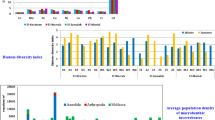
Abstract
Chemical measures combined with biological data (biomarkers) are recommended in monitoring programs of marine environments. In the present research, the use of multiples biogeochemical indicators allowed interrelating different environmental measurements to deepen the knowledge of the quality/status of the intertidal flat from Puerto Rosales (Bahía Blanca estuary, Argentina) subjected to anthropogenic pressure. The sediments from this site presented a eutrophic status and high organic matter concentration with high nutritional value for the benthic community. The TPR/TCH ratio (~ 10) would evidence the untreated sewage discharge contribution and increments in protein content due to the complexation of nitrogen during phytodetritus accumulation and degradation. Trace metals levels in the fine sediments were lower than those recommended by international guides for uncontaminated sites. In the sediments, except Cu, all metals analyzed were rarely associated with adverse biological effects. Finally, metallothioneins levels in the burrowing crab Neohelice granulata were lower than those found in the literature and significantly higher in females than in males. Even though the different analyses and indices performed indicate that this intertidal flat is in good environmental condition, the wastewater discharge influenced it. Thus, it is advisable to continue with this kind of study by applying multi-combined proxies in this and other impacted tidal flats.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams SM, Shepard KL, Greeley MS, Jimenez BD, Ryon MG, Shugart LR et al (1989) The use of bioindicators for assessing the effects of pollutant stress on Wsh. Mar Environ Res 28:459–464
Albano MJ, da Cunha LP, Bremec et al (2013) Macrobenthos and multi-molecular markers as indicators of environmental contamination in a South American port (Mar del Plata, Southwest Atlantic). Mar Pollut Bull 73:102–114
Amiard JC, Amiard-Triquet C, Barka S, Pellerin J, Rainbow PS (2006) Metallothioneins in aquatic invertebrates: their role in metal detoxification and their use as biomarkers. Aquat Toxicol 76:160–202
Andrade VS, Wiegand C, Pannard A, Gagneten AM, Pédrot M, Bouhnik-Le Coz M, Piscart C (2019) How can interspecific interactions in freshwater benthic macroinvertebrates modify trace element availability from sediment? Chemosphere 245:125594
Angeletti S, Cervellini PM, Lescano L (2018a) Burrowing activity of the Neohelice granulata crab (Brachyura, Varunidae) in southwest Atlantic intertidal area. Ciencias Marinas 44(3):155–167
Angeletti S, Pierini JO, Cervellini PM (2018b) Suspended sediment contribution resulting from bioturbation in intertidal sites of a SW Atlantic mesotidal estuary: data analysis and numerical modelling. Sci Mar 82(4):000–000. https://doi.org/10.3989/scimar.04799.07A
Angulo E (1996) The Tomlinson pollution load index applied to heavy metal ‘Mussel-Watch’ data: a useful index to assess coastal pollution. Sci Total Environ 187:49–56
APHA-AWWA-WEF (1998) In: Clesceri LS, Greenberg AE, Eaton AD (eds) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20 edn. American Public Health Association, Washington
Arena M, Delgado AL, Celleri C, Pratolongo PD (2019) Preliminary assessment of spatial and short-term variability of bio-optical properties in a tidal dominated estuary (Bahía Blanca, Argentina). Reg Stud Mar Sci 29:100639
Attrill MJ, Rundle SD (2002) Ecotone or ecocline: ecological boundaries in estuaries. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 55:929–936
Ballan-Dufrançais C, Jeantet AY, Geffard A, Amiard JC, Amiard-Triquet C (2001) Cellular and tissular distribution of copper in an intrasedimentary bivalve, the Baltic clam Macoma balthica, originating from a clean or a metal-rich site. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 58(10):1964–1974
