Abstract
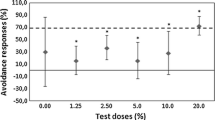
The toxicity and metal bioavailability were studied in dredged sediments from Rodrigo de Freitas Lagoon (Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil) using acute and avoidance tests with Eisenia andrei, and reproduction tests with Folsomia candida. The sediment was mixed with an artificial soil, and two natural soils (ferralsol and chernosol—representative Brazilian tropical soils) to obtain the following doses: 1, 3, 6, 12, 18, 24 and 30%. Total metal concentrations were determined in the sediment to support the interpretation of ecotoxicological data. Metal concentrations in the mixtures were in agreement with the threshold limits established by Brazilian law. However, significant avoidance responses were found on doses ≥ 3% and were the most sensitive endpoint. Earthworm mortality found in artificial soil mixtures (LC50 = 3.9) suggests higher toxicity levels than those obtained in ferralsol (LC50 = 7.6%) and chernosol (11.0%) treatments. Earthworm mortality, avoidance responses and collembolan reproduction levels found in ferralsol mixtures (LC50 = 9.2; avoidance EC50 = 2.3%; reproduction EC50 = 2.8%) were higher compared to chernosol treatments (LC50 = 11.0%; avoidance EC50 = 4.3%; reproduction EC50 = 4.9%). The reduction of toxicity levels in chernosol mixtures is probably due to the abundance of expansive clay minerals in chernosols with capacity of adsorbing metals and other xenobiotic substances from soil pore water, decreasing metal bioavailability. Finally, threshold limits defined by Brazilian legislation for soil quality and land disposal of dredged sediments are not sufficient to prevent noxious effects on soil fauna and should be complemented with a preliminary ecotoxicological evaluation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alamino RCJ, Polivanov H, Campos TMPC, Silva VHG, Santos LV, Mendes JC (2007) Biodisponibilidade de cádmio em latossolo acrescido de lodo de esgoto. Anuário do Instituto de Geociências 30(2):45–54
Almeida MSS, Borma LS, Barbosa MC (2001) Land disposal of river and lagoon dredged sediments. Engin Geol 60(1–4):21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-7952(00)00085-5
Araújo DF, Boaventura GR, Machado W, Viers J, Weiss D, Patchineelam SR, Ruiz I, Rodrigues APC, Babinski M, Dantas E (2017) Tracing of anthropogenic zinc sources in coastal environments using stable isotope composition. Chem Geol 449:226–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.12.004
Bianchi MO (2013) Ensaios Ecotoxicológicos como ferramenta para avaliação do impacto ambiental de resíduos de mineração sobre o solo. Dissertation, Rural Federal University of Rio de Janeiro
Carbonell G, Gómez JPN, Babín MM, Fernández C, Alonso E, Tarazona JV (2009) Sewage sludge applied to agricultural soil: ecotoxicological effects on representative soil organisms. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 72:1309–1319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2009.01.007
Cesar RG, Egler S, Polivanov H, Castilhos ZC, Rodrigues AP (2011) Mercury, copper and zinc contamination in soils and fluvial sediments from an abandoned gold mining area in southern Minas Gerais State, Brazil. Environ Earth Sci 64:211–222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0840-8
Cesar RG, Silva MB, Colonese JP, Bidone ED, Egler S, Castilhos ZC, Polivanov H (2012) Influence of the properties of tropical soils in the toxicity and bioavailability of heavy metals in sewage sludge-amended lands. Environ Earth Sci 66:2281–2292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1449-2
Cesar RG, Natal-da-Luz T, Sousa JPF, Colonese J, Bidone ED, Castilhos ZC, Egler SG, Polivanov H (2014) Disposal of dredged sediments in tropical soils: ecotoxicological effects on earthworms. Environ Monitor Assess 186:1487–1497
Cesar RG, Natal-Da-Luz T, Silva F, Bidone E, Castilhos Z, Polivanov H, Sousa JP (2015a) Ecotoxicological assessment of a dredged sediment using bioassays with three species of soil invertebrates. Ecotoxicol 24:414–423. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1390-8
Cesar RG, Natal-Da-Luz T, Bidone E, Castilhos Z, Polivanov H, Sousa JP (2015b) Disposal of dredged sediments in tropical soils: ecotoxicological evaluation based on bioassays with springtails and enchytraeids. Environ Sci Poll Res 22:2916–2924. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3559-3
Cesar RG, Rodrigues AP, Rocha BCRC, Campos TMP, Monte C, Dealtry S, Castilhos ZC, Machado W (2017) Ecotoxicological assessment of dredged sediments from Guanabara and Sepetiba bays (Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil) using bioassays with earthworms. In: Araujo C, Shinn C Ecotoxicology in Latin America, 1 st edn, vol 1. Nova Publishers, New York, pp 309–324
