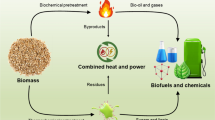
Abstract
A large number of potential technological alternatives exist for the development of microalgal biorefinery to produce a variety of end-products from microalgal biomass and their residues. The design of the promising biorefinery configurations considering preliminary and uncertain nature of technologies is one of the major biorefinery challenges, and it must be addressed systematically. This article presents key issues, challenges and opportunities for the modeling and optimization of microalgae-based biorefinery configurations. It reviews the processing pathways/networks for producing biofuels and various platform chemicals from microalgae with an emphasis on the development of the systematic modeling framework. Superstructure-based modeling and optimization can be a useful tool to identify the optimal/promising biorefinery configurations. Key components of the superstructure-based modeling framework are described, along with a comprehensive review of the existing studies on the superstructure-based optimization of biofuels/bioenergy production from microalgae. This paper also identifies potential perspectives for future research focusing on the application of the superstructure-based approach for the systematic design of sustainable microalgal biorefineries. Perspectives on the future integrated biorefineries considering carbon mitigation as well as heat and power integration are presented. Issues on sustainability and uncertainties modeling in the biorefinery design phase are also discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harun, R., Singh, M., Forde, G.M., Danquah, M.K.: Bioprocess engineering of microalgae to produce a variety of consumer products. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 14(3), 1037–1047 (2010)
Borowitzka, M.A.: High-value products from microalgae—their development and commercialisation. J. Appl. Phycol. 25(3), 743–756 (2013)
Chisti, Y.: Biodiesel from microalgae. Biotechnol. Adv. 25(3), 294–306 (2007)
Li, Y., Horsman, M., Wu, N., Lan, C.Q., Dubois-Calero, N.: Biofuels from microalgae. Biotechnol. Progr. 24(4), 815–820 (2008)
Gouveia, L.: Microalgae as a Feedstock for Biofuels. Springer, Heidelberg (2011)
Posten, C., Schaub, G.: Microalgae and terrestrial biomass as source for fuels—a process view. J. Biotechnol. 142(1), 64–69 (2009)
Ahmad, A.L., Yasin, N.H.M., Derek, C.J.C., Lim, J.K.: Microalgae as a sustainable energy source for biodiesel production: a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 15(1), 584–593 (2011)
Suali, E., Sarbatly, R.: Conversion of microalgae to biofuel. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 16(6), 4316–4342 (2012)
Singh, J., Gu, S.: Commercialization potential of microalgae for biofuels production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 14(9), 2596–2610 (2010)
Pires, J.C.M., Alvim-Ferraz, M.C.M., Martins, F.G., Simões, M.: Carbon dioxide capture from flue gases using microalgae: engineering aspects and biorefinery concept. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 16(5), 3043–3053 (2012)
Rizwan, M.: Superstructure-based identification of optimal processing pathways for microalgae-based biorefinery. PhD Thesis, KAIST, South Korea (2015)
Gong, J., You, F.: Global optimization for sustainable design and synthesis of algae processing network for CO2 mitigation and biofuel production using life cycle optimization. AlChE J. 60(9), 3195–3210 (2014)
Pham, V., El-Halwagi, M.: Process synthesis and optimization of biorefinery configurations. AlChE J. 58(4), 1212–1221 (2012)