Barakat A, El Baghdadi M, Rais J, Nadem S (2012) Assessment of heavy metal in surface sediments of day river at Beni-Mellal Region, Morocco. Res J Environ Earth Sci 4(8):797–806
Barrento S, Marques B, Teixeira A, Carvalho ML, Vaz-Pires P, Nunes ML (2009) Accumulation of elements (S, As, Br, Sr, Cd, Hg, Pb) in two populations of Cancer pagurus: ecological implications to human consumption. Food Chem Toxicol 47(1):150–156
Berasategui AA, Biancalana F, Fricke A, Fernández Severini MD, Uibrig R, Dutto MS, Marcovecchio JE, Calliari DL, Hoffmeyer MS (2018) The impact of sewage effluents on the fecundity and survival of Eurytemora americana in a eutrophic estuary of Argentina. Estuar Coast Shelf S 211:208
Bergamino L, Rodríguez-Gallego L, Pérez-Parada A et al (2018) Autochthonous organic carbon contributions to the sedimentary pool: a multi-analytical approach in Laguna Garzón. Org Geochem 125:55–65
Bianchi TS (2007) Biogeochemistry of Estuaries. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Bigus K, Astel A, Stec M, Pisku P (2017) Spatiotemporal variation of biochemical composition of organic matter and number of bacteria in core sediments of selected beaches of the southern baltic sea. Baltic Coastal zone. J Ecol Prot Coast 21:155–176
Blankson ER, Klerks PL (2017) The effect of sediment characteristics on bioturbation-mediated transfer of lead, in fresh water laboratory microcosms with Lumbriculus variegatus. Ecotoxicol 26(2):227–237
Buchman MF (1999) NOAA screening quick reference tables, NOAA HAZMAT Report 99–1. Coastal Protection and Restoration Division, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Seattle WA, pp 12
Botto F, Iribarne O, Gutierrez J, Bava J, Gagliardini A, Valiela I (2006) Ecological importance of passive deposition of organic matter into burrows of the SW Atlantic crab Chasmagnathus granulatus. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 312:201–210
Buggy CJ, Tobin JM (2008) Seasonal and spatial distribution of metals in surface sediment of an urban estuary. Environ Pollut 155:308–319
Buhl-Mortensen L (1996) Amphipod fauna along offshore-fjord gradient. J Nat Hist 30:23–49
Burdige EJ (2011) Estuarine and coastal sediments—coupled biogeochemical cycling. Treatise on estuarine and coastal science. In: Laane R, Únd Middelburg JJ (eds) Biogeochemistry, vol 5. Academic Press, New York
Buzzi N, Marcovecchio J (2016) A baseline study of the metallothioneins induction and its reversibility in Neohelice granulata from the Bahía Blanca Estuary (Argentina). Mar Pollut Bull 112:452–458
Caçador I, Costa AL, Vale C (2004) Carbon storage in Tagus salt marsh sediments. Water Air Soil Pollut Focus 4:701–714
Caeiro S, Costa MH, Ramos TB, Fernande F et al (2005) Assessing heavy metal contamination in Sado Estuary sediment: an index analysis approach. Ecol Indicators 5(2):151–169
Cauwet G (1978) Organic chemistry of sea water particulates concepts and developments. Oceanol Acta 1:99–105
Cheriyan E, Sreekanth A, Mrudulrag SK, Sujatha CH (2015) Evaluation of metal enrichment and trophic status on the basis of biogeochemical analysis of shelf sediments of the southeastern Arabian Sea, India. Cont Shelf Res 108:1–11
Cividanes S, Incera M, López J (2002) Temporal variability in the biochemical composition of sedimentary organic matter in an intertidal flat of the Galician coast (NW Spain). Oceanol Acta 25:1–12
Comoglio L, Goldsmit J, Amin O (2008) Starvation effects on physiological parameters and biochemical composition of the hepatopancreas of the southern king crab Lithodes santolla (Molina, 1782). Rev Biol Mar Oceanogr 43:345–353
Cotano U, Villate F (2006) Anthropogenic influence on the organic fraction of sediments in two contrasting estuaries: a biochemical approach. Mar Pollut Bull 52:404–414
