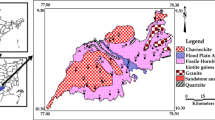
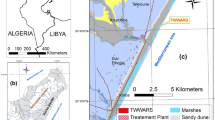
Abstract
222Rn is widely used as a tracer to detect and calculate submarine groundwater discharge in coastal zones, rivers and lakes. Relatively few investigations, however, have used this element for other applications in hydrogeology. We analyze the relationship between 222Rn activity in groundwater and variations in the water cycle in the sandy aquifer of Buenos Aires coast, Argentina. Groundwater levels, electrical conductivity and 222Rn activity were measured in situ in wells in March 2016 and November 2018, representing two different hydrological conditions. Groundwater flow maps were drawn, hydrological gradients and flux velocities were calculated. An inverse correlation between 222Rn activity and recharge conditions was found. Lower water surplus shows higher 222Rn activity and vice versa, potentially due to dilution of high 222Rn activity water with ‘newer’ lower activity recent recharge. A variability in 222Rn spatial distribution was identified along the sand dune barrier. A correlation between 222Rn and groundwater electrical conductivity was not observed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akawwi E (2014) Radon-222 concentrations in the groundwater along Eastern Jordan Rift. Res J Appl Sci 14(4):309–316
Allen RG, Pereira LS, Raes D, Martin Smith M (1998) Crop evapotranspiration. Guidelines for computing crop water requirements, FAO Irrigation and drainage papers 56. FAO, Rome
Ball TK, Cameron DG, Colman TB, Robert PD (1991) Behaviour of radon in the geological environment: a review. Q J Eng Geol Hydrogeol 24(2):169–182
Beysens D, Ohayon C, Muselli M, Clus O (2006) Chemical and biological characteristics of dew and rain water in an urban coastal area (Bordeaux, France). Atmos Environ 40(20):3710–3723
Burnett WC, Dulaiova H (2003) Estimating the dynamics of groundwater input into the coastal zone via continuous radon-222 measurements. J Environ Radioact 69(1–2):21–35
Burnett WC, Dulaiova H (2006) Radon as a tracer of submarine groundwater discharge into a boat basin in Donnalucata, Sicily. Cont Shelf Res 26(7):862–873
Burnett WC, Peterson R, Moore WS, de Oliveira J (2008) Radon and radium isotopes as tracers of submarine groundwater discharge–results from the Ubatuba, Brazil SGD assessment intercomparison. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 76(3):501–511
Carretero S (2011) Comportamiento hidrológico de las dunas costeras en el sector nororiental de la provincia de Buenos Aires [Hydrological behavior of coastal dunes on the northeastern coast of Buenos Aires province]. PhD Thesis. Facultad de Ciencias Naturales y Museo, Universidad Nacional de La Plata, La Plata. Argentina. http://sedici.unlp.edu.ar/search/request.php?id_document=ARG-UNLP-TPG-0000002075&request=request. Accessed 10 Aug 2019
Carretero S, Kruse E (2012) Relationship between precipitation and water-table fluctuation in a coastal dune aquifer: northeastern coast of the Buenos Aires province, Argentina. Hydrogeol J 20:1613–1621
Carretero S, Kruse E (2015) Iron and manganese content in groundwater on the northeastern coast of the Buenos Aires province, Argentina. Environ Earth Sci 73(5):1983–1995
Carretero S, Dapeña C, Kruse E (2013) Hydrogeochemical and isotopic characterisation of groundwater in a sand-dune phreatic aquifer in the northeastern coast of the province of Buenos Aires Argentina. Isot Environ Health S 49(3):399–419
Carretero S, Rapaglia J, Perdomo S, Martínez CA, Rodrigues Capítulo L, Gómez L, Kruse E (2019) A multi-parameter study of groundwater–seawater interactions along Partido de La Costa, Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. Environ Earth Sci 78(16):513
Cho BW, Choo CO (2019) Geochemical Behavior of Uranium and Radon in Groundwater of Jurassic Granite Area, Icheon, Middle Korea. Water 11:1278–1294
D’Onofrio E, Fiore M, Pousa J (2008) Changes in the regime of storm surges at Buenos Aires, Argentina. J Coast Res 24:260–265
Forte Lay JA, Aiello JL, Kuba J (1995) Software AGROAGUA v.5.0. CIBIOM CONICET, Buenos Aires
Hamada H (2000) Estimation of groundwater flow rate using the decay of 222Rn in a well. J Environ Radioact 47:1–13
Hoehn E, Von Gunten HR (1989) Radon in groundwater: a tool to assess infiltration from surface waters to aquifers. Water Resour Res 25(8):1795–1803. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR025i008p01795
Hoehn E, Von Gunten HR, Stauffer F, Dracos T (1992) Radon-222 as a groundwater tracer. A Laboratory Study. Eviron Sci Technol 26:734–738
Kafri U (2001) Radon in groundwater as a tracer to assess flow velocities: two test cases from Israel. Environ Geol 40(3):392–398
Kasztovszky Z, Sajó-Bohus L, Fazekas B (2000) Parametric changes of radon (222 Rn) concentration in ground water in Northeastern Hungary. J Environ Radioact 49:171–180