Romero-García, J.M., Niño, L., Martínez-Patiño, C., Álvarez, C., Castro, E., Negro, M.J.: Biorefinery based on olive biomass. State of the art and future trends. Bioresour. Technol. 159, 421–432 (2014)
Frombo, F., Minciardi, R., Robba, M., Rosso, F., Sacile, R.: A dynamic decision model for the optimal use of forest biomass for energy production. Energy Syst. 7(4), 615–635 (2016)
Nigam, P.S., Singh, A.: Production of liquid biofuels from renewable resources. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 37(1), 52–68 (2011)
Collet, P., Spinelli, D., Lardon, L., Hélias, A., Steyer, J.-P., Bernard, O.: Chapter 13—life-cycle assessment of microalgal-based biofuels. In: Lee, D.-J., Chisti, Y., Soccol, C.R. (eds.) Biofuels from Algae, pp. 287–312. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2014)
Yen, H.-W., Hu, I.C., Chen, C.-Y., Ho, S.-H., Lee, D.-J., Chang, J.-S.: Microalgae-based biorefinery—from biofuels to natural products. Bioresour. Technol. 135, 166–174 (2013)
Rawat, I., Ranjith Kumar, R., Mutanda, T., Bux, F.: Biodiesel from microalgae: a critical evaluation from laboratory to large scale production. Appl. Energy 103, 444–467 (2013)
Rizwan, M., Lee, J.H., Gani, R.: Optimal design of microalgae-based biorefinery: economics, opportunities and challenges. Appl. Energy 150, 69–79 (2015)
Rashid, N., Rehman, M.S.U., Han, J.-I.: Recycling and reuse of spent microalgal biomass for sustainable biofuels. Biochem. Eng. J. 75, 101–107 (2013)
Fresewinkel, M., Rosello, R., Wilhelm, C., Kruse, O., Hankamer, B., Posten, C.: Integration in microalgal bioprocess development: design of efficient, sustainable, and economic processes. Eng. Life Sci. 14(6), 560–573 (2014)
Khan, S.A., Rashmi Hussain, M.Z., Prasad, S., Banerjee, U.C.: Prospects of biodiesel production from microalgae in India. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 13(9), 2361–2372 (2009)
Schneider, R.C.S., Bjerk, T.R., Gressler, P.D., Souza, M.P., Corbellini, V.A., Lobo, E.A.: Potential production of biofuel from microalgae biomass produced in wastewater. In: Fang, Z. (ed.) Biodiesel—Feedstock, Production and Applications, pp. 3–24. InTech, Croatia (2012)
Zhu, L.: Biorefinery as a promising approach to promote microalgae industry: an innovative framework. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 41, 1376–1384 (2015)
Barsanti, L., Gualtieri, P.: Is exploitation of microalgae economically and energetically sustainable? Algal Res. 31, 107–115 (2018)
Poddar, T., Jagannath, A., Almansoori, A.: Use of reactive distillation in biodiesel production: a simulation-based comparison of energy requirements and profitability indicators. Appl. Energy 185, 985–997 (2017)
Demirbas, A.: Competitive liquid biofuels from biomass. Appl. Energy 88(1), 17–28 (2011)
Morrison, G.M., Parker, N.C., Witcover, J., Fulton, L.M., Pei, Y.: Comparison of supply and demand constraints on US biofuel expansion. Energy Strateg. Rev. 5, 42–47 (2014)
Raheem, A., Prinsen, P., Vuppaladadiyam, A.K., Zhao, M., Luque, R.: A review on sustainable microalgae based biofuel and bioenergy production: recent developments. J. Clean. Prod. 181, 42–59 (2018)
Najafi, G., Ghobadian, B., Yusaf, T.F.: Algae as a sustainable energy source for biofuel production in Iran: a case study. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 15(8), 3870–3876 (2011)
Rizwan, M., Lee, J.H., Gani, R.: Optimal processing pathway for the production of biodiesel from microalgal biomass: a superstructure based approach. Comput. Chem. Eng. 58, 305–314 (2013)
Pagliaro, M., Ciriminna, R., Kimura, H., Rossi, M., Della Pina, C.: From glycerol to value-added products. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46(24), 4434–4440 (2007)
