Abstract
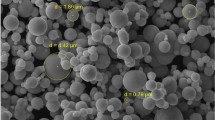
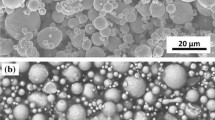
In this study, the effect of powder loading of 4605 low-alloy steel has been investigated on the rheological and mechanical properties of the final part manufactured by metal injection molding process. For this, two binder systems consisting of different percentages of paraffin wax (PW), polypropylene (PP), carnauba wax (CW) and stearic acid (SA) have been compounded with 55, 60 and 65 vol% of the powder. The manufactured samples were then tested for tensile, hardness, density and rheological properties. The results showed that with the increase in the powder loading, the tensile strength, hardness and density increase. It was observed that the higher percentage of the backbone polymer and surfactant resulted in higher mechanical properties of the final part. The optimum was made using the feedstock consisting of 55 wt% PW, 25 wt% PP, 15 wt% CW and 5 wt% SA along with 65 vol% of powder loading.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
German R M, Powder Injection Molding, Metal Powder Industries Federation, Princeton, New Jersey (1990), p 521.
German R, and Hens K F, Ceram. Bull 70 (1991) 1294.
Supati R, Loh N H, and Khor K A, Tor S B, Mater Lett 46 (2006) 109.
Westcot E J, Andrandall C B, and German M, Powder Metall 46 (2003) 61.
Liu L, Loh N H, Tay B Y, Tor S B, Murakoshi Y, and Maeda R, Mater Charact 54 (2005) 230.
Li Y, Li L, and Khalil K A, J Mater Process Technol 183 (2007) 432.
Sotomayor M E, Várez A, and Levenfeld, B Powder Technol 200 (2010) 30.
Sotomayor M E, Levenfeld B, and Várez A, Mater Sci Eng A 528 (2011) 3480.
Kong X, Barriere T, and Gelin J C, J Mater Process Technol 212 (2012) 2173.
Yang G, Li J, Song W, and Meng J, Adv Mater Res 753–755 (2013) 167.
Ibrahim R, Azmirruddin M, Jabir M, Ismail M R, Muhamad M, Awang R, Muhamad S, Park K H, Bangi B B, and Lumpur K, Am J Appl Sci 7 (2010) 811.
Thavanayagam G, Pickering K L, Swan J E, and Cao P, Powder Technol 269 (2015) 227.
Mutsuddy B C, and Ford R G, Ceramic Injection Molding, Chapman and Hall, United Kingdom (1995), p 368.
Liu F, and Chou K, Ceram Int 26 (2000) 159.
García H, J Eur Ceram Soc 32 (2012) 4063.
Aggarwal G, Park S J, and Smid I, Int J Refract Met Hard Mater 24 (2006) 253.
Miura H, Honda T, and German R M, J Jpn Soc Powder Powder Metall 38 (1991) 767.
Miura H, Honda T, and German R M, J Jpn Soc Powder Powder Metall 39 (1992) 254.
Miura H, Urakami K, Ando S, and Honda T, J Jpn Soc Powder Powder Metall 40 (1993) 388.
Baba T, and Miura H, J Jpn Soc Powder Powder Metall 44 (1997) 1014.
Miura H, and Matsuda M, Mater Trans 43 (2002) 343.
Lin K-H, Mater Des 32 (2011) 1273.
Pogodina N V, Cerclé C, Avérous L, Thomann R, Bouquey M, and Muller R, Annu Eur Rheol Conf 47 (2008) 543.
Matsuda M, and Miura H, Met Mater Int 9 (2003) 537.
Özgün Ö, Gulsoy H O, Yilmaz R, and Findik F, J Alloys Compd 576 (2013) 140.
Wright M, Hughes L J, and Gressel S H, J Mater Eng Perform 3 (1994) 300.
Bigg D M, and Barry R G, Annu Tech Conf – ANTEC Conf. Proc 1 (1998) 997.
Gerling R, Aust E, Limberg W, Pfuff M, and Schimansky F P, Mater Sci Eng A 423 (2006) 262.
German R M, and Bose A, Injection Molding of Metals and Ceramics, Metal Powder Industries Federation (1997), p 413.
Lal A, German R M, Acta Mater 47 (1999) 4615.
Li D, Hou H, Liang L, and Lee K, Int J Adv Manuf Technol 49 (2010) 105.
Fan J, Han Y, Liu T, Cheng H, Gao Y, and Tian J, Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 23 (2003) 1709.
Yi-min L, Xiang-quan L, Feng-hu L, Jian-ling W E, Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 17 (2007) 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Momeni, V., Askari, A., Alaei, M.H. et al. The Effect of Powder Loading and Binder System on the Mechanical, Rheological and Microstructural Properties of 4605 Powder in MIM Process. Trans Indian Inst Met 72, 1245–1254 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01615-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01615-1