Cresson P, Ruitton S, Fontaine M-F, Harmelin-Vivien M (2012) Spatio-temporal variation of suspended and sedimentary organic matter quality in the Bay of Marseilles (NW Mediterranean) assessed by biochemical and isotopic analyses. Mar Pollut Bull 64:1112–1121
Cronk JK, Fennessy MS (2001) Wetland plants: biology and ecology. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton
Cuadrado DG, Ginsberg SS, Gómez EA (2004) Geomorfología Ecosistema del Estuario de BahÍa Blanca. Instituto Argentino de Oceanografía, Bahía Blanca, pp 29–38
Cuadrado DG, Gómez EA, Ginsberg SS (2005) Tidal and longshore sediment transport associated to a coastal structure. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 62:291–300
Cuadrado DG, Gómez EA, Pierini JO, Federici GA (2006) A possible solution to Rosales Harbour excessive siltation rate (Bahía Blanca Estuary, Argentina). J Coast Res 39:419–423
Cuadrado DG, Bournod CN, Pan J, Carmona NB (2013) Microbially-induced sedimentary structures (MISS) under storm influence in an estuarine setting. Sediment Geol 296:1–8
Dame RF (2008) Estuaries. In: Encyclopedia of ecology, 2nd edn, pp 484–490
Danovaro R, Dell’Anno A, Fabiano M (2001) Bioavailability of organic matter in the sediments of the Porcupine Abyssal Plain, northeastern Atlantic. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 220:25–32
Danovaro R, Fabiano M, Della Croce N (1993) Labile organic matter and microbial biomasses in deep-sea sediments (Eastern Mediterranean Sea). Deep-Sea Res I 40(5):953–965
Danovaro R, Marrale D, Della Croce N, Parodi P, Fabiano M (1999) Biochemical composition of sedimentary organic matter and bacterial distribution in the Aegean Sea: trophic state and pelagic–benthic coupling. J Sea Res 42:117–129
de Brouwer JFC, de Deckere EMGT, Stal LJ (2003) Distribution of extracellular carbohydrates in three intertidal mudflats in Western Europe. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 56:313–324
De Souza Machado AA, Spencer K, Kloas W, Toffolon M, Zarfl C (2016) Metal fate and effects in estuaries: a review and conceptual model for better understanding of toxicity. Sci Tot Environ 541:268–281
Dell’Anno A, Mei ML, Pusceddu A, Danovaro R (2002) Assessing the trophic state and eutrophication of coastal marine systems: a new approach based on the biochemical composition of sediment organic matter. Mar Pollut Bull 44:611–622
Duan L, Song J, Liang X, Yin M, Yuana H, Li X, Ren C, Zhou B, Kang X, Yin X (2019) Dynamics and diagenesis of trace metals in sediments of the Changjiang Estuary. Sci Total Environ 675:247–259
Elías R, Iribarne O, Bremec CS, Martínez DE (2007) Comunidades bentónicas de fondos blandos. In: Hoffmeyer MS (ed) Piccolo MC. Ecosistema del Estuario de Bahía Blanca. ediUNS, Bahía Blanca, pp 179–190 (ISBN 987-9281-96-9)
Ergin M, Saydam C, Baştürk Ö, Erdem E, Yörük R (1991) Heavy metal concentration in surface sediments from 2 inlets (Golden Horn Estuary and İzmit Bay) of the north eastern Sea of Marmara. Chem Geol 91:269–285
Escapa M, Perillo GME, Iribarne O (2008) Sediment dynamics modulated by burrowing crab activities in contrasting SW Atlantic intertidal habitats. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 80:365–373
Fabiano M, Danovaro R, Fraschetti S (1995) A three-year time series of elemental and biochemical composition of organic matter in subtidal sandy sediments of the Ligurian Sea (northwestern Mediterranean). Cont Shelf Res 15:1453–1469
Fanjul E, Escapa M, Montemayor D, Addino M, Alvarez MF, Grela MA, Iribarne O (2015) Effect of crab bioturbation on organic matter processing in South West Atlantic intertidal sediments. J Sea Res 95:206–216
Federal Register (1984) Definition and procedure for determination of the method detection limit. EPA, 40 CFR Part 136, Appendix B, Revision 1.11 1 (11), pp 198–199.