Subhadra, B.G., Edwards, M.: Coproduct market analysis and water footprint of simulated commercial algal biorefineries. Appl. Energy 88(10), 3515–3523 (2011)
Moon, C., Ahn, J.-H., Kim, S.W., Sang, B.-I., Um, Y.: Effect of biodiesel-derived raw glycerol on 1,3-propanediol production by different microorganisms. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 161(1), 502–510 (2010)
Mu, Y., Teng, H., Zhang, D.-J., Wang, W., Xiu, Z.-L.: Microbial production of 1,3-propanediol by Klebsiella pneumoniae using crude glycerol from biodiesel preparations. Biotechnol. Lett. 28(21), 1755–1759 (2006)
Moncada, J., Jaramillo, J.J., Higuita, J.C., Younes, C., Cardona, C.A.: Production of bioethanol using Chlorella vulgaris cake: a technoeconomic and environmental assessment in the Colombian context. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 52(47), 16786–16794 (2013)
Holm-Nielsen, J.B., Al Seadi, T., Oleskowicz-Popiel, P.: The future of anaerobic digestion and biogas utilization. Bioresour. Technol. 100(22), 5478–5484 (2009)
Amaro, H.M., Macedo, Â.C., Malcata, F.X.: Microalgae: an alternative as sustainable source of biofuels? Energy 44(1), 158–166 (2012)
Uggetti, E., Sialve, B., Trably, E., Steyer, J.-P.: Integrating microalgae production with anaerobic digestion: a biorefinery approach. Biofuels, Bioprod. Biorefin. 8(4), 516–529 (2014)
Miao, X., Wu, Q., Yang, C.: Fast pyrolysis of microalgae to produce renewable fuels. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 71(2), 855–863 (2004)
Miao, X., Wu, Q.: High yield bio-oil production from fast pyrolysis by metabolic controlling of Chlorella protothecoides. J. Biotechnol. 110(1), 85–93 (2004)
Du, Z., Li, Y., Wang, X., Wan, Y., Chen, Q., Wang, C., Lin, X., Liu, Y., Chen, P., Ruan, R.: Microwave-assisted pyrolysis of microalgae for biofuel production. Bioresour. Technol. 102(7), 4890–4896 (2011)
Ghirardi, M.L., Zhang, L., Lee, J.W., Flynn, T., Seibert, M., Greenbaum, E., Melis, A.: Microalgae: a green source of renewable H2. Trends Biotechnol. 18(12), 506–511 (2000)
Rashid, N., Choi, W., Lee, K.: Optimization of two-staged bio-hydrogen production by immobilized Microcystis aeruginosa. Biomass Bioenergy 36, 241–249 (2012)
Ferreira, A.F., Ortigueira, J., Alves, L., Gouveia, L., Moura, P., Silva, C.M.: Energy requirement and CO2 emissions of bioH2 production from microalgal biomass. Biomass Bioenergy 49, 249–259 (2013)
Lv, P., Wu, C., Ma, L., Yuan, Z.: A study on the economic efficiency of hydrogen production from biomass residues in China. Renew. Energy 33(8), 1874–1879 (2008)
Yang, Z., Guo, R., Xu, X., Fan, X., Li, X.: Enhanced hydrogen production from lipid-extracted microalgal biomass residues through pretreatment. Int. J. Hydrog Energy 35(18), 9618–9623 (2010)
Suganya, T., Varman, M., Masjuki, H.H., Renganathan, S.: Macroalgae and microalgae as a potential source for commercial applications along with biofuels production: a biorefinery approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 55, 909–941 (2016)
Trivedi, J., Aila, M., Bangwal, D.P., Kaul, S., Garg, M.O.: Algae based biorefinery—how to make sense? Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 47, 295–307 (2015)
Brennan, L., Owende, P.: Biofuels from microalgae—a review of technologies for production, processing, and extractions of biofuels and co-products. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 14(2), 557–577 (2010)
Kim, J., Yoo, G., Lee, H., Lim, J., Kim, K., Kim, C.W., Park, M.S., Yang, J.-W.: Methods of downstream processing for the production of biodiesel from microalgae. Biotechnol. Adv. 31(6), 862–876 (2013)
Rizwan, M., Zaman, M., Lee, J.H., Gani, R.: Optimal processing pathway selection for microalgae-based biorefinery under uncertainty. Comput. Chem. Eng. 82, 362–373 (2015)
