Abstract
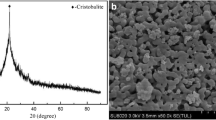
The development of sustainable and environmentally friendly techniques for synthesizing zeolites has attracted much attention, as the use of solvents in the hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites is a major obstacle for realizing green and sustainable synthesis ways. As a solid waste, it still has a challenge for zeolites synthesis from rice husk ash by solvent-free method to increase its recovery rate and economic value. Our approach focused on reutilization of rice husk ash by converting it to ZSM-5 zeolite without employing solvents. The influence of TPABr/SiO2, Na2CO3·10H2O/SiO2 and synthesis time on ZSM-5 crystal growth and ZSM-5 zeolite properties were evaluated by various analytical methods. The results suggested that the optimal conditions of TPABr/SiO2, Na2CO3·10H2O/SiO2 and synthesis time for the ZSM-5 synthesis were 0.125, 0.3 and 72 h, respectively. Base on the optimal synthesis condition, the recovery rate of Si and Al were 98%, which were 70% compared with that of hydrothermal method. The synthesis process was solid phase conversion, Na2CO3·10H2O played key role in promoting hydrolysis and condensation of Si–O–Si and Si–O–Al bonds during synthesis process. The resultant ZSM-5 zeolite exhibited well-defined crystallinity and porosity, ZSM-5 aggregate particles possessed micro-/meso-porous structures. The BET surface area of synthetic ZSM-5 zeolite was 304 m2/g, comparable to hydrothermal synthetic ZSM-5 zeolite (320 m2/g). Overall, proposed synthetic route provides novel green alternative for the recovery of rice husk ash, further mitigating the environmental and health care concerns.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prasertsan, S., Sajjakulnukit, B.: Biomass and biogas energy in Thailand: potential, opportunity and barriers. Renew. Energy 31, 599–610 (2006)
Kumar, A., Priyadarshinee, R., Singha, S., et al.: Rice husk ash-based silica-supported iron catalyst coupled with Fenton-like process for the abatement of rice mill wastewater. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 18, 2565 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-016-1165-4
Nagrale, S.D., Hajare, H., Modak, P.R.: Utilization of rice husk ash. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2, 1–5 (2012)
Geraldo, R.H., Fernandes, L.F.R., Camarini, G.: Water treatment sludge and rice husk ash to sustainable geopolymer production. J. Clean. Prod. 149, 146–155 (2017)
Mor, S., Chhoden, K., Ravindra, K.: Application of agro-waste rice husk ash for the removal of phosphate from the wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 129, 673–680 (2016)
Prasetyoko, D., Ramli, Z., Endud, S., Hamdan, H., Sulikowski, B.: Conversion of rice husk ash to zeolite beta. Waste Manag. 26, 1173–1179 (2006)
Kamseu, E., Beleuk à Moungam, L.M., Cannio, M., Billong, N., Chaysuwan, D., Chinje Melo, U., Leonelli, C.: Substitution of sodium silicate with rice husk ash-NaOH solution in metakaolin based geopolymer cement concerning reduction in global warming. J. Clean. Prod. 142, 3050–3060 (2017)
Prasara-A, J., Gheewala, S.H.: Sustainable utilization of rice husk ash from power plants: a review. J. Clean. Prod. 167, 1020–1028 (2017)
Mowla, O., Kennedy, E., Stockenhuber, M.: Hydroesterification of bio-oils over HZSM-5, BETA and Y zeolites. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-017-1423-0
Na, Y.K., Woo, S.I., Yu, J.L., Bae, J., Choi, W.C., Park, Y.K.: Enhanced hydrothermal stability of ZSM-5 formed from nanocrystalline seeds for naphtha catalytic cracking. J. Mater. Sci. 51, 3735–3749 (2016)