Fernándes L, Nayak GN, Ilangovan D, Borole DV (2011) Accumulation of sediment, organic matter and trace metals with space and time, in a creek along Mumbai coast, India. Estuar, CoastShelf Sci 91:388–399
Fernández EM, Spetter CV, Martinez AM, Cuadrado DG, Avena MJ, Marcovecchio JE (2016) Carbohydrate production by microbial mats communities in tidal flat from Bahía Blanca Estuary (Argentina). Environ Earth Sci 75(8):641
Fernández Severini MD, Botté SE, Hoffmeyer MS, Marcovecchio JE (2009) Spatial and temporal distribution of cadmium and copper in water and zooplankton in the Bahía Blanca estuary, Argentina. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 85:57–66
Fernández Severini MD, Hoffmeyer MS, Marcovecchio JE (2013) Heavy metals concentrations in zooplankton and suspended particulate matter in a southwestern Atlantic temperate estuary (Argentina). Environ Monit Assess 185:1495–1513
Fernández Severini MD, Villagran DM, Biancalana F, Berasategui AA, Spetter CV, Tartara MN, Menéndez MC, Guinder VA, Marcovecchio JE (2017) Heavy metal concentrations found in seston and microplankton from an impacted temperate shallow estuary along the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean. J Coast Res 33(5):1196–1209
Fernández Severini MD, Carbone ME, Villagran DM, Marcovecchio JE (2018) Toxic metals in a highly urbanized industry-impacted estuary (Bahia Blanca Estuary, Argentina): spatio-temporal analysis based on GIS. Environ Earth Sci 77:393
Ferreira M, Moradas-Ferreira P, Reis-Henriques MA (2006) The effect of long-term depuration on phase I and phase II biotransformation in mullets (Mugil cephalus) chronically exposed to pollutants in River Douro Estuary, Portugal. Mar Environ Res 61:326–338
Garcia-Rodriguez F, del Puerto L, Venturini N, Pita AL, Brugnoli E, Burone L, Muniz P (2011) Diatoms, protein and carbohydrate sediment content as proxies for coastal eutrophication in Montevideo, Rio de la plata Estuary, Uruguay. Braz J Oceanogr 59(4):293–310
Gelós EM, Marcos OA, Spagnuolo JO, Schillizzi RA (2004) Textura y Mineralogía de los sedimentos. In: Piccolo MC, Hoffmeyer M (eds) Ecosistema del Estuario de Bahía Blanca, 3rd edn. Ediuns, Bahía Blanca, pp 43–50
GESAMP (IMO/FAO/IJNESCO/WMO/IAEA/UN/IJNEP) (1982) The health of the oceans: Rep Stad GESAMP 15, pp 108.
Gómez N, Donato JC, Giorgi A, Guasch H, Mateo P, Sabater S (2009) La biota de los ríos: los microorganismos autótrofos. In: Elosegi A, Sabater S (eds) Conceptos y Técnicas en Ecología Fluvial. Valant, España, pp 234–236
Gómez-Ramírez Eddy H, Corzo A, García-Robledo E et al (2019) Benthic-pelagic coupling of carbon and nitrogen along a tropical estuarine gradient (Gulf of Nicoya, Costa Rica). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 228(106362):1–11
Griffiths JR, Kadin M, Nascimento FJA et al (2017) The importance of benthic–pelagic coupling for marine ecosystem functioning in a changing world. Glob Change Biol 23:2179–2196
Hadlich HL, Venturini N, Martins CC et al (2018) Multiple biogeochemical indicators of environmental quality in tropical estuaries reveal contrasting conservation opportunities. Ecol Indic 95:21–31
Hamza-Chaffai A, Amiard JC, Cosson RP (1999) Relationship between metallothioneins and metals in a natural population of the clam Ruditapes decussatus from Sfax coast: a non-linear model using Box-Cox transformation. Comp Biochem Physiol C Comp Pharmacol Toxicol 123:153–163
Hayes MO (1979) Barrier Island morphology as a function of tidal and wave regime. In: Leatherman S (ed) Proceedings of the coastal symposium of Barrier Islands. New York Academic Press, New York, pp 1–28
He Y, Men B, Yang X, Li Y, Xu H, Wang D (2019) Relationship between heavy metals and dissolved organic matter released from sediment by bioturbation/bioirrigation. J Environ Sci 75:216–223
Hetsroni G (1989) Particles-turbulence interaction. Int J Multiphase Flows 15:735–746
IAEA (1990) Guidebook on applications of radiotracers in industry. Technical report series No. 316
Incera M, Cividanes SP, Lastra López MJ (2003) Temporal and spatial variability of sedimentary organic matter in sandy beaches on the northwest coast of the Iberian Peninsula. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 58S:55–61
