Abstract
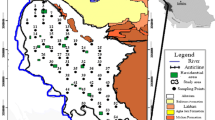
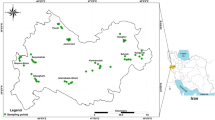
Soil contamination poses a severe threat in terms of deteriorated environmental quality and badly influences human health. Agricultural soils, mainly in the suburban areas, need detailed investigations for their heavy metal contents to avoid food chain contamination. This study was done to examine the heavy metals (Cu, Ni, Pb, Cr, Zn, and Mn) enrichment and accounts for contamination in arable soils of the Islamabad Capital Territory of Pakistan. Forty soil samples (soil depth 15–25 cm) were collected from cultivated areas of 41.88 km2 using a predefined GIS-based grid. Soil samples were analyzed for physico-chemical properties and total heavy metal content. Different types of environmental factors to assess the ecological risk were calculated to examine the contamination level in soils of the surveyed area. Results indicated that soil pH, in the surveyed area ranged from 7.27 to 7.98 with the mean value (7.54 ± 0.19). The Average Cu, Ni, Pb, Cr, Zn, and Mn contents in the soils were 11.7, 31, 33, 42, 86, and 1407 mg kg−1, respectively. The spatial dependence ranged from moderate to strong, provided an opportunity to prepare contour maps. The pollution load index of the surveyed area indicated a need for a more detailed study to monitor the enrichment of heavy metals. The whole area was classified into various zones based on differential heavy metal content for regional-scale information.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed H, Siddique MT, Ali S et al (2014) Micronutrient indexing in the apple orchards of Northern Punjab, Pakistan using geostatistics and GIS as diagnostic tools. Soil Environ 33:07–16
Ahmed H, Siddique MT, Iqbal M, Hussain F (2017) Comparative study of interpolation methods for mapping soil pH in the apple orchards of Murree, Pakistan. Soil Environ 36:70–76. https://doi.org/10.25252/se/17/41154
Aishah AW, Zauyah S, Anuar AR, Fauziah CI (2010) Spatial variability of selected chemical characteristics of paddy soils in sawah sempadan, selangor, Malaysia. Malays J Soil Sci 14:27–39
Amina AQ, Bano QKR, Yousaf B (2015) Accessing potential bioaccumulation of heavy metals in selective vegetables from Gujranwala District, Pakistan. J Environ Earth Sci 5:58–70
Cambardella CA, Moorman TB, Novak JM et al (1994) Field-scale variability of soil properties in central Iowa soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 58:1501–1511. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1994.03615995005800050033x
FAO/WHO, Codex Alimentarius Commission (2001) Food Additives and Contaminants. Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards programme, ALINORM01/12A:1-289
Gee GW, Bauder JW (1986) Particle size analysis. In: Klute A (ed) Methods of soil analysis. Part-1 physical and mineralogical methods. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, Wisconsin, USA, pp 383–411
Gong L, Wang J, Abbas T et al (2021) Immobilization of exchangeable Cd in soil using mixed amendment and its effect on soil microbial communities under paddy upland rotation system. Chemosphere 262:127828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127828
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
Hani A, Pazira E, Manshouri M et al (2010) Spatial distribution and mapping of risk elements pollution in agricultural soils of southern Tehran, Iran. Plant Soil Environ. https://doi.org/10.17221/16/2010-pse
Harikumar PS, Nasir UP, Mujeebu Rahman MP (2009) Distribution of heavy metals in the core sediments of a tropical wetland system. Int J Environ Sci Technol 6:225–232
Hooda PS (2003) A special issue on heavy metals in soils: editorial foreword. Adv Environ Res 8:1–3
Kumar Sharma R, Agrawal M, Marshall F (2007) Heavy metal contamination of soil and vegetables in suburban areas of Varanasi, India. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.11.007
Likuku AS, Mmolawa KB, Gaboutloeloe GK (2013) Assessment of heavy metal enrichment and degree of contamination around the copper-nickel mine in the Selebi Phikwe Region, Eastern Botswana. Environ Ecol Res 1(2):15–17
Nelson DW, Sommers LE (1982) Total carbon, organic carbon and organic matter. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2 chemical and microbiological properties. American Society of Agronomy Madison, WI, USA, pp 539–579
Odat S (2013) Calculating pollution indices of heavy metal along Irbid/Zarqa highway-Jordan. Int J Appl Sci Technol 3(8):72–76
Omran E-S (2012) Mapping and screening risk assessment of heavy metals concentrations in soils of the Bahr El-Baker Region, Egypt. J Soil Sci Environ Manag. https://doi.org/10.5897/jssem12.010
Page AL (1982) Methods of soil analysis—part 2: chemical and Microbiological properties, 2nd edn. Am Soc Agron Inc Publ, Madison, p 9
Panseriya HZ, Gosai HB, Sankhwal AO et al (2020) Distribution, speciation and risk assessment of heavy metals: geochemical exploration of Gulf of Kachchh, Gujarat, India. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-08972-x
Raza A, Habib M, Kakavand SN et al (2020) Phytoremediation of cadmium: physiological, biochemical, and molecular mechanisms. Biology (Basel) 9:1–46. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9070177
Robinson TP, Metternicht G (2006) Testing the performance of spatial interpolation techniques for mapping soil properties. Comput Electron Agric. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2005.07.003
Rodríguez-Barroso MR, García-Morales JL, Coello Oviedo MD, Quiroga Alonso JM (2010) An assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface sediment using statistical analysis. Environ Monit Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0852-6
Sinem Atgin R, El-Agha O, Zararsiz A et al (2000) Investigation of the sediment pollution in Izmir Bay: trace elements. Spectrochim Acta Part B At Spectrosc. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0584-8547(00)00231-7
Sutherland RA, Tolosa CA, Tack FMG, Verloo MG (2000) Characterization of selected element concentrations and enrichment ratios in background and anthropogenically impacted roadside areas. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002449910057
Tomlinson DL, Wilson JG, Harris CR, Jeffrey DW (1980) Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02414780
Turekian KK, Wedepohl KH (1961) Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust. Bull Geol Soc Am. https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606(1961)72[175:DOTEIS]2.0.CO;2
Wang H, Lu S (2011) Spatial distribution, source identification and affecting factors of heavy metals contamination in urban-suburban soils of Lishui city, China. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1005-0
Webster R (2008) Soil sampling and methods of analysis—edited by M.R. Carter & E.G. Gregorich. Eur J Soil Sci. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.2008.01052_5.x
Wilding LP (1985) Spatial variability: It's documentation, accommodation and implication to soil surveys. In: Nielsen DR, Bouma J (eds) Soil spatial variablility. Pudoc, Wageningen, Netherland, pp 166–194
Yang Q, Xu Y, Liu S, He J et al (2011) Concentration and potential health risk of heavy metals in market vegetables in Chongqing, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.05.006
Yisa J, Jacob JO, Onoyima CC (2012) Assessment of toxic levels of some heavy metals in road deposited sediments in Suleja, Nigeria. Am J Chem. https://doi.org/10.5923/j.chemistry.20120202.08
Zhang C (2006) Using multivariate analyses and GIS to identify pollutants and their spatial patterns in urban soils in Galway, Ireland. Environ Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.10.028
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the Higher Education Commission of Pakistan and Soil Science Institute of Pir Mehr Ali Shah Arid Agriculture University, Rawalpindi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbas, T., Akmal, M., Aziz, I. et al. Risk assessment and GIS-based mapping of heavy metals in the secondary rock deposits derived soils of Islamabad, Pakistan. Environ Earth Sci 80, 102 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09397-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09397-w