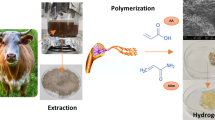
Abstract
The present work reports significant improvement in the performance of keratin based hydrogels. These hydrogels were synthesized by graft copolymerization of acrylic acid monomers on the hydrolyzed keratin proteins’ backbones in the presence of a crosslinker (N,N-methylenebis (acrylamide)) and initiators (sodium bisulfite and potassium persulfate). The grafting was confirmed by means of Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The contributions of the crosslinker, initiator and neutralization degree to the hydrogels were investigated through differential scanning calorimetry, swelling tests, and scanning electron microscopy. The highest equilibrium swelling of hydrogel in distilled water reached 501 g/g of hydrogel in 48 h. The swelling properties of the optimized hydrogel formulation were also studied at various pH and saline concentrations.
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hill, P., Brantley, H., Van Dyke, M.: Some properties of keratin biomaterials: kerateines. Biomaterials 31(4), 585–593 (2010)
Yang, Y., Tong, Z., Geng, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, M.: Biobased polymer composites derived from corn stover and feather meals as double-coating materials for controlled-release and water-retention urea fertilizers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 61(34), 8166–8174 (2013)
Singh, B., Sharma, D.K., Dhiman, A., Gupta, A.: Applications of natural polysaccharide-based beads for slow release herbicide formulation. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 93(4), 616–622 (2011)
Sojka, R.E., Lentz, R.D.: Reducing furrow irrigation erosion with polyacrylamide (PAM). JPA 10(1), 47–52 (1997)
Bakass, M., Mokhlisse, A., Lallemant, M.: Absorption and desorption of liquid water by a superabsorbent polymer: effect of polymer in the drying of the soil and the quality of certain plants. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 83(2), 234–243 (2002)
Pourjavadi, A., Ghasemzadeh, H., Soleyman, R.: Synthesis, characterization, and swelling behavior of alginate-g-poly(sodium acrylate)/kaolin superabsorbent hydrogel composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 105(5), 2631–2639 (2007)
Zohuriaan-Mehr, M.J., Kabiri, K.: Superabsorbent polymer materials: a review. Iran. Polym. J. 17(6), 451–477 (2008)
Pourjavadi, A., Kurdtabar, M., Mahdavinia, G.R., Hosseinzadeh, H.: Synthesis and super-swelling behavior of a novel protein-based superabsorbent hydrogel. Polym. Bull. 57(6), 813–824 (2006)
Pourjavadi, A., Salimi, H.: New protein-based hydrogel with superabsorbing properties: effect of monomer ratio on swelling behavior and kinetics. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 47(23), 9206–9213 (2008)
Zhang, B., Cui, Y., Yin, G., Li, X., You, Y.: Synthesis and swelling properties of hydrolyzed cottonseed protein composite superabsorbent hydrogel. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 59(12), 1018–1032 (2010)
Shi, W., Dumont, M.-J., Ly, E.B.: Synthesis and properties of canola protein-based superabsorbent hydrogels. Eur. Polym. J. 54, 172–180 (2014)
Li, M., Jin, E., Zhang, L.: Effects of graft modification on the water solubility, apparent viscosity, and adhesion of feather keratin for warp sizing. J. Text. Inst. 107, 395–404 (2016)
Hu, X., Cebe, P., Weiss, A.S., Omenetto, F., Kaplan, D.L.: Protein-based composite materials. Mater. Today 15(5), 208–215 (2012)
McGovern, V.: Recycling poultry feathers: more bang for the cluck. Environ. Health Perspect. 108(8), A366–A369 (2000)
Ullah, A., Wu, J.: Feather fiber-based thermoplastics: effects of different plasticizers on material properties. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 298(2), 153–162 (2013)
Reddy, N., Chen, L., Yang, Y.: Biothermoplastics from hydrolyzed and citric acid crosslinked chicken feathers. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 33(3), 1203–1208 (2013)
Aluigi, A., Varesano, A., Montarsolo, A., Vineis, C., Ferrero, F., Mazzuchetti, G., et al.: Electrospinning of keratin/poly(ethylene oxide)blend nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 104(2), 863–870 (2007)
Hadas, A., Kautsky, L.: Feather meal, a semi-slow-release nitrogen fertilizer for organic farming. Fertil. Res. 38(2), 165–170 (1994)
Gurav, R., Jadhav, J.: A novel source of biofertilizer from feather biomass for banana cultivation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 20(7), 4532–4539 (2013)
Kavitha, A., Boopalan, K., Radhakrishnan, G., Sankaran, S., Das, B.N., Sastry, T.P.: Preparation of feather keratin hydrolyzate-gelatin composites and their graft copolymers. J Macromol. Sci. Part A 42(12), 1703–1713 (2005)
García-Sabido, D., López-Mesas, M., Carrillo-Navarrete, F.: Chicken feather fibres waste as a low-cost biosorbent of acid Blue 80 dye. Desalin. Water Treat. 57, 3732–3740 (2016)
