., Zajdel, D. P., & Amen, A. M. (2010). Pilot controlled trial of mindfulness meditation and education for dementia caregivers. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 16, 1031–1038.
Oken, B. S., Fonareva, I., & Wahbeh, H. (2011). Stress-related cognitive dysfunction in dementia caregivers. Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry and Neurology, 24, 192–199. doi:10.1177/0891988711422524.
Oken, B. S., Chamine, I., & Wakeland, W. (2015). A systems approach to stress, stressors, and resilience in humans. Behavioural Neuroscience, 282, 144–154. doi:10.1155/2015/902708.
Ospina, M.B., Bond, K., Karkhaneh, M., et al. (2007). Meditation practices for health: state of the research (AHRQ). Evidence Report/Technology Assessment (Full Report), Number 155, Publication No. 07-E010., 1-263.
Ottaviani, C., Shahabi, L., Tarvainen, M., Cook, I., Abrams, M., & Shapiro, D. (2014). Cognitive, behavioral, and autonomic correlates of mind wandering and perseverative cognition in major depression. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 8, 433. doi:10.3389/fnins.2014.00433.
Ottaviani, C., Thayer, J. F., Verkuil, B., Lonigro, A., Medea, B., Couyoumdjian, A., & Brosschot, J. F. (2016). Physiological concomitants of perseverative cognition: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 142(3), 231–259. doi:10.1037/bul0000036.
Ownby, R. L., Crocco, E., Acevedo, A., John, V., & Loewenstein, D. (2006). Depression and risk for Alzheimer disease: systematic review, meta-analysis, and metaregression analysis. Archives of General Psychiatry, 63(5), 530–538. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.63.5.530.
Plassman, B. L., Langa, K. M., Fisher, G. G., Heeringa, S. G., Weir, D. R., Ofstedal, M. B.,…Wallace, R. B. (2007). Prevalence of dementia in the United States: the aging, demographics, and memory study. Neuroepidemiology, 29(1-2), 125–132. doi: 10.1159/000109998
Plassman, B. L., Langa, K. M., Fisher, G. G., Heeringa, S. G., Weir, D. R., Ofstedal, M. B.,…Wallace, R. B. (2008). Prevalence of cognitive impairment without dementia in the United States. Annals of Internal Medicine, 148(6), 427–434. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-148-6-200803180-00005
Pocock, S. J., & Simon, R. (1975). Sequential treatment assignment with balancing for prognostic factors in the controlled clinical trial. Biometrics, 31, 103–115. doi:10.2307/2529712.
Radloff, L. (1977). The CES-D scale: a self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Applied Psychological Measurement, 1, 385–401. doi:10.1177/014662167700100306.
Schwarzer, R., & Jerusalem, M. (1995). Generalized self-efficacy scale. In J. Weinman, S. Wright, & M. Johnston (Eds.), Measures in health psychology: a user’s portfolio. Causal and control beliefs (pp. 35–37). Windsor: Nfer-Nelson.
Seeman, T. E., McEwen, B. S., Rowe, J. W., & Singer, B. H. (2001). Allostatic load as a marker of cumulative biological risk: MacArthur studies of successful aging. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 98, 4770–4775. doi:10.1073/pnas.081072698.
Segal, Z. V., Williams, J. M. G., & Teasdale, J. D. (2002). Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy for depression: a new approach to preventing relapse. New York: Guilford.
Segerstrom, S. C., Boggero, I. A., Smith, G. T., & Sephton, S. E. (2014). Variability and reliability of diurnal cortisol in younger and older adults: implications for design decisions. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 49, 299–309. doi:10.1016/j.psyneuen.2014.07.022.
Semple, R. J. (2010). Does mindfulness meditation enhance attention? A randomized controlled trial. Mindfulness, 1, 121–130. doi:10.1007/s12671-010-0017-2.
Shiffman, S., Stone, A. A., & Hufford, M. R. (2008). Ecological momentary assessment. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 4, 1–32. doi:10.1146/annurev.clinpsy.3.022806.091415.
Stawski, R. S., Sliwinski, M. J., & Smyth, J. M. (2006). Stress-related cognitive interference predicts cognitive function in old age. Psychology and Aging, 21, 535–544. doi:10.1037/0882-7974.21.3.535.
Tang, Y. Y., Ma, Y., Wang, J., Fan, Y., Feng, S., Lu, Q.,…Posner, M. I. (2007). Short-term meditation training improves attention and self-regulation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104(43), 17152–17156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0707678104
Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology, NASPE. (1996). Heart rate variability—standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use. Circulation, 93, 1043–1065.