Brownbridge, G., Azadi, P., Smallbone, A., Bhave, A., Taylor, B., Kraft, M.: The future viability of algae-derived biodiesel under economic and technical uncertainties. Bioresour. Technol. 151, 166–173 (2014)
Liu, P., Pistikopoulos, E.N., Li, Z.: Energy systems engineering: methodologies and applications. Front. Energy Power Eng. China 4(2), 131–142 (2010)
Yue, D., You, F., Snyder, S.W.: Biomass-to-bioenergy and biofuel supply chain optimization: overview, key issues and challenges. Comput. Chem. Eng. 66, 36–56 (2014)
Yeomans, H., Grossmann, I.E.: A systematic modeling framework of superstructure optimization in process synthesis. Comput. Chem. Eng. 23(6), 709–731 (1999)
Grossmann, I.E.: Papers from the 25th CONICET international conference mixed-integer programming approach for the synthesis of integrated process flowsheets. Comput. Chem. Eng. 9(5), 463–482 (1985)
Grossmann, I.E.: Mixed-integer optimization techniques for algorithmic process synthesis. In: John, L.A. (ed.) Advances in Chemical Engineering, vol. 23, pp. 171–246. Academic Press, London (1996)
Farkas, T., Rev, E., Lelkes, Z.: Process flowsheet superstructures: structural multiplicity and redundancy: Part II: Ideal and binarily minimal MINLP representations. Comput. Chem. Eng. 29(10), 2198–2214 (2005)
Quaglia, A., Sarup, B., Sin, G., Gani, R.: Integrated business and engineering framework for synthesis and design of enterprise-wide processing networks. Comput. Chem. Eng. 38, 213–223 (2012)
Land, A.H., Doig, A.G.: An automatic method of solving discrete programming problems. Econometrica 28(3), 497–520 (1960)
Geoffrion, A.M.: Generalized benders decomposition. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 10(4), 237–260 (1972)
Duran, M.A., Grossmann, I.E.: An outer-approximation algorithm for a class of mixed-integer nonlinear programs. Math. Program. 36(3), 307–339 (1986)
Fletcher, R., Leyffer, S.: Solving mixed integer nonlinear programs by outer approximation. Math. Program. 66(1), 327–349 (1994)
Edgar, T.F., Himmelblau, D.M., Lasdon, L.S.: Optimization of Chemical Processes. McGraw-Hill, New York (2001)
Grossmann, I.E.: Mixed-integer nonlinear programming techniques for the synthesis of engineering systems. Res. Eng. Des. 1(3), 205–228 (1990)
Yuan, Z., Chen, B., Gani, R.: Applications of process synthesis: moving from conventional chemical processes towards biorefinery processes. Comput. Chem. Eng. 49, 217–229 (2013)
Alvarado-Morales, M., Terra, J., Gernaey, K.V., Woodley, J.M., Gani, R.: Biorefining: computer aided tools for sustainable design and analysis of bioethanol production. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 87(9), 1171–1183 (2009)
Bertran, M.-O., Frauzem, R., Sanchez-Arcilla, A.-S., Zhang, L., Woodley, J.M., Gani, R.: A generic methodology for processing route synthesis and design based on superstructure optimization. Comput. Chem. Eng. 106, 892–910 (2017)
Zondervan, E., Nawaz, M., de Haan, A.B., Woodley, J.M., Gani, R.: Optimal design of a multi-product biorefinery system. Comput. Chem. Eng. 35(9), 1752–1766 (2011)
Yuan, Z., Chen, B.: Process synthesis for addressing the sustainable energy systems and environmental issues. AlChE J. 58(11), 3370–3389 (2012)
Yılmaz, S., Selim, H.: A review on the methods for biomass to energy conversion systems design. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 25, 420–430 (2013)
Daoutidis, P., Kelloway, A., Marvin, W.A., Rangarajan, S., Torres, A.I.: Process systems engineering for biorefineries: new research vistas. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2(4), 442–447 (2013)
Rizwan, M., Lee, J.H., Gani, R.: Superstructure optimization of biodiesel production from microalgal biomass. IFAC Proc. Vol. 46(32), 111–116 (2013)