Ghosh, A., Collie, S.R.: Keratinous materials as novel absorbent systems for toxic pollutants. Def. Sci. J. 64(3), 209–221 (2014)
Zhou, L.-T., Yang, G., Yang, X.-X., Cao, Z.-J., Zhou, M.-H.: Preparation of regenerated keratin sponge from waste feathers by a simple method and its potential use for oil adsorption. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 21(8), 5730–5736 (2014)
Lin, H., Sritham, E., Lim, S., Cui, Y., Gunasekaran, S.: Synthesis and characterization of pH- and salt-sensitive hydrogel based on chemically modified poultry feather protein isolate. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 116(1), 602–609 (2010)
Ozaki, Y., Takagi, Y., Mori, H., Hara, M.: Porous hydrogel of wool keratin prepared by a novel method: an extraction with guanidine/2-mercaptoethanol solution followed by a dialysis. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 42, 146–154 (2014)
Calvo, P., Nelson, L., Kloepper, J.: Agricultural uses of plant biostimulants. Plant Soil 383(1–2), 3–41 (2014)
Arai, K.M., Takahashi, R., Yokote, Y., Akahane, K.: Amino-acid sequence of feather keratin from fowl. Eur. J. Biochem. 132(3), 501–507 (1983)
Erra, P., Gómez, N., Dolcet, L.M., Juliá, M.R., Lewis, D.M., Willoughby, J.H.: FTIR analysis to study chemical changes in wool following a sulfitolysis treatment1. Text. Res. J. 67(6), 397–401 (1997)
Woodin, A.M.: Structure and composition of soluble feather keratin. Biochem. J. 63(4), 576–581 (1956)
Liu, P., Xu, H., Mi, X., Xu, L., Yang, Y.: Oxidized sucrose: a potent and biocompatible crosslinker for three-dimensional fibrous protein scaffolds. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 300(4), 414–422 (2015)
Lee, L.D., Baden, H.P.: Organisation of the polypeptide chains in mammalian keratin. Nature 264(5584), 377–379 (1976)
Gurd, F.R.: Carboxymethylation. Methods Enzymol. 11, 532–541 (1967)
Schrooyen, P.M.M., Dijkstra, P.J., Oberthur, R.C., Bantjes, A., Feijen, J.: Partially carboxymethylated feather keratins. 1. Properties in aqueous systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 48(9), 4326–4334 (2000)
Park, T.G.: Degradation of poly(d,l-lactic acid) microspheres: effect of molecular weight. J. Control. Release. 30(2), 161–173 (1994)
Liardon, R., Ledermann, S.: Racemization kinetics of free and protein-bound amino acids under moderate alkaline treatment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 34(3), 557–565 (1986)
Bardajee, G., Pourjavadi, A., Soleyman, R.: Novel highly swelling nanoporous hydrogel based on polysaccharide/protein hybrid backbone. J. Polym. Res. 18(3), 337–346 (2011)
Laemmli, U.K.: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227(5259), 680–685 (1970)
Tsuda, Y., Nomura, Y.: Properties of alkaline-hydrolyzed waterfowl feather keratin. Anim. Sci. J. 85(2), 180–185 (2014)
Pourjavadi, A., Ayyari, M., Amini-Fazl, M.S.: Taguchi optimized synthesis of collagen-g-poly(acrylic acid)/kaolin composite superabsorbent hydrogel. Eur. Polym. J. 44(4), 1209–1216 (2008)
Zhang, B., Cui, Y., Yin, G., Li, X., Liao, L., Cai, X.: Synthesis and swelling properties of protein-poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylamide) superabsorbent composite. Polym. Compos. 32(5), 683–691 (2011)
Bagheri Marandi, G., Mahdavinia, G., Ghafary, S.: Swelling behavior of novel protein-based superabsorbent nanocomposite. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 120(2), 1170–1179 (2011)
Silverstein, R., Webster, F.: Spectrometric identification of organic compounds. Wiley, New York (2006)
Iqbal, H.M.N., Kyazze, G., Tron, T., Keshavarz, T.: Laccase-assisted approach to graft multifunctional materials of interest: keratin-EC based novel composites and their characterisation. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 300, 712–720 (2015)
Maurer, J.J., Eustace, D.J., Ratcliffe, C.T.: Thermal characterization of poly(acrylic acid). Macromolecules 20(1), 196–202 (1987)
Stutz, H., Illers, K.H., Mertes, J.: A generalized theory for the glass transition temperature of crosslinked and uncrosslinked polymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys. 28(9), 1483–1498 (1990)
Kabiri, K., Zohuriaan-Mehr, M.J.: Porous superabsorbent hydrogel composites: synthesis, morphology and swelling rate. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 289(7), 653–661 (2004)
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Fonds de recherche du Québec-Nature et technologies (FRQNT). We gratefully acknowledge the use of laboratory equipment of Dr. Valérie Orsat and Dr. Michael Ngadi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wattie, B., Dumont, MJ. & Lefsrud, M. Synthesis and Properties of Feather Keratin-Based Superabsorbent Hydrogels. Waste Biomass Valor 9, 391–400 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9773-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9773-0