Abstract
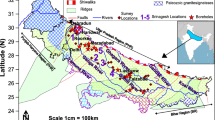
The microtremor horizontal-to-vertical spectral ratio (HVSR, or H/V spectral ratio) method is an effective tool for detecting sediment thickness. Firstly, single-station microtremor measurements were taken beside 52 boreholes located in Pearl River Delta, China. Sediment thicknesses revealed by those boreholes range from 7.9 to 39.6 m. Then, those microtremor data were analyzed using HVSR method, and peak frequency of each site was extracted. According to those peak frequencies of HVSR and corresponding sediment thicknesses, the frequency-to-thickness fitting (f–Z) equation which is suitable for Pearl River Delta area was established. And this equation was compared with several fitting equations derived from different regions by other researchers. Finally, this fitting equation was applied in a collapse area in Guangzhou city to estimate site sediment thickness. Compared with data from five boreholes in this collapse area, the consistency between estimated sediment thickness and real value was relatively good. Karst sinkholes are generally located in regions where thickness of sediments is shallow. Therefore, the method described in this paper can provide support for delineating potential collapse areas.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aki K (1957) Space and time spectra of stationary stochastic waves, with special reference to microtremors. Bull Earthq Res Inst Tokyo Univ 35:415–456
Ansary MA, Rahman MS (2013) Site amplification investigation in Dhaka, Bangladesh, using H/V ratio of microtremor. Environ Earth Sci 70(2):559–574
Bignardi S (2017) The uncertainty of estimating the thickness of soft sediments with the HVSR method: a computational point of view on weak lateral variations. J Appl Geophys 145:28–38
Büyüksaraç A, Bektaş Ö, Yılmaz H, Arısoy MÖ (2013) Preliminary seismic microzonation of Sivas city (Turkey) using microtremor and refraction microtremor (ReMi) measurements. J Seismol 17(2):425–435
Capon J (1970) Applications of detection and estimation theory to large array seismology. Proc IEEE 58(5):760–770
D’Amico V, Picozzi M, Baliva F, Albarello D (2008) Ambient noise measurements for preliminary site-effects characterization in the urban area of Florence, Italy. Bull Seismol Soc Am 98(3):1373–1388
Delgado J, Casado CL, Estevez A, Giner J, Cuenca A, Molina S (2000a) Mapping soft soils in the Segura river valley (SE Spain): a case study of microtremors as an exploration tool. J Appl Geophys 45(1):19–32
Delgado J, Casado CL, Giner J, Estevez A, Cuenca A, Molina S (2000b) Microtremors as a geophysical exploration tool: applications and limitations. Pure appl Geophys 157(9):1445–1462
Farahani JV, Zaré M (2014) Site characterizations for the Tehran network (TDMMO) in Tehran region using micro-earthquake, microtremor and quarry blast data. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 63:235–247
Gosar A, Lenart A (2010) Mapping the thickness of sediments in the Ljubljana Moor basin (Slovenia) using microtremors. Bull Earthq Eng 8(3):501–518
Guéguen P, Cornou C, Garambois S, Banton J (2007) On the limitation of the H/V spectral ratio using seismic noise as an exploration tool: application to the Grenoble valley (France), a small apex ratio basin. Pure appl Geophys 164(1):115–134
He Z, Ding Z, Jia H, Ye T (2007) To determine the velocity structure of shallow crust with surface wave information in microtremors. Chin J Geophys 50(2):441–448
Ibs-von Seht M, Wohlenberg J (1999) Microtremor measurements used to map thickness of soft sediments. Bull Seismol Soc Am 89(1):250–259
Lane JW, White EA, Steele GV, Cannia JC, Williams JH (2008) Estimation of bedrock depth using the horizontal-to-vertical (H/V) ambient-noise seismic method. Near Surface 2008-14th EAGE European meeting of environmental and engineering geophysics
Motamed R, Ghalandarzadeh A, Tawhata I, Tabatabaei SH (2007) Seismic microzonation and damage assessment of Bam city, southeastern Iran. J Earthq Eng 11(1):110–132
Nakamura Y (1989) A method for dynamic characteristics estimation of subsurface using microtremor on the ground surface. Railway Tech Res Inst Q Rep 30(1):25–33
Parolai S, Bormann P, Milkereit C (2002) New relationships between vs, thickness of sediments, and resonance frequency calculated by the H/V ratio of seismic noise for the Cologne area (Germany). Bull Seismol Soc Am 92(6):2521–2527
Paudyal YR, Yatabe R, Bhandary NP, Dahal RK (2013) Basement topography of the Kathmandu Basin using microtremor observation. J Asian Earth Sci 62:627–637
Saenger EH, Torres A, Rentsch S, Lambert M, Schmalholz SM, Mendez-Hernandez E (2007) A hydrocarbon microtremor survey over a gas field: identification of seismic attributes. Seg technical program expanded, pp 1277–1281
Steiner B, Saenger EH, Schmalholz SM (2008) Time reverse modeling of low-frequency microtremors: application to hydrocarbon reservoir localization. Geophys Res Lett 35(3):L03307
Sylvette BC, Cécile C, Pierre-Yves B, Fabrice C, Peter M, Jozef K, Donat F (2006) H/V ratio: a tool for site effects evaluation. Results from 1-D noise simulations. Geophys J Int 167(2):827–837
Wang Z (1986) The micromotional spatial autocorrelation method and its practical technique. Geophys Geoch Explor 10(2):123–133
Xu P, Li S, Du J, Ling S, Guo H, Tian B (2013) Microtremor survey method: a new geophysical method for dividing strata and detecting the buried fault structures. Acta Petrol Sin 29(5):1841–1845
Ye T (2004) The exploration technique for microtremor array and its application. Earthq Res China 20(1):47–52
Acknowledgements
This work was jointly supported by China Geological Survey Project (Grant No. DD20160254) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41402284). The authors thank Xiaozhen Jiang and Fucai Wei for the helpful suggestions. We extend sincere gratitude to the editors of Environmental Earth Sciences and the anonymous reviews for the valuable advice on how to improve this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is a part of the Topical Collection in Environmental Earth Sciences on Karst Hydrogeology: Advances in Karst Collapse Studies, edited by Dr. Zhou Wanfang.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, D., Gan, F., Zhang, W. et al. The application of HVSR method in detecting sediment thickness in karst collapse area of Pearl River Delta, China. Environ Earth Sci 77, 259 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7439-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7439-x