Gong, J., You, F.: Optimal design and synthesis of algal biorefinery processes for biological carbon sequestration and utilization with zero direct greenhouse gas emissions: MINLP model and global optimization algorithm. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 53(4), 1563–1579 (2014)
Yu, N., Dieu, L.T.J., Harvey, S., Lee, D.-Y.: Optimization of process configuration and strain selection for microalgae-based biodiesel production. Bioresour. Technol. 193, 25–34 (2015)
Gupta, S.S., Shastri, Y., Bhartiya, S.: Model-based optimisation of biodiesel production from microalgae. Comput. Chem. Eng. 89, 222–249 (2016)
Gupta, S.S., Shastri, Y., Bhartiya, S.: Optimization of integrated microalgal biorefinery producing fuel and value-added products. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 11(6), 1030–1050 (2017)
Martín, M., Grossmann, I.E.: Simultaneous optimization and heat integration for biodiesel production from cooking oil and algae. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 51(23), 7998–8014 (2012)
Slegers, P.M., Koetzier, B.J., Fasaei, F., Wijffels, R.H., van Straten, G., van Boxtel, A.J.B.: A model-based combinatorial optimisation approach for energy-efficient processing of microalgae. Algal Res. 5, 140–157 (2014)
Gebreslassie, B.H., Waymire, R., You, F.: Sustainable design and synthesis of algae-based biorefinery for simultaneous hydrocarbon biofuel production and carbon sequestration. AlChE J. 59(5), 1599–1621 (2013)
Nodooshan, K.G., Moraga, R.J., Chen, S.-J.G., Nguyen, C., Wang, Z., Mohseni, S.: Environmental and economic optimization of algal biofuel supply chain with multiple technological pathways. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 57(20), 6910–6925 (2018)
García Prieto, C.V., Ramos, F.D., Estrada, V., Villar, M.A., Diaz, M.S.: Optimization of an integrated algae-based biorefinery for the production of biodiesel, astaxanthin and PHB. Energy 139, 1159–1172 (2017)
IPCC: IPCC Special Report on Carbon Dioxide Capture and Storage: Prepared by Working Group III of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Metz, B., Davidson, O., de Coninck, H., Loos, M., Meyer, L. (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, New York (2005)
Thomson, D., Khare, A.: Carbon capture and storage (CCS) deployment—can Canada capitalize on experience? J. Technol. Manage. Innovation 3, 111–118 (2008)
Wennersten, R., Sun, Q., Li, H.: The future potential for Carbon Capture and Storage in climate change mitigation—an overview from perspectives of technology, economy and risk. J. Clean. Prod. 103, 724–736 (2015)
Singham, D.I., Cai, W., White, J.A.: Optimal carbon capture and storage contracts using historical CO2 emissions levels. Energy Syst. 6(3), 331–360 (2015)
DOE/NETL: DOE/NETL Carbon Dioxide Capture and Storage R&D Roadmap. US Department of Energy and National Energy Technology Laboratory (2010)
Huang, Y., Rebennack, S., Zheng, Q.P.: Techno-economic analysis and optimization models for carbon capture and storage: a survey. Energy Syst. 4(4), 315–353 (2013)
Gutiérrez-Arriaga, C.G., Serna-González, M., Ponce-Ortega, J.M., El-Halwagi, M.M.: Sustainable integration of algal biodiesel production with steam electric power plants for greenhouse gas mitigation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2(6), 1388–1403 (2014)
Olaizola, M.: Microalgal removal of CO2 from flue gases: changes in medium pH and flue gas composition do not appear to affect the photochemical yield of microalgal cultures. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 8(6), 360–367 (2003)
