Abstract
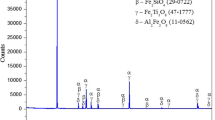
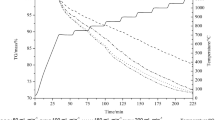
In India, ilmenite is considered as a major mineral reserve for the extraction of titanium. During the processing of ilmenite to produce titanium dioxide, huge amount of iron oxide is generated and dumped as waste. According to an approximation, 0.7 ton of iron oxide waste is generated for one ton of synthetic rutile production. This waste iron oxide has great potential to be utilized as resource of iron. Therefore, the present work deals with the carbothermic reduction studies of iron oxide waste generated during the ilmenite processing. The spent graphite electrode of electric arc furnace was used as reductant for the reduction studies. Different parameters such as reduction temperature, residence time and weight ratio of iron oxide/reductant were investigated. Reduction studies were carried out by varying the residence time at 15, 30, 60 and 120 min. With an increase in reduction temperature and residence time, percent reduction was found to be increased. Maximum reduction value of 95% was obtained at optimized reduction condition. After reduction, fine powder of metallic iron was obtained, which was characterized by XRD and particle size analyzer. The generated fine powder of metallic iron had direct application and high market value.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Indian Bureau of Mines (Iron and Steel Vision—2020). Chapter 4—Agglomeration.
Nakamato M, Nakazato H O, Kawabata H, and Usui T, ISIJ Int 44 (2004) 2100.
Liu G, Strezov V, Lucas J A, and Wibberley L J, Thermochim Acta 410 (2004) 133.
Luo S, Zhou Y, Chuijie Y, J Renew Sustain Energy 5 (2013) 063114.
Nyankson E, Kolbeinsen L, Int J Eng Technol 4 (2015) 934.
Haque R, Ray H S, Mukherjee A, ISIJ Int 31 (1991) 1279.
Man Y, Feng J, Ge Q, Li F, J Chem Pharm Res 6 (2014) 2484.
Dutta S K, Ghosh A, ISIJ Int 33 (1993), 1168.
Junaidi M, Ken Ninez N P, Pramusiwi S, Ismail I, Snugging P, Int J Electr Electron Data Commun 2 (2014) 43.
Hashem N M, Salah B A, El-Hussiny N A, Sayed S A, Khalifa M G, Shalabi M E H, ISIJ Int 6 (2014) 846.
32nd Annual World Petroleum Conference, Titanium Oxide: Market Overview and the Impact on the Global Chlor-Alkali Market (2017).
55th Edition, Ilmenite and Rutile. Indian Minerals Yearbook (2016).
Loveson V J, Misra D D, Sustainable Development of Coastal Placer Minerals, Allied Publishers Pvt Ltd, New Delhi (2004) p 223.
Migas P, Karbowniczek M, Selected Aspects of Graphite Applications in Ferrous Metallurgy, AGH University of Science and Technology, Kraków (2013).
Chokshi Y, Dutta S K, Iron Steel Rev 58 (2014) 192.
Indian Bureau of Mines (Iron and Steel Vision—2020). Chapter 7—Steel Making.
Bechara R, Hamadeh H, Mirgaux O, Patisson F, Materials 11 (2018) 1094.
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to the Director of CSIR-National Metallurgical Laboratory (CSIR-NML), Jamshedpur, for giving permission to publish the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raj, R., Kumari, A., Sahu, D.K. et al. Carbothermic Reduction of Iron Oxide Waste Generated During the Processing of Ilmenite. Trans Indian Inst Met 72, 11–16 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-018-1451-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-018-1451-4