Chelinho S, Domene X, Campana P, Natal-da-Luz T, Scheffczyk A, Römbke J, Andrés P, Sousa JP (2011) Improving ecological risk assessment in the Mediterranean area: selection of reference soils and evaluating the influence of soil properties on avoidance and reproduction of two oligochaete species. Environ Toxicol Chem 30(5):1050–1058. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.480
CONAMA (Conselho Nacional de Meio Ambiente). 2009. Resolução 420. http://www.mma.gov.br/port/conama/legiabre.cfm?codlegi=506>. Accessed Feb 2018
Corporale AG. Violante A (2015) Chemical processes affecting the mobility of heavy metals and metalloids in soil environments. Curr Pollut Rep 2(1):15–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40726-015-0024-y
Crouau Y, Chenon P, Gisclard C (1999) The use of Folsomia candida (Collembola, Isotomidae) for the bioassay of xenobiotic substances and soil pollutants. Applied Soil Ecol 12(2):103–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0929-1393(99)00002-5
EMBRAPA (Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária) (1997) Centro Nacional de Pesquisa de Solos. Serviço nacional de levantamento e conservação do solo. Manual de métodos de análise de solo. Rio de Janeiro: Embrapa Solos, p 212
Fountain MT, Hopkins SP (2001) Continuous monitoring of folsomia candida (insecta: collembola) in a metal exposure test. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 48:275–286. https://doi.org/10.1006/eesa.2000.2007
Garcia M (2004) Effects of pesticides on soil fauna: development of ecotoxicology test methods for tropical regions. In: Vlek PLG, et al (eds) Ecology and development series, vol 19. Cuvillier, Gottingen, p 282
Gonzalez AM, Paranhos R, Lutterbach (2006) Heterotrophic bacteria abundances in Rodrigo de Freitas Lagoon (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil). Braz J Microbiol 37(4):1678–4405. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-83822006000400005
Hinton J, Veiga MM (2002) Earthworms as bioindicators of mercury pollution from mining and other industrial activities. Geochem Expl Environ Anal 2(3):269–274. https://doi.org/10.1144/1467-787302-031
ISO - International Organization for Standardization (2008) Soil quality—avoidance test for determining the quality of soils and effects of chemicals on behaviour—part 1: Test with earthworms (Eisenia fetida and Eisenia andrei). Geneva, ISO 17512-1
ISO (International Organization for Standardization) (1999) Soil Quality— inhibition of reproduction of collembola (Folsomia candida) by Soil Pollutants. ISO 11267. Geneva, Switzerland
ISO (International Organization for Standardization) (2012) Soil quality—effects of pollutants on earthworms (Eisenia fetida)—part 1: Determination of acute toxicity to Eisenia fetida/andrei. Geneve, Switzerland, ISO 11268-11262
Kaasalainen M, Yli-Halla (2003) Use of sequential extraction to assess metal partitioning in soils. Environ Poll 126(2):225–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(03)00191-X
Kavlock RJ, Daston GP, DeRosa C, Fenner-Crisp P, Gray LE, Kaattari S, Lucier G, Mac MJ, Maczka C, Miller R, Moore J, Rolland R, Scott G, Sheehan DM, Sinks T, Tilson HA (1996) Research needs for the risk assessment of health and environmental effects of endocrine disruptors: a report of the U.S. EPA-sponsored workshop. Environ Health Perspect 10(4):715–740
Loureiro DD, Fernandez MA, Herms FW, Lacerda LD (2009) Heavy metal inputs evolution to an urban hypertrophic coastal lagoon, Rodrigo de Freitas Lagoon, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Environ Monit Assess 159:577–588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0652-4
Loureiro DD, Fernandez M, Herms F, Araújo C, Lacerda LD (2012) Distribuição dos metais pesados em sedimentos da Lagoa Rodrigo de Freitas. Oecol Aust 16(3):353–364
Machado W, Silva-Filho EV, Oliveira RR, Lacerda LD (2002) Trace metal retention in mangrove ecosystems in Guanabara Bay, SE Brazil. Mar Poll Bull 44:1277–1280. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-326X(02)00232-1
Maioli OLG, Rodrigues KC, Knoppers BA, Azevedo DA (2010) Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments from two Brazilian estuarine systems. J Braz Chem Soc 21(8):1543–1551. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-50532010000800020
Monteiro FF, Cordeiro RC, Santelli RE, Machado W, Evangelista H, Villar LS, Viana LCA, Bidone ED (2011) Sedimentary geochemical record of historical anthropogenic activities affecting Guanabara Bay (Brazil) environmental quality. Environ Earth Sci 65(6): 1661–1669. https://doi.org/10.1007%2Fs1