Hyun, S.H., Song, J.K., Kwak, B.I., Kim, J.H., Hong, S.A.: Synthesis of ZSM-5 zeolite composite membranes for CO2 separation. J. Mater. Sci. 34, 3095–3105 (1999)
Luo, W., Yang, X.Y., Wang, Z.R., Huang, W.F., Chen, J.Y., Jiang, W., Wang, L.J., Cheng, X.W., Deng, Y.H., Zhao, D.Y.: Synthesis of ZSM-5 aggregates made of zeolite nanocrystals through a simple solvent-free method. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 243, 112–118 (2017)
Barakov, R., Shcherban, N., Yaremov, P., Gryn, S., Solomakha, V., Bezverkhyy, I., Kasian, N., Ilyin, V.: Low-temperature and alkali-free dual template synthesis of micro-mesoporous aluminosilicates based on precursors of zeolite ZSM-5. J. Mater. Sci. 51, 4002–4020 (2016)
Jiang, Z., Yang, J., Ma, H., et al.: Synthesis of pure NaA zeolites from coal fly ashes for ammonium removal from aqueous solutions. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 18, 629 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-015-1072-0
Wdowin, M., Franus, M., Panek, R., et al.: The conversion technology of fly ash into zeolites. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 16, 1217 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-014-0719-6
Remenárová, L., Pipíška, M., Florková, E., et al.: Zeolites from coal fly ash as efficient sorbents for cadmium ions. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 16, 1551 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-014-0728-5
Zhang, H.B., Ma, Y.C., Song, K.S., Zhang, Y.H., Tang, Y.: Nano-crystallite oriented self-assembled ZSM-5 zeolite and its LDPE cracking properties: effects of accessibility and strength of acid sites. J. Catal. 302, 115–125 (2013)
Jia, Y., Wang, J., Zhang, K., Feng, W., Liu, S., Ding, C., Liu, P.: Nanocrystallite self-assembled hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolite microsphere for methanol to aromatics. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 247, 103–115 (2017)
Wan, Z., Wu, W., Chen, W., Yang, H., Zhang, D.: Direct synthesis of hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolite and its performance in catalyzing methanol to gasoline conversion. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 53, 19471–19478 (2014)
Xiao, F.S., Wang, L.F., Yin, C.Y., Lin, K.F., Di, Y., Li, J.X., Xu, R.R., Su, D.S., Schlogl, R., Yokoi, T., Tatsumi, T.: Catalytic properties of hierarchical mesoporous zeolites templated with a mixture of small organic ammonium salts and mesoscale cationic polymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45, 3090–3093 (2006)
Na, K., Jo, C., Kim, J., Cho, K., Jung, J., Seo, Y., Messinger, R.J., Chmelka, B.F., Ryoo, R.: Directing zeolite structures into hierarchically nanoporous architectures. Science 333, 328–332 (2011)
Wu, Q., Liu, X., Zhu, L., Ding, L., Gao, P., Wang, X., Pan, S., Bian, C., Meng, X., Xu, J., Deng, F., Maurer, S., Muller, U., Xiao, F.S.: Solvent-free synthesis of zeolites from anhydrous starting raw solids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 1052–1055 (2015)
Khoshbin, R., Karimzadeh, R.: The beneficial use of ultrasound in free template synthesis of nanostructured ZSM-5 zeolite from rice husk ash used in catalytic cracking of light naphtha: effect of irradiation power. Adv. Powder Technol. 28, 973–982 (2017)
Kordatos, K., Gavela, S., Ntziouni, A., Pistiolas, K.N., Kyritsi, A., Kasselouri-Rigopoulou, V.: Synthesis of highly siliceous ZSM-5 zeolite using silica from rice husk ash. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 115, 189–196 (2008)
Naskar, M.K., Kundu, D., Chatterjee, M.: A facile hydrothermal conversion of rice husk ash to ZSM-5 zeolite powders. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 95, 925–930 (2012)
