Abstract
Purpose
Bulimia is a common cause of sialadenosis. This paper presents a case of bilateral parotid sialadenosis associated with long-standing bulimia, and reviews the relevant literature and current treatment options.
Methods and Results
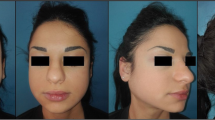
A 32-year-old woman had severe bilateral parotid sialomegaly for the last 6 years, which had occurred secondary to bulimia nervosa, which she had since 14 years. Treatment with pilocarpine was unsuccessful, so she underwent bilateral conservative parotidectomy. This procedure not only improved the aesthetic appearance of the patient but also improved her social and work life and overall quality of life.
Conclusions
Sialomegaly secondary to bulimia results in a major alteration of the aesthetics of a patient’s face. Conservative measures are not enough in many cases, and parotidectomy may be the only viable option, as it can also significantly improve adherence to psychiatric treatment for bulimia, in addition to correcting the facial aesthetics.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Donath K (1976) Sialadenosis of the parotid gland. Ultrastructural, clinical and experimental findings in disturbances of secretion. Veroff Pathol 103:1–122
Watt J (1977) Bening parotid swelling: a review. Proc R Soc Med 70:483–486
Devlin MJ, Steinglass JE (2010) Eating disorders. In: Cutler JL, Marcus ER (eds) Psychiatry, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Lavender S (1969) Vomiting and parotid enlargement. Lancet 1:426
Kessler RC, Berglund PA, Chiu WT et al (2013) The prevalence and correlates of binge eating disorder in the WHO World Mental Health Surveys. Biol Psychiatry 73:904–914
Ogren FP, Huerter JV, Pearson PH, Antonson CW, Moore GF (1987) Transient salivary gland hypertrophy in bulimics. Laryngoscope 97:951–953
Mitchell JE, Hatsukami D, Eckert ED, Pyle RL (1985) Characteristics of 275 patients with bulimia. Am J Psychiatry 142:482–485
Mandel L, Kaynar A (1992) Bulimia and parotid swelling: a review and case report. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 50:1122–1125
Price C, Schmidt MA, Adam EJ, Lacey H (2008) Parotid gland enlargement in eating disorders: an insensitive sign? Eat Weight Disord 13:79–83
Nassour DN, Patel SV, Kosseifi SG, Jordan RM, Peiris AN (2007) Marked bilateral parotid enlargement in metabolic syndrome: a case report and review of the literature. Tenn Med 100:39–41
Wilson T, Price T (2003) Revisiting a controversial surgical technique in the treatment of bulimic parotid hypertrophy. Am J Otolaryngol 24:85–88
Herrlinger P, Gundlach P (2001) Hypertrophy of the salivary glands in bulimia. HNO 49:557–559
Monteleone P, Santonastaso P, Pannuto M, Favaro A, Caregaro L, Castaldo E, Zanetti T, Maj M (2005) Enhanced serum cholesterol and triglyceride levels in bulimia nervosa: relationships to psychiatric comorbidity, psychopathology and hormonal variables. Psychiatry Res 134:267–273
Wolfe BE, Jimerson DC, Smith A, Keel PK (2011) Serum amylase in bulimia nervosa and purging disorder: differentiating the association with binge eating versus purging behavior. Physiol Behav 104:684–686
Colevas AD (1998) Re: “Sialadenosis: a presenting sign in bulimia”. Head Neck 20:758–762 (Head Neck. 1999;2:582)
Mehler PS, Wallace JA (1993) Sialadenosis in bulimia. A new treatment. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 119:787–788
Hay PJ, Claudino AM (2015) Bulimia nervosa: online interventions. BMJ Clin Evid 1:1009
Berke GS, Calcaterra TC (1985) Parotid hypertrophy with bulimia: a report of surgical management. Laryngoscope 95:597–598
Rauch S, Herzog D (1987) Parotidectomy for bulimia: a dissenting view. Am J Otolaryngol 8:376–380
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The researchers declare no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garcia Garcia, B., Dean Ferrer, A., Diaz Jimenez, N. et al. Bilateral Parotid Sialadenosis Associated with Long-Standing Bulimia: A Case Report and Literature Review. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 17, 117–121 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-016-0913-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-016-0913-7