Iribarne O, Botto F, Martinetto P, Gutiérrez JL (2000) The role of burrows of the SW Atlantic intertidal crab Chasmagnathus granulata in trapping debris. Mar Pollut Bull 40:1057–1062
Joseph MM, Kumar CSR, Kumar TRG, Renjith KR, Chandramohanakumar N (2008) Biogeochemistry of surficial sediments in the intertidal systems of a tropical environment. Chem Ecol 24(4):247–258
Joy A, Anoop PP, Rajesh R, Mathew A, Gopinath A (2019) Spatial variability of biochemical composition in coral reef sediments of Kavaratti and Pitti islands, Lakshadweep archipelago. Indian J Geo Mar Sci 48(03):369–378
Kägi JHR (1993) Evolution, structure and chemical activity of class I metallothioneins: an overview. In: Suzuki KT, Imura N, Kimura M (eds) Metallothioneins III—biological roles and medical implications. Birkhäuser, Basel, pp 29–55
Kumar BS, Sarma VVSS, Krishna MS (2013) Distribution of biochemical constituents in the surface sediments of western coastal Bay of Bengal: influence of river discharge and water column properties. Environ Earth Sci 69:1033–1043
Lam PKS, Gray JS (2003) The use of biomarkers in environmental monitoring programmes. Mar Pollut Bull 46:182–186
Laut LLM, Alves Martins MV, Fontana LF, Da Silva FS et al (2016) Ecological status evaluation of itaipu lagoon (niterói) based on biochemical composition of organic matter. J Sediment Environ 1(3):304–323
Laut L, Alves Martins MV, Frontalini F et al (2017) Assessment of the trophic state of a hypersaline-carbonatic environment: Vermelha Lagoon (Brazil). PLoS ONE 12(9):1–19
Lavradas RT, Hauser-Davis RA, Lavandier RC, Chávez Rocha RC, Saint’Pierre TD, Seixas T, Kehrig HA, Moreira I (2014) Metal, metallothionein and glutathione levels in blue crab (Callinectes sp.) specimens from south eastern Brazil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 107:55–60
Le Hir P, Roberts W, Cazaillet O, Christie M, Bassaullet P, Bacher C (2000) Characterization of intertidal flat hydrodynamics. Cont Shelf Res 20:1433–1459
Legras S, Mouneyrac C, Amiard JC, Amiard-Triquet C, Rainbow PS (2000) Changes in metallothionein concentrations in response to variation in natural factors (salinity, sex, weight and metal contamination in crabs from a metal-rich estuary. J Exp Mar Biol 246:259–279
Lessen AE (2006) Sediment organic matter composition and dynamics in San Francisco Bay, California, USA: Seasonal variation and interactions between water column chlorophyll and the benthos. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 66:501–512
Long ER, Field LJ, MacDonald DD (1998) Predicting toxicity in marine sediments with numerical sediment quality guidelines. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:714–727
Long ER, MacDonald DD, Severn CG, Hong CB (2000) Classifying probabilities of acute toxicity in marine sediments with empirically derived sediment quality guidelines. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:2598–2601
López Greco LS, Rodríguez EM (1999) Annual reproduction and growth of adult crabs Chasmagnathus granulata (Crustacea, Brachyura, Grapsidae). Cah Biol Mar 40:155–164
Lorenzen CJ (1967) Determination of chlorophyll and pheopigments: spectrophotometric equations. Limnol Oceanogr 12:343–346
MacDonald DD, Scott Carr R, Calder FD, Long ER, Ingersoll CG (1996) Development and evaluation of sediment quality guidelines for Florida coastal waters. Ecotoxicol 5:253–278
MacDonald DD, Ingersoll CG, Berger TA (2000) Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:20–31
Marcovecchio JE (2000) Land-based sources and activities affecting the marine environment at the upper southwestern Atlantic Ocean: an overview. UNEP Regional Seas Reports and Studies N°170, p 67
Marcovecchio JE, Ferrer LD (2005) Distribution and geochemical partitioning of heavy metals in sediments of the Bahía Blanca Estuary, Argentina. J Coast Res 21:826–834
Marcovecchio JE, Botté SE, Delucchi F, Arias AH, Fernández Severini MD, De Marco S, Tombesi N, Andrade S, Ferrer LD, Freije RH (2008) Pollution processes in Bahía Blanca Estuarine Environment. In: Neves R, Baretta JW, Mateus M (eds) Perspectives on integrated coastal zone management in South America. IST Press, Lisboa, pp 301–314