Thayer, J. F., Friedman, B. H., & Borkovec, T. D. (1996). Autonomic characteristics of generalized anxiety disorder and worry. Biological Psychiatry, 39(4), 255–266. doi:10.1016/0006-3223(95)00136-0.
Wahbeh, H., & Oken, B. (2013). Salivary cortisol lower in posttraumatic stress disorder. Journal of Traumatic Stress, 26, 1–8. doi:10.1002/jts.21798.
Wahbeh, H., Kishiyama, S., Zajdel, D., & Oken, B. (2008). Salivary cortisol awakening response in mild Alzheimer’s disease, caregivers, and non-caregivers. Alzheimer’s Disease & Related Disorders, 22, 181–183. doi:10.1097/WAD.0b013e31815a9dff.
Wahbeh, H., Zwickey, H., & Oken, B. (2011). One method for objective adherence measurement in mind-body medicine. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 17, 1–3. doi:10.1089/acm.2010.0316.
Wahbeh, H., Lane, J. B., Goodrich, E., Miller, M., & Oken, B. S. (2014a). One-on-one mindfulness meditation trainings in a research setting. Mindfulness, 5, 88–99. doi:10.1007/s12671-012-0155-9.
Wahbeh, H., Svalina, M. N., & Oken, B. S. (2014b). Group, one-on-one, or internet?: preferences for mindfulness meditation delivery format and their predictors. Open Medicine Journal, 1, 66–74.
Wahbeh, H., Goodrich, E., Goy, E., & Oken, B. S. (2016). Mechanistic pathways of mindfulness meditation in combat veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 72, 365–383.
Walach, H. (2001). The efficacy paradox in randomized controlled trials of CAM and elsewhere: beware of the placebo trap. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 7, 213–218.
Ware, J. E. (1993). SF-36 health survey: manual interpretation guide. Boston: The Health Institute.
Ware, J. E. (2000). SF-36 health survey update. Spine, 25(24), 3130–3139.
Watson, D., Clark, L. A., & Tellegen, A. (1988). Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: the PANAS scales. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54(6), 1063–1070. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.54.6.1063.
Wechsler, D. (2008). Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (4th ed.). San Antonio: Pearson.
White, L., Small, B. J., Petrovitch, H., Ross, G. W., Masaki, K., Abbott, R. D.,…Markesbery, W. (2005). Recent clinical-pathologic research on the causes of dementia in late life: update from the Honolulu-Asia Aging Study. Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry and Neurology, 18(4), 224–227. doi: 10.1177/0891988705281872
Wilson, R. S., Evans, D. A., Bienias, J. L., Mendes De Leon, C. F., Schneider, J. A., & Bennett, D. A. (2003). Proneness to psychological distress is associated with risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology, 61(11), 1479–1485. doi:10.1212/01.WNL.0000096167.56734.59.
Wilson, R. S., Arnold, S. E., Schneider, J. A., Li, Y., & Bennett, D. A. (2007). Chronic distress, age-related neuropathology, and late-life dementia. Psychosomatic Medicine, 69(1), 47–53. doi:10.1097/01.psy.0000250264.25017.21.
Wilson, R. S., Begeny, C. T., Boyle, P. A., Schneider, J. A., & Bennett, D. A. (2011). Vulnerability to stress, anxiety, and development of dementia in old age. The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 19(4), 327–334. doi:10.1097/JGP.0b013e31820119da.
Zeidan, F., Johnson, S. K., Diamond, B. J., David, Z., & Goolkasian, P. (2010). Mindfulness meditation improves cognition: evidence of brief mental training. Consciousness and Cognition, 19(2), 597–605. doi:10.1016/j.concog.2010.03.014.
Acknowledgments
Roger Ellingson is acknowledged for engineering support. Jeff Proulx helped edit the paper. Preliminary results were presented at the International Conference on Integrative Medicine and Health 2016 annual meeting.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
There were no conflicts of interest by any authors. This study was funded in part by Oregon Health & Science University and by grants from National Institutes of Health (AT005121 and UL1TR000128).
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oken, B.S., Wahbeh, H., Goodrich, E. et al. Meditation in Stressed Older Adults: Improvements in Self-Rated Mental Health Not Paralleled by Improvements in Cognitive Function or Physiological Measures. Mindfulness 8, 627–638 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-016-0640-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-016-0640-7