Ghorbani, A., Rahimpour, H.R., Ghasemi, Y., Zoughi, S., Rahimpour, M.R.: A review of carbon capture and sequestration in Iran: microalgal biofixation potential in Iran. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 35, 73–100 (2014)
Zhao, B., Su, Y.: Process effect of microalgal-carbon dioxide fixation and biomass production: a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 31, 121–132 (2014)
de Queiroz Fernandes Araújo, O., de Luiz Medeiros, J., Yokoyama, L., do Rosário Vaz Morgado, C.: Metrics for sustainability analysis of post-combustion abatement of CO2 emissions: Microalgae mediated routes and CCS (carbon capture and storage). Energy 92(3), 556–568 (2015)
Baral, S.S., Singh, K., Sharma, P.: The potential of sustainable algal biofuel production using CO2 from thermal power plant in India. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 49, 1061–1074 (2015)
Cheah, W.Y., Show, P.L., Chang, J.-S., Ling, T.C., Juan, J.C.: Biosequestration of atmospheric CO2 and flue gas-containing CO2 by microalgae. Bioresour. Technol. 184, 190–201 (2015)
Cuellar-Bermudez, S.P., Garcia-Perez, J.S., Rittmann, B.E., Parra-Saldivar, R.: Photosynthetic bioenergy utilizing CO2: an approach on flue gases utilization for third generation biofuels. J. Clean. Prod. 98, 53–65 (2015)
Zhao, B., Su, Y., Zhang, Y., Cui, G.: Carbon dioxide fixation and biomass production from combustion flue gas using energy microalgae. Energy 89, 347–357 (2015)
Gupta, S.S., Shastri, Y., Bhartiya, S.: Integrated microalgae biorefinery: impact of product demand profile and prospect of carbon capture. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 11(6), 1065–1076 (2017)
Rezvani, S., Moheimani, N.R., Bahri, P.A.: Techno-economic assessment of CO2 bio-fixation using microalgae in connection with three different state-of-the-art power plants. Comput. Chem. Eng. 84, 290–301 (2016)
Reen, C.S., Wayne, C.K., Loke, S.P., Jiun, Y.Y., Chyuan, O.H., Chuan, L.T., Jo-Shu, C.: Analysis of economic and environmental aspects of microalgae biorefinery for biofuels production: a review. Biotechnol. J. 13(6), 1700618 (2018)
Ng, R.T.L., Tay, D.H.S., Ng, D.K.S.: Simultaneous process synthesis, heat and power integration in a sustainable integrated biorefinery. Energy Fuels 26(12), 7316–7330 (2012)
Martín, M., Grossmann, I.E.: Optimal engineered algae composition for the integrated simultaneous production of bioethanol and biodiesel. AlChE J. 59(8), 2872–2883 (2013)
Hariskos, I., Posten, C.: Biorefinery of microalgae—opportunities and constraints for different production scenarios. Biotechnol. J. 9(6), 739–752 (2014)
Azapagic, A.: Life cycle assessment and its application to process selection, design and optimisation. Chem. Eng. J. 73(1), 1–21 (1999)
Azapagic, A., Clift, R.: The application of life cycle assessment to process optimisation. Comput. Chem. Eng. 23(10), 1509–1526 (1999)
Zaimes, G.G., Khanna, V.: Chapter 8—life cycle sustainability aspects of microalgal biofuels. In: Klemes, J. (ed.) Assessing and Measuring Environmental Impact and Sustainability, pp. 255–276. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford (2015)
Singh, A., Olsen, S.I.: A critical review of biochemical conversion, sustainability and life cycle assessment of algal biofuels. Appl. Energy 88(10), 3548–3555 (2011)
Quinn, J.C., Davis, R.: The potentials and challenges of algae based biofuels: a review of the techno-economic, life cycle, and resource assessment modeling. Bioresour. Technol. 184, 444–452 (2015)
Thomassen, G., Van Dael, M., Lemmens, B., Van Passel, S.: A review of the sustainability of algal-based biorefineries: towards an integrated assessment framework. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 68, 876–887 (2017)