Kordatos, K., Ntziouni, A., Iliadis, L., Kasselouri-Rigopoulou, V.: Utilization of amorphous rice husk ash for the synthesis of ZSM-5 zeolite under low temperature. J. Mater. Cycles Waste 15, 571–580 (2013)
Dey, K.P., Ghosh, S., Naskar, M.K.: Organic template-free synthesis of ZSM-5 zeolite particles using rice husk ash as silica source. Ceram. Int. 39, 2153–2157 (2013)
Sari, Z.G.L.V., Younesi, H., Kazemian, H.: Synthesis of nanosized ZSM-5 zeolite using extracted silica from rice husk without adding any alumina source. Appl. Nanosci. 5, 737–745 (2015)
Meng, X., Xiao, F.S.: Green routes for synthesis of zeolites. Chem. Rev. 114, 1521–1543 (2014)
Zhang, P., Wang, L., Ren, L., Zhu, L., Sun, Q., Zhang, J., Meng, X., Xiao, F.S.: “Solvent-free” synthesis of thermally stable and hierarchically porous aluminophosphates (SF-APOs) and heteroatom-substituted aluminophosphates (SF-MAPOs). J. Mater. Chem. 21, 12026–12033 (2011)
Jin, Y., Sun, Q., Qi, G., Yang, C., Xu, J., Chen, F., Meng, X., Deng, F., Xiao, F.S.: Solvent-free synthesis of silicoaluminophosphate zeolites. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 52, 9172–9175 (2013)
Wu, Q., Wang, X., Qi, G., Guo, Q., Pan, S., Meng, X., Xu, J., Deng, F., Fan, F., Feng, Z., Li, C., Maurer, S., Muller, U., Xiao, F.S.: Sustainable synthesis of zeolites without addition of both organotemplates and solvents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 4019–4025 (2014)
Ren, L., Wu, Q., Yang, C., Zhu, L., Li, C., Zhang, P., Zhang, H., Meng, X., Xiao, F.S.: Solvent-free synthesis of zeolites from solid raw materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 15173–15176 (2012)
Petkowicz, D.I., Canal, S., Finger, P.H., Mignoni, M.L., Santos, J.H.Z.D.: Synthesis of hybrid zeolites using a solvent-free method in the presence of different organosilanes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 241, 98–106 (2017)
Cheng, S., Mazonde, B., Zhang, G., Javed, M., Dai, P., Cao, Y., Tu, S., Wu, J., Lu, C., Xing, C., Shan, S.: Co-based MOR/ZSM-5 composite zeolites over a solvent-free synthesis strategy for improving gasoline selectivity. Fuel 223, 354–359 (2018)
Chevella, D., Mameda, N., Kodumuri, S., Banothu, R., Gajula, K.S., Kutepov, B.I., Nama, N.: Three-component synthesis of amidomethylarenes and -heteroarenes over Hβ zeolite under solvent-free conditions. Catal. Commun. 105, 20–25 (2018)
Xiao, Y., Sheng, N., Chu, Y., Wang, Y., Wu, Q., Liu, X., Deng, F., Meng, X., Feng, Z.: Mechanism on solvent-free crystallization of NaA zeolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 237, 201–209 (2017)
Yu, Y., Xiong, G., Li, C., Xiao, F.S.: Characterization of aluminosilicate zeolites by UV Raman spectroscopy. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 46, 23–34 (2001)
Muller, D., Gessner, W., Behrens, H.J., Scheler, G.: Determination of the aluminium coordination in aluminium-oxygen compounds by solid-state high-resolution 27Al NMR. Chem. Phys. Lett. 79, 59–62 (1981)
Perez-Ramirez, J., Verboekend, D., Bonilla, A., Abello, S.: Hierarchical zeolite catalysts: zeolite catalysts with tunable hierarchy factor by pore-growth moderators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 19, 3972–3979 (2009)
Yue, Y.Y., Liu, H.Y., Yuan, P., Li, T.S., Yu, C.Z., Bi, H., Bao, X.J.: From natural aluminosilicate minerals to hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolites: a nanoscale depolymerization-reorganization approach. J. Catal. 319, 200–210 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Li, S. & Bao, S. Sustainable Synthesis of ZSM-5 Zeolite from Rice Husk Ash Without Addition of Solvents. Waste Biomass Valor 10, 2825–2835 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0356-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0356-0