Abstract
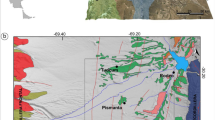
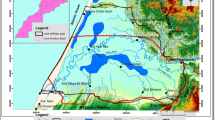
The town of Orvieto, located on the Rock of the same name, is an example of “vulnerable town”; problems of slope instability connected with the lithological and morphological characteristics of the Rock have been thoroughly examined and discussed during previous research studies. Hydrogeochemical data about groundwater recharging the springs present in the area were never taken into account. Pollution of the springs is well known but still occurs for unclear reasons. The aim of this work is therefore to present the results of a hydrogeological and geochemical investigation of all the springs along the slopes of Orvieto hill and at the foot of the tuffaceous Rock, to characterize the groundwater flow paths and to suggest a possible source of contamination. The research study was carried out during three hydrogeochemical surveys in the years 1998–1999, 2003–2004, and 2007–2008.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez W, Gordon A, Rashak EP (1975) Eruptive source of the “Tufo rosso a scorie nere”, a Pleistocene ignimbrite, North of Rome. Geologica Romana 14:141–154
ASTM D4646 -03 (2008) Standard test method for 24-h batch-type measurement of contaminant sorption by soils and sediments. Book of Standards Volume 11.04
Bowen HJM (1979) Environmental chemistry of the elements. Academic Press, London
Bradley D J, Mc Vay G L, Coles D G (1980) Leach test methodology for the Waste/Rock Interactions Technology Program. Technical Report. Battelle Pacific Northwest Labs., Richland, WA (USA)
Celico P (2003) Elementi di Idrogeologia. Liguori Editore, Napoli
Cencetti C, Conversini P, Tacconi P (2005) The Rock of Orvieto, Umbria, Central Italy. Giornale di Geologia Applicata 1(2005):103–112. doi:10.1474/GGA.2005-01.0-10.0010
Clark ID, Fritz P (1997) Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology. Lewis Publishers CRC Press, New York
Conversini P, Lupi S, Martini E, Pialli G, Sabatini P (1977) Rupe d’Orvieto. Indagini geologico-tecniche. Quaderni Regione dell’Umbria, Studi, Perugia
Conversini P, Martini E, Pane V, Pialli G, Tacconi P, Tortoioli L, Ubertini L. (1995) La Rupe di Orvieto e il colle di Todi: due casi di città fragili. Geologia Applicata e Idrogeologia XXX: 211–224
Faraone D, Stoppa F (1988) Il tufo di Orvieto nel quadro dell’evoluzione vulcano-tettonica della caldera di Bolsena, Monti Vulsini. Boll Soc Geol Ital 107:383–397
Freeze RA, Cherry JA (1979) Groundwater. Prentice-Hall, New York. ISBN 0-13-365312-9
Fukada T, Hiscick KM, Tennis PF (2004) A dual-isotope approach to the nitrogen hydrochemistry of an urban aquifer. Appl Geochem 19:709–719
Giaquinto S, Marchetti G, Mattioli B (1982) Caratteri Idrogeologici del bacino del fiume Paglia (Umbria-Toscana). In Bacino del fiume Paglia (Umbria-Toscana). Studi strutturali, idrogeologici e geochimici. PFE Sottoprogetto Energia Geotermica, CNR, RF-16, Roma
Hem JD (1985) Study and Interpretation of the Chemical Characteristics of Natural Water. US Geological Survey Water Supply Paper 2254, US Geological Survey, Alexandria, Virginia
Langella A, De Gennaro M, Colella C, Buondonno A (1995) Effects of phillipsite- or chabazite-rich tuff addition to soil on the growth and yield of Beta vulgaris and Raphanus sativus. Proceedings of III Conv. Naz. Scienza e Tecnologia delle Zeoliti. R. Aiello ed., De Rose, Montalto, Cosenza, pp 277–285
Latham AG, Schwarcz HP (1987) On the possibility of determining rates of removal of uranium from crystalline igneous rocks using U-series disequilibria–1: a U-leach model, and its applicability to whole-rock data. Appl Geochem 2(1):55–65
Lenzi G, Passaglia E (1974) Fenomeni di zeolitizzazione nelle formazioni vulcaniche della regione Sabatina. Boll Soc Geol Ital 93:623–645
Mariotti A (1984) Utilisation des variations naturelles d’abondance isotopique en 15N pour tracer l’origine des pollutions des aquiferes par les nitrates. Isotope Hydrology, Proceedings of a symposium, Vienna, 12–16 Sept. 1983. IAEA STI/PUB/650. ISBN 92-0-040084-1
Meinzer OE (1932) Outline of methods for estimating ground water supplies. US Geol Survey Paper 638-C. Washington
Passaglia E, Vezzalini G, Carnevali R (1990) Diagenetic chabazites and phillipsites in Italy: crystal chemistry and genesis. Eur J Mineral 2:827–839
Passaglia E, Marchi E, Barbieri L, Bedogni G, Taschini G, Azzolini P (1997) Le zeoliti nel ciclo di depurazione delle acque reflue e loro successivo impiego in agricoltura. Noi L’Ambiente 52–53:56–61
Pitcairn IK, Teagle DAH, Kerrich R, Craw D, Brewer TS (2005) The behaviour of nitrogen isotopes during metamorphism and mineralization: evidence from the Otago and Alpine Schists, New Zealand. Earth Planet Sci Lett 233:229–246
Snellings R, van Haren T, Machiels L, Mertens G, Vandenberghe N, Elsen J (2008) Mineralogy, geochemistry, and diagenesis of clinoptilolite tuffs (miocene) in the central simav graben, western turkey. Clays Clay Miner 56(6):622–632
Tandia AA, Gaye CB, Faye A (1998) Origin, process and migration of nitrate compounds in the aquifers of Dakar Region, Senegal. Application of isotope techniques to investigate groundwater pollution. IAEA-TECDOC-1046 ISSN 1011-4289 ©IAEA, 1998
http://www.idrografico.roma.it/: ufficio idrografico e mareografico-regione lazio. Annali idrologici (hydrological annals)
Zanon V, Peccerillo A, Conversini P, Pacheco J, Pimentel A (2007) Utilization of photographic techniques to recognize zeolitized facies in the Orvieto ignimbrite, as potential pollutant for the underneath aquifer. Poster at XXIV IUGG 2007, Perugia, 2–13 Luglio 2007
Zhou X, Stetzenbach KJ, Yu Z, Johannesson KH (2005) Origin of rare earth element signatures in groundwater of south Nevada, USA: implications from preliminary batch leach tests using aquifer rocks. In: Johannesson KH (ed) Rare earth elements in groundwater flow systems. Springer, Netherlands, pp 141–160
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Alessandra Norici for her valuable assistance in reviewing the document, Fausto Metteucci for the execution of lab tests, Regional Authority of Umbria (Dep. of Territorial Policies, Environment and Infrastructure) for the funding of this research project and Prof. Giulio Sergio for having inspired this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tazioli, A., Conversini, P. & Peccerillo, A. Hydrogeological and geochemical characterisation of the Rock of Orvieto. Environ Earth Sci 66, 55–65 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1206-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1206-6