Gong, J., You, F.: Value-added chemicals from microalgae: Greener, more economical, or both? ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 3(1), 82–96 (2015)
Rizwan, M., Lee, J.H., Gani, R.: Synthesis of optimal processing pathway for microalgae-based biorefinery under uncertainty. Comput. Aided Chem. Eng. 37, 2303–2308 (2015)
Birge, J.R., Louveaux, F.: Introduction to Stochastic Programming (Springer Series in Operation Research). Springer, New York (1999)
Dua, V., Pistikopoulos, E.N.: Optimization techniques for process synthesis and material design under uncertainty. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 76(3), 408–416 (1998)
Grossmann, I.E.: Enterprise-wide optimization: a new frontier in process systems engineering. AlChE J. 51(7), 1846–1857 (2005)
Karuppiah, R., Grossmann, I.E.: Global optimization of multiscenario mixed integer nonlinear programming models arising in the synthesis of integrated water networks under uncertainty. Comput. Chem. Eng. 32(1–2), 145–160 (2008)
Kim, J., Realff, M.J., Lee, J.H.: Optimal design and global sensitivity analysis of biomass supply chain networks for biofuels under uncertainty. Comput. Chem. Eng. 35(9), 1738–1751 (2011)
Gebreslassie, B.H., Yao, Y., You, F.: Design under uncertainty of hydrocarbon biorefinery supply chains: multiobjective stochastic programming models, decomposition algorithm, and a comparison between CVaR and downside risk. AlChE J. 58(7), 2155–2179 (2012)
Quaglia, A., Sarup, B., Sin, G., Gani, R.: A systematic framework for enterprise-wide optimization: synthesis and design of processing networks under uncertainty. Comput. Chem. Eng. 59, 47–62 (2013)
Tang, M.C., Chin, M.W.S., Lim, K.M., Mun, Y.S., Ng, R.T.L., Tay, D.H.S., Ng, D.K.S.: Systematic approach for conceptual design of an integrated biorefinery with uncertainties. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 15(5), 783–799 (2013)
Cheali, P., Quaglia, A., Gernaey, K.V., Sin, G.: Effect of market price uncertainties on the design of optimal biorefinery systems—a systematic approach. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 53(14), 6021–6032 (2014)
Gong, J., You, F.: Optimal processing network design under uncertainty for producing fuels and value-added bioproducts from microalgae: two-stage adaptive robust mixed integer fractional programming model and computationally efficient solution algorithm. AlChE J. 63(2), 582–600 (2017)
Sy, C.L., Ubando, A.T., Aviso, K.B., Tan, R.R.: Multi-objective target oriented robust optimization for the design of an integrated biorefinery. J. Clean. Prod. 170, 496–509 (2018)
Mulvey, J.M., Vanderbei, R.J., Zenios, S.A.: Robust optimization of large-scale systems. Oper. Res. 43(2), 264–281 (1995)
Gabrel, V., Murat, C., Thiele, A.: Recent advances in robust optimization: an overview. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 235(3), 471–483 (2014)
Rockafellar, R.T., Uryasev, S.: Conditional value-at-risk for general loss distributions. J. Bank. Financ. 26(7), 1443–1471 (2002)
Eppen, G.D., Martin, R.K., Scharge, L.: OR practice—a scenario approach to capacity planning. Oper. Res. 37(4), 517–527 (1989)
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the research office of the Petroleum Institute, Abu Dhabi for providing the financial support for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rizwan, M., Almansoori, A. & Elkamel, A. An overview on synthesis and design of microalgal biorefinery configurations by employing superstructure-based optimization approach. Energy Syst 10, 941–966 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12667-018-0296-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12667-018-0296-6