Munns WR, Berry WJ, Dewitt WT (2002) Toxicity testing, risk assessment, and options for dredged material management. Mar Poll Bull 44:294–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-326X(01)00250-8
Nascimento JR, Sabadini-Santos E, Carvalho C, Keunecke KA, Cesar R, Bidone ED (2016) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals by shrimp (Litopenaeus schmitti): a dose-response approach for coastal resources management. Mar Poll Bull 114:1007–1013
Natal-da-Luz T, Römbke J, Sousa JP (2008) Avoidance tests in site-specific risk assessment—influence of soil properties on the avoidance response of collembola and earthworms. Enviro Toxicol Chem 27(5):1112–1117. https://doi.org/10.1897/07-386.1
Natal-da-Luz T, Tidona S, Jesus B, Morais PV, Sousa JP (2009) The use of sewage sludge as soil amendment: the need for an ecotoxicological evaluation. J Soils Sedim 9:246–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-009-0077-x
Neuhauser EF, Loehr RC, Milligan DL, Malecki MR (1985) Toxicity of metals to the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Biol Fertility of Soils 1:149–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00301782
Owojori OJ, Reinecke AJ, Rozanov AB (2009) The combined stress effects of salinity and copper on the earthworm Eisenia fétida. Applied Soil Ecol 41:277 – 285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2008.11.006
Pereira CS, Lopes I, Sousa JP, Chelinho S (2015) Effects of NaCl and seawater induced salinity on survival and reproduction of three soil invertebrate species. Chemosphere 135:116–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.03.094
Perez A, Machado W, Gutierrez D, Borges AC, Patchineelam SR, Sanders CJ (2018) Carbon accumulation and storage capacity in mangrove sediments three decades after deforestation within a eutrophic bay. Mar Poll Bull 126:275–280
Rodrigues SK, Abessa DMS, Rodrigues APC, Soares-Gomes A, Freitas CB, Santelli RE, Freire AS, Machado W (2017) Sediment quality in a metal-contaminated tropical bay assessed with a multiple lines of evidence approach. Environ Pollut 228:265–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.05.045
Sakuma M (1998) Probit analysis of preference data. Appl Entomol Zool 33:339–347
Selivanovskaya SY, Latypova VZ (2003) The use of bioassays for evaluating the toxicity of sewage sludge and sewage sludge-amended soil. J Soils Sedim 3(2):85–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02991073
Silveira AEF, Nascimento JR, Sabadini-Santos E, Bidone ED (2017) Screening-level risk assessment applied to dredging of polluted sediments from Guanabara Bay, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Mar Pollut Bull 118:368–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.03.016
Straalen NM, Donker MH, Vijver MG, Gestel CAM (2005) Bioavailability of contaminants estimated from uptake rates into soil invertebrates. Env Poll 136:409–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.01.019
Topuz E, van Gestel CAM (2017) The effect of soil properties on the toxicity and bioaccumulation of Ag nanoparticles and Ag ions in Enchytraeus crypticus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 144:330–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.06.037
Vašíčková J, Kalábová T, Komprdová K, Priessnitz J, Dymák M, Lána J, Škulcová L, Šindelářová L, Sáňka M, Čupr P, Vácha R, Hofman J (2013) Comparison of approaches towards ecotoxicity evaluation for the application of dredged sediment on soil. J Soils Sedim 13:906–915. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-013-0670-x
Vezzone M, Cesar RG, Polivanov H, Castilhos ZC, Campos TM (2018) Contaminação por metais pesados em sedimentos superficiais de fundo da Lagoa Rodrigo de Freitas, Estado do Rio de Janeiro (RJ). Anuário do Instituto de Geociências da UFRJ (in press)
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the CNPq (National Brazilian Council for Scientific and Technological Development) for providing grants for Mariana Vezzone (Doctorage/CNPq), Aline Serrano (IC/CNPq) and Danielle Siqueira.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vezzone, M., Cesar, R., Polivanov, H. et al. Ecotoxicological evaluation of dredged sediments from Rodrigo de Freitas Lagoon (Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil) using bioassays with earthworms and collembolans. Environ Earth Sci 77, 743 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7930-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7930-4