McComb J, Turquoise CA, Fengxiang XH, Tchounwou PB (2014) Understanding biogeochemical cycling of trace elements and heavy metals in estuarine ecosystems. J Bioremed Biodeg 5:3
Menéndez MC, Piccolo MC, Hoffmeyer MS (2012) Short-term variability on mesozooplankton community in a shallow mixed estuary (Bahía Blanca, Argentina): Influence of tidal cycles and local winds. Estuar Coast and Shelf Sci 112:11–22
Middelburg JJ, Herman PMJ (2007) Organic matter processing in tidal estuaries. Mar Chem 106:127–147
Moreno S, Niell FX (2004) Scales of variability in the sediment chlorophyll content of the shallow Palmones River Estuary, Spain. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 60:49–57
Mouneyrac C, Amiard-Triquet C, Amiard JC, Rainbow PS (2001) Comparison of metallothionein concentrations and tissue distribution of trace metals in crabs (Pachygrapsus marmoratus) from a metal-rich estuary, in and out of the reproductive season. Comp Biochem Physiol C 129:193–209
Müller G (1979) Schwermetalle in den Sedimenten des Rheins-Veränderungen seit 1971. Umschau 79(24):778–783
Muller G (1981) The heavy metal content of the sediments of the Neckar and its tributaries: an Inventory. Chem Zeitung 105:157–164
Muniz P, Venturini N, Martins C et al (2015) Integrated assessment of contaminants and monitoring of an urbanized temperate harbor (Montevideo, Uruguay): a 12-year comparison. Braz J Oceanogr 63(3):311–330
Murray JM, Meadows A, Meadows PS (2002) Biogeomorphological implications of microscale interactions between sediment geotechnics and marine benthos: a review. Geomorphology 47:15–30
Nair MP, Sujatha CH (2012) Biogeochemical quality assessment of the sediments in Kerala coast. Int J Environ Sci 3(1):707–719
Negrin VL, Spetter CV, Guinder VA, Perillo GME, Marcovecchio JE (2013) The role of Sarcocornia perennis and tidal flooding on sediment biogeochemistry in a South American wetland. Mar Biol Res 9:703–715
Negrin VL, Botté SE, La Colla NS, Marcovecchio JE (2019) Uptake and accumulation of metals in Spartina alterniflora salt marshes from a South American estuary. Sci Total Environ 649:808–820
Niell FX (1980) Incidencias de vertidos industriales en la estructura de poblaciones intermareales. Algunas variables de los sistemas sedimentarios en el espacio. Invest Pesq 44:337–345
NOAA (2018) What is an estuary? National Ocean Service website. https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/estuary.html. 06/25/18
Overnell J, McIntosh R, Fletcher TC (1987) The levels of liver metallothionein and zinc in plaice, Pleuronectes platessa L., during the breeding season, and the effect of oestradiol injection. J Fish Biol 30:539–546
Paucot H, Wollast R (1997) Transport and transformation of trace metals in the Scheldt estuary. Mar Chem 58:229–244
Pavičić J, Ivanković D, Lucu Č, Hamer B, Erk M, Tušek-Žnidarič M, Falnoga I (2006) Ecotoxicological evaluation of metallothionein level in selected tissues of estuarine invertebrates. Toxicol Lett 164S:S1–S324
Pereira E, Abreu SN, Coelho JP, Lopes CB, Pardal MA, Vale C, Duarte AC (2006) Seasonal fluctuations of tissue mercury contents in the European shore crab Carcinus maenas from low and high contamination areas (Ria de Aveiro, Portugal). Mar Pollut Bull 52:1450–1457
Perillo GME, Piccolo MC (1991) Tidal response in the Bahía Blanca estuary, Argentina. J Coast Res 7:437–449
Perillo GME, Sequeira ME (1989) Geomorphologic and sediment transport characteristics of the middle reach of the Bahía Blanca estuary, Argentina. J Geophys Res Oceans 94:14351–14362
Perillo GME, Piccolo MC, Parodi E, Freije RH (2001) The Bahía Blanca Estuary, Argentina. In: Seeliger U, Kjerfve B (eds) Coastal marine ecosystems of Latin America, ecological studies. Springer, Berlin, pp 205–217
Piccolo MC, Diez PG (2004) Meteorología del Puerto Coronel Rosales. In: Hoffmeyer MS (ed) Ecosistema del Estuario de Bahía Blanca. ediUNS, Bahía Blanca, pp 87–91
Piccolo MC, Perillo GME, Melo WD (2008) The Bahía Blanca Estuary: an integrated overview of its geomorphology and dynamics. In: Neves R, Baretta J, Mateus M (eds) Perspectives on integrated coastal zone management in South America. IST Press, Lisbon, pp 219–230
