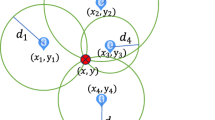
Abstract
Outdoor localization of non-cooperative moving discrete target tracking is a demanding and challenging due to inherent constraints of “target tracking wireless sensor networks” such as battery capacity, processing capacity, memory capacity. Current methods use either an active sensor or perform additional processing of the data received from multiple passive sensor nodes that increases power consumption. The work presented here proposes approximate localization of non-cooperative moving target in large open secluded area with optimal power consumption and sufficient accuracy. Binary passive infrared (PIR) sensor is used, resulting in reduced power consumption by the sensor. In order to deal with sensor’s technical limitation, a node is developed using variable range binary PIR sensors which results in variable sensing sectors. Deterministic directional, spatial–temporal domain of network topology along with activation log of node and its sectors is mapped with a dynamic target motion trajectory, resulting in sufficiently accurate target localization. Simulation results of the algorithm for “position estimation of random direction linearly moving target with positive slope motion model” indicate significant tracking of target with sufficient accuracy and reduced sensing power compared to existing methods.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- OTWSN:
-
Object tracking wireless sensor network
- DPWSN:
-
Directional passive wireless sensor node
- PIR:
-
Passive infrared sensor
- PW:
-
Proposed work
- PF:
-
Particle filter
- BS:
-
Base station
- EP:
-
Estimated position
- TT:
-
Target trajectories
References
Abd El Aziz M (2017) Source localization using TDOA and FDOA measurements based on modified cuckoo search algorithm. Wirel Netw 23:487–495. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-015-1158-y
Akbas S, Efe MA, Ozdemir S (2014) Performance evaluation of PIR sensor deployment in critical area surveillance networks. In: IEEE international conference on distributed computing in sensor systems, Marina Del Rey
Amin F, Rashid A, Abdul R et al (2019) An advanced algorithm for higher network navigation in social Internet of Things using small world networks. Sensors 19(9):2007
Byunghum S, HakSoo C, HyungSu L (2008) Surveillance tracking system using passive infrared motion sensors in wireless sensor networks. ICOIN 2008, Busan
Chen J, Li J, Yang S et al (2017) Weighted optimization-based distributed Kalman filter for nonlinear target tracking in collaborative sensor networks. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(11):3892–3905
Choubisa T, Upadrashta R, Panchal S et al (2016) Challenges in developing and deploying a PIR sensor-based intrusion classification system for an outdoor environment. In: IEEE 11th Int. workshop on practical issues in building sensor network applicat. Sens App, pp 148–155.
Choubisa T, Mohanty SB, Kashyap M et al (2017) An optical-camera complement to a PIR sensor array for intrusion detection and classification in an outdoor environment. In: 2017 IEEE. 42nd Conference on local computer networks workshops, Singapore, pp 44–52
Dusadee A, Kittipat A, Teerasit K (2013) A moving target tracking algorithm using support vector machine in binary sensor network, 13th ISCIT, SuratThani, pp 529–534
FayaziBarjni E, Davood G, Mohammad bagher S (2019) Target tracking in wireless sensor networks using NGEKF algorithm. J AIHC. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12625-019-01536-3
Gami H (2018) Movement direction and distance classification using a single PIR sensor. IEEE Sens Lett 2(1):1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/LSENS.2017.2782179
Haixia J, Haiyan W, Zhengguo et al (2018) DOA estimation for underwater target by active detection on virtual time reversal using a uniform linear array. Sensors 18:2458
Hao Q, Hu F, Xiao Y (2009) Multiple human tracking and identification with wireless distributed pyroelectric sensor systems. IEEE Syst J 3(4):428–439. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSYST.2009.2035734
He J, Yishang G, Fei L et al (2014) CC-KF; enhanced TOA performance in multipath and NLOUS indoor extreme environment. IEEE SENS J 14(11):3766–3774
Jia Z, Guan B (2018) Received signal strength difference based tracking estimation method for arbitrarily moving target in wireless sensor networks. Int J Distrib Sens Netw. https://doi.org/10.1177/1550147718764875
Katenka N, Elizaveta L, George M (2013) Tracking multiple targets using binary decisions from wireless sensor networks. J Am Stat Assoc 108(502):398–410
Lai KC, Ku BH, Chih-Yu W (2018) Using cooperative PIR sensing for human indoor localization. In: The 27th wireless and optical communication conference (WOCC). IEEE, Hualien, pp 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/WOCC.2018.8372703
Narayana S, Venkatesha Prasad R, Rao VS (2015) PIR sensors: characterization and novel localization technique. In: IPSN '15: Proceedings of the 14th international conference on information processing in sensor networks, Seattle Washington, ACM pp 142–153
Raviteja U, Tarun C, Praneeth A et al (2016) Animation and chirplet-based development of a PIR sensor array for intruder classification in an outdoor environment. arXivPrePrintarXiv: 1604.03829
Talari S, Shafie-khah M, Siano P, Loia V, Tommasetti A, Catalão JPS (2017) A review of smart cities based on the internet of things concept. Energies 10:421
Wu L, Wang Y (2019) A low power electric-mechanical driving approach for true occupancy detection using a shuttered passive infrared sensor. IEEE Sens J 19(1):47–57
Xiaomu L, Huoyuan T, Qiuju G et al (2016) Abnormal activity detection using pyroeletric infrared sensors. Sensors 16:822
Xiong J, Li FM, Jing YZ et al (2014) Human tracking system based on PIR sensor network and video. Advanced Technologies in Ad Hoc and Sensor Networks, Springer, pp 13–25
Yu Z, Yuan L, Luo W et al (2016) Spatio-temporal constrained human trajectory generation from the PIR motion detector sensor network data: a geometric algebra approach. Sensors 16:43
Yun J, Lee SS (2014) Human movement detection and identification using pyroelectric infrared sensors. Sensors 14(5):8057–8081
Zade ND, Deshpande S, Kamatchi Iyer R (2020a) A review on object tracking wireless sensor network an approach for smart surveillance. In: Smys S, Iliyasu AM, Bestak R, Shi F (eds) New trends in computational vision and bio-inspired computing. ICCVBIC 2018. Springer, Cham, pp 909–921. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-41862-5_92
Zade N, Deshpande S, Sita D (2020b) Analysis of passive infrared detector for target detection in an Iot based outdoor environment. In: Proceeding of IC-RACT 2020. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3696476
Zade N, Deshpande S, Sita D (2020c) Approximate localization of non-cooperative moving target in outdoor deterministic directional passive sensor networks. In: Proceeding of first doctoral symposium on natural computing research. Lecture notes in networks and systems, vol 169. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-4073-2
Zhang Z, Gao X, Biswas J et al (2007) Moving targets detection and localization in passive infrared sensor networks. In: 10th International conference on information fusion, Quebec
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zade, N., Deshpande, S. & Kamatchi Iyer, R. Target tracking based on approximate localization technique in deterministic directional passive sensor network. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 12, 10171–10181 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02783-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02783-5