Abstract
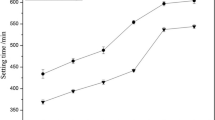
The early-strength characteristics and mechanism of eight kinds of early-strength agents in low-strength cementitious materials prepared with manganese tailings were studied, and then the optimum mixing amount was obtained by means of progressing and superimposing optimization. The phase composition and morphology of hydration products were characterized through X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy. The results indicated that there existed good superimposing effect among triethanolamine, ferric chloride and lithium carbonate. When the mixing amount of triethanolamine, ferric chloride and lithium carbonate were 0.04, 0.3 and 0.7%, the compressive strength of 3- and 7-day net paste samples increased by 105.5 and 34.5%, while the porosity of 3- and 7-day decreased by 8.3 and 7.4%, respectively. The initial setting time shortened from 130 to 65 min. Therefore, the combination of early-strength agents could accelerate the dissolution of tailings, shorten hydration cycle, increase the amount of ettringite and calcium silicate hydrate, compact the internal structure further, reduce the porosity, which could achieve the compressive strength improved in short time.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi P, Yun KK (2014) Experimental analysis of latex-solid content effect on early-age and autogenous shrinkage of very-early strength latex-modified concrete. Constr Build Mater 65:396–404
Ercikdi B, Cihangir F, Kesimal A, Deveci H, Alp I (2009) Utilization of industrial waste products as pozzolanic material in cemented paste backfill of high sulphide mill tailings. J Hazard Mater 168:848–856
Felekoğlu Burak (2012) A method for improving the early strength of pumice concrete blocks by using alkyl alkoxy silane (AAS). Constr Build Mater 28:305–310
Gao Y, Xu J, Bai E, Luo X, Zhu J, Nie L (2015) Static and dynamic mechanical properties of high early strength alkali activated slag concrete. Ceram Int 41:12901–12909
Hao X, Zhou X, Luo Z, Tao Z, Chen X (2015) Effects of compound admixtures on the properties of ferrochrome slag based composite materials. J Funct Mater 46:13029–13034
Jiang MF, Xian-Jun LV (2014) Research and application progresses of concrete early strength agent. Bull Chin Ceram Soc 33:2527–2532
Kim K, Park S, Kim YJ (2013) Utilization of separator bag filter dust for high early strength cement production: part 2—properties of concrete. Constr Build Mater 40:746–752
Li GH, Zhang GC, Ge JJ, Zhou S, Liu YL (2013) Coagulation effect of cationic microspheres with residual hydrolyzed polyacrylamide. Acta Pet Sin 34:1157–1162
Liu J, Ma H, Qiang L, Chen S, Zhang Y (2011) Study on optimization of high performance concrete admixtures. J Nanjing Univ Aeronaut Astronaut 28:206–210
Liu JM, Ou ZW, Xiao HB, Mo JC, Yang KH (2017) Early strength of stabilized soil affected by functional components. Rock Soil Mech 38:755–761
Min TB, Cho IS, Park WJ, Choi HK, Lee HS (2014) Experimental study on the development of compressive strength of early concrete age using calcium-based hardening accelerator and high early strength cement. Constr Build Mater 64:208–214
Thomas JJ, Allen AJ, Jennings HM (2012) Density and water content of nanoscale solid C–S–H formed in alkali-activated slag (AAS) paste and implications for chemical shrinkage. Cem Concr Res 42:377–383
Wang CW, Wang RH, Chen ED, Peng ZG, Bu YH (2011) Performance and mechanism of the lithium-salt accelerator in improving properties of the oil-well cement under low temperature. Acta Petrol Sin 32:140–144
Wang C, Zhang HB, Luo YL, Zhou LM (2015) Preparation and mechanism analysis of fast-setting and rapid-high-strength concrete. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol 43:89–93
Won JP, Hwang UJ, Kim CK, Lee SJ (2013) Mechanical performance of shotcrete made with a high-strength cement-based mineral accelerator. Constr Build Mater 49:175–183
Wu P, Lu X, Liang Z, Zhu C, Chen Y (2014) The mechanism and application of concrete hardening accelerator. Metal Mine 12:20–25
Zhai MY, Zhao JH, Wang DM (2017) Applying lithium slag powders to cement-based materials as supplementary cementitious component: an overview. Mater Rev 31:139–144
Zhang XW, Xiao RM, Zhang X (2012) Preparation of high performance composites strength accelerator for cement containing fly ash and ground granulated blast-furnace slag. J Build Mater 15:249–254
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China through Program Nos. 51574141 and 51274109.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Zhang, S. & Wu, B. Experimental study on selection of early-strength agent for low-strength cementitious materials prepared with manganese tailings. Environ Earth Sci 77, 231 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7415-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7415-5