Lee BK, Hong SH, Lee DS (2000) Chemical composition of precipitation and wet deposition of major ions on the Korean peninsula. Atmos Environ 34(4):563–575
Lekouch I, Mileta M, Muselli M, Milimouk-Melnytchouk I, Šojat V, Kabbachi B, Beysens D (2010) Comparative chemical analysis of dew and rain water. Atmos Res 95(2–3):224–234
Mayer A, Bach Thao N, Banton O (2016) Using radon-222 to study coastal groundwater/surface-water interaction in the Crau coastal aquifer (southeastern France). Hydrogeol J 24(7):1775–1789
Mullinger NJ, Pates JM, Binley AM, Crook NP (2009) Controls on the spatial and temporal variability of 222Rn in riparian groundwater in a lowland Chalk catchment. J Hydrol 376:58–69
Radolić V, Vuković B, Šmit G, Stanić D, Planinić J (2005) Radon in the spas of Croatia. J Environ Radioact 83(2):191–198
Rapaglia J, Grant C, Bokuniewicz H, Pick T, Scholten J (2015) A GIS typology to locate sites of submarine groundwater discharge. J Environ Radioact 145:10–18
Rodrigues Capítulo L (2015) Evaluación geohidrológica en la región costera oriental de la provincia de Buenos Aires. Caso de estudio Pinamar (Geohydrological evaluation in the eastern coast of the Province of Buenos Aires. Case of study Pinamar), Doctoral thesis, Facultad de Ciencias Naturales y Museo, La Plata
Sala J, González N, Hernández M, Martín de Uliana E, Cheli E, Kruse E (1976) Factibilidad de provisión de agua subterránea a la localidad de San Clemente de Tuyú-El Tala: Provincia de Buenos Aires. Informe técnico [Practicability of Groundwater provision to San Clemente del Tuyú-El Tala town: Buenos Aires Province. Technical report]. Cátedra de Hidrogeología. Facultad de Ciencias Naturales-Cooperativa de Obras Sanitarias de San Clemente del Tuyú, La Plata, Argentina
Schubert M, Brueggemann L, Knoeller K, Schirmer M (2011) Using radon as an environmental tracer for estimating groundwater flow velocities in single-well tests. Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010WR009572
Sequeira R, Lung F (1995) A critical data analysis and interpretation of the pH, ion loadings and electrical conductivity of rainwater from the territory of Hong Kong. Atmos Environ 29(18):2439–2447
Sexsmith KS (1996) A detailed examination of the chemical, hydrological, and geological properties influencing the mobility of 222 radon and parent radionuclides in groundwater. Master thesis. Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO (United States). https://inis.iaea.org/collection/NCLCollectionStore/_Public/30/013/30013510.pdf?r=1&r=1. Accessed 15 Aug 2019
Soil Survey Staff (2014) Keys to soil taxonomy, 12th edn. USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service, Washington
Srilatha MC, Rangaswamy DR, Sannappa J (2014) Studies on concentration of radon and physicochemical parameters in ground water around Ramanagara and Tumkur districts, Karnataka, India. Int J Adv Sci Tech Res 2(4):641–660
Surbeck H, Voelkel H (1988) Radionuclide content vs grain size in soil samples. Sci Total Environ 69:379–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-9697(88)90353-1
Szabo Z, Vincent T, Fischer JM, Kraemer TF, Jacobsen E (2012) Occurrence and geochemistry of radium in water from principal drinking-water aquifer systems of the United States. Appl Geochem 27(3):729–752
Tabar E, Yakut H (2014) Radon measurements in water samples from the thermal springs of Yalova basin Turkey. J Radioanal Nucl Ch 299(1):311–319
Thornthwaite C, Mather J (1955) The water balance. Climatol 8:1–37
Wang X, Li H, Zhang Y, Qu W, Schubert M (2019) Submarine groundwater discharge revealed by 222 Rn: comparison of two continuous on-site 222 Rn-in-water measurement methods. Hydrogeol J 27(5):1879–1887. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-019-01988-z
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica, Grant number PICT 2016–2522, 2017–2020 and Universidad Nacional de La Plata, Grant number PPID/N021, 2017–2018. The authors would like to thank the Cooperativa de Provisión de Obras y Servicios Públicos de San Clemente del Tuyú Ltda. for their collaboration as well as the reviewers and editors for the valuable comments that improved the quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is a part of the Topical Collection in Environmental Earth Sciences on “Advances in Environmental Geochemistry” guest edited by Dr. Eleanor Carol, Dr. Lucia Santucci and Dr. Lia Botto.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carretero, S., Rapaglia, J., Rodrigues Capítulo, L. et al. Variability of 222Rn in the sandy aquifer of Buenos Aires coast. Environ Earth Sci 80, 109 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09388-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09388-x