Abstract
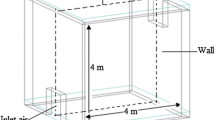
The aim of this work is to studying indoor radon distribution using the Finite Volume Method (FVM). This paper focuses on effects of exhalation from different sources (wall, floor and ceiling) and the ventilation profile on distribution the concentrations of radon indoor. The rate of radon exhalation and ventilation were measured and are used as input in FVM simulation. It has been found that the radon concentration is distributed in non homogeneous way in the room. The radon concentration is much larger near floor, and decreases in the middle of the room. The experimental validation was performed by measuring radon concentration at different locations in room using active and passive techniques. We notice that the results of simulation and experimental are in agreement. The annual effective dose of radon in the model room has been also investigated.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Steinhausler, Environmental 220Rn: a review, Enviro. Intern., 22 (1996) 1111–1123.
Q. Guo, J. Sun and W. Zhuo, Potential of high thoron exposure in China, J. Nucl. Sci. Technol., 37 (2000) 716–719.
K.K. Dwivedi, R. Mishra, S.P. Tripathy, A. Kulshreshtha, D. Sinha, A. Srivastava, P. Deka, B. Bhattacharjee, T.V. Ramachandran and K.S.V. Nambi, Simultaneous determination of radon, thoron and their progeny in dwellings, Rad. Meas., 33 (2001) 7–11.
S. Singh, A. Kumar and B. Singh, Radon level in dwellings and its correlation with uranium and radium content in some areas of Himachal Pradesh, India. Enviro. Int., 28 (2002) 97–101.
T. Iyogi, S. Ueda, S. Hisamatsu, K. Kondo, N. Sakurai and J. Inaba, Radon concentration in indoor occupational environments in Aomori Prefecture, Japan, J. Enviro. Radioact., 67 (2003) 91–108.
M.H. Magalhaes, E.C.S. Amaral, I. Sachett and E.R.R. Rochedo, Radon-222 in Brazil: an outline of indoor and outdoor measurements, J. Enviro. Radioact., 67 (2003) 131–143.
R.S. Saini, M. Nain, R.P. Chauhan, N. Kishore and S.K. Chakarvarti, Radon, thoron and their progeny levels in some dwellings of northern Haryana, India using SSNTDs, India. J. Phys., 83 (2009) 1197–1200.
R.W. Field, D.J. Steck, B.J. Smith, C.P. Brus, E.F. Fisher, J.S. Neuberger, C.E. Platz, R.A. Robinson, R.F. Woolson and C.F. Lynch, Residential radon gas exposure and lung cancer, Am. J. Epidemiol., 151 (2000) 1091–1102.
J. Ma, H. Yonehara, T. Aoyama, M. Doi, S. Kobayashi and M. Sakanoue, Influence of air flow on the behaviour of thoron and its progeny in a traditional Japanese house, Health Phys., 72 (1997) 86–91.
[10] W. Jacobi, Activity and Potential Alpha-energy of 222Radon and 220Radon-daughters in Different Air Atmospheres, Health Phys., 22 (1972) 429–507.
J. Postendorfer, A. Wicke and A. Schraub, The