Pierini JO, Streitenberger ME, Baldini MD (2012) Evaluation of faecal contamination in Bahía Blanca estuary (Argentina) using a numerical model. Rev Biol Mar Oceanogr 47(2):193–202
Pizani N (2008) Valorización de las interacciones microfitobentos—sedimentos en planicies de marea impactadas por el dragado hidráulico. Ph.D Thesis, Universidad Nacional del Sur, Bahía Blanca, Argentina, p 224 (in Spanish)
Pratolongo P, Gerardo ME, Perillo GME, Cintia Piccolo MC (2010) Combined effects of waves and plants on a mud deposition event at a mudflat-saltmarsh edge in the Baháa Blanca estuary. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 87:207–212
Quintas PY, Fernández EM, Spetter CV, Arias AH, Garrido M, Marcovecchio JE (2019) Preliminary studies about the role of physicochemical parameters on the organotin compound dynamic in a South American estuary (Bahía Blanca, Argentina). Environ Monit Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7260-3
Rainbow PS, Luoma SN (2011) Trace metals in aquatic invertebrates. Taylor and Francis Books, Boca Raton, pp 231–252
Reddy KR, DeLaune RD (2008) Biogeochemistry of wetlands: science and applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton, p 744
Renzi M, Provenza F, Pignattelli S, Cilenti L, Specchiulli A, Pepi M (2019) Mediterranean Coastal Lagoons: the importance of monitoring in sediments the biochemical composition of organic matter. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16:1–20
Rundle SD, Attrill MJ, Arshad A (1998) Seasonality in macroinvertebrates community composition across a neglected ecological boundary, the freshwater-estuarine transition zone. Aquat Ecol 32:211–216
Sabatini SE, Chaufan G, Juárez ÁB, Coalova I, Bianchi L, Eppis MR, Ríos de Molina MC (2009) Dietary copper effects in the estuarine crab, Neohelice (Chasmagnathus) granulata, maintained at two different salinities. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C 150:521–527
Salomons V, Förstner U (1984) Metals in the hydrocycle. Springer, Berlin, p 349
Santisteban JI, Mediavilla R, López-Pamo E, Dabrio CJ, Ruiz Zapata MB, Gil García MJ, Castaño S, Martínez-Alfaro PE (2004) Loss on ignition: a qualitative or quantitative method for organic matter and carbonate mineral content in sediments? J Paleolimnol 32:287–299
Selvaraj K, Ram Mohan V, Szefer P (2004) Evaluation of metal contamination in coastal sediments of the Bay of Bengal, India: geochemical and statistical approaches. Mar Pollut Bull 49:174–185
Simonetti P, Botte SE, Marcovecchio JE (2018) Heavy metal bioconcentration factors in the burrowing crab Neohelice granulata of a temperate ecosystem in South America: Bahía Blanca estuary, Argentina. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(34):34652–34660
Simpson SL, Batley GE, Chariton AA, Stauber JL, King CK, Chapman JC et al (2005) Handbook for sediments quality assessment. CSIRO, Bangor
Sousa RS, Dias LG, Antunes C (2008) Minho River tidal freshwater wetlands: threats to faunal biodiversity. Aquat Biol 3:237–250
Speake MA, Carbone ME, Spetter CV (2020) Análisis del sistema socio-ecológico del estuario Bahía Blanca (Argentina) y su impacto en los servicios ecosistémicos y el bienestar humano. Investigaciones Geográficas 73:121–145. https://doi.org/10.14198/INGEO2020.SCS
Spencer KL, MacLeod CL (2002) Distribution and partitioning of heavy metals in estuarine sediment cores and implications for the use of sediment quality standards. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 6:989–998
Spetter CV, Buzzi NS, Fernández EM, Cuadrado DG, Marcovecchio JE (2015) Assessment of the physicochemical conditions sediments in a polluted tidal flat colonized by microbial mats in Bahía Blanca Estuary (Argentina). Mar Pollut Bull 91:491–505
Sutherland RA (2000) Bed sediment associated trace metals in an urban stream Oahu. Hawaii Environ Geol 39(6):611–627
Szkokan-Emilson EJ, Watmough SA, Gunn JM (2014) Wetlands as long-term sources of metals to receiving waters in mining-impacted land scapes. Environ Pollut 192:91–103
Thibault A, Derenne S, Parlanti E, Anquetil C, Sourzac M, Budzinski H, Fuster L, Laverman A, Roose-Amsaleg C, Viollier E, Huguet A (2019) Dynamics of organic matter in the Seine Estuary (France): bulk and structural approaches. Mar Chem 212:108–119
Tomlinson DL, Wilson JG, Hariis CR, Jeffrey DW (1980) Problems in the assessment of heavy metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgol Wiss Meeresunters 33:566–575
Truchet DM, Buzzi NS, Carcedo MC, Marcovecchio JE (2019) First record of the fiddler crab Leptuca (=Uca) uruguayensis in the Bahía Blanca Estuary (Buenos Aires, Argentina) with comments on its biology in South America. Reg Stud Mar Sci 27:100539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsma.2019.100539
Turekian KK, Wedepohl HK (1961) Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust. Geol Soc Am Bull 72:175–192
Venturini N, Pita AL, Brugnoli E, García-Rodríguez F, Burone L, Kandratavicius N, Hutton M, Muniz P (2012) Benthic trophic status of sediments in a metropolitan area (Rio de la Plata estuary): Linkages with natural and human pressures. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 112:139–152
Viarengo A, Ponzano E, Dondero F, Fabbri R (1997) A simple spectrophotometric method for metallothionein evaluation in marine organisms: an application to Mediterranean and Antarctic molluscs. Mar Environ Res 44:69–84
Villaescusa-Celaya JA, Gutiérrez-Galindo EA, Flores-Muñoz G (2000) Heavy metals in the fine fraction of coastal sediments from Baja California (Mexico) and California (USA). Environ Pollut 108(3):453–462
Wallschlager D, Desai MVM, Spengler M, Windmoller CC, Wilken RD (1998) How humic substances dominate mercury geochemistry in contaminated floodplain soils and sediments. J Environ Qual 27(5):1044–1054
Wang H, Liu R, Wang Q et al (2016) Bioavailability and risk assessment of arsenic in surface sediments of the Yangtze River estuary. Mar Pollut Bull 113(1):125–131
Wedderburn J, Cheung V, Bamber S, Bloxham M, Depledge MH (1998) Biomarkers of biochemical and cellular stress in Carcinus maenas: an in situ field study. Mar Environ Res 46(1):321–324
Yang Y, Chen F, Zhang L, Liu J, Wu S, Kang M (2012) Comprehensive assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediment of the Pearl River Estuary and adjacent shelf. Mar Pollut Bull 64(9):1947–1955
Ysebaert T, Herman PMJ, Meire P, Craeymeersch J, Verbeek H, Heip CHR (2003) Large-scale spatial patterns in estuaries: estuarine macrobenthic communities in the Schelde estuary, NW Europe. Estuar, Coast Shelf Sci 57:335–355
Zapperi G, Pratolongo P, Piovan MJ, Marcovecchio JE (2016) Benthic-pelagic coupling in an intertidal mudflat in the Bahía Blanca estuary (SW Atlantic). J Coast Res 32:629–637
Acknowledgements
We thank the organizing committee of V RAGSU (Reunión Argentina de Geoquímica de la Superficie); part of this work was presented at the congress. We thank to P. Simonetti, F. García and J. Arlenghi for assistance in the laboratory and in the field, to W. Melo for providing the map and collaborating with figures elaboration and to A. Vitale for providing the environmental parameters. We also thank the IADO executive directors and Chemical Oceanography Area's staff. This research was supported by the Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (ANPCyT; PICT 2012-1383 and PICT 2012-2794, Granted Dr. N. S. Buzzi and Dr. C. V. Spetter, respectively) and the Universidad Nacional del Sur (UNS, PGI 24/Q109, also granted to C. V. Spetter and PGI 24/B299 granted to N. S. Buzzi)—all from Argentina.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is a part of the Topical Collection in Environmental Earth Sciences on “Advances in Environmental Geochemistry” guest edited by Dr. Eleanor Carol, Dr. Lucia Santucci and Dr. Lia Botto.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buzzi, N.S., Fernández, E.M., Fernández Severini, M.D. et al. Environmental quality assessment by multiple biogeochemical indicators of an intertidal flat under anthropogenic influence from the southwest of Buenos Aires (Argentina). Environ Earth Sci 80, 256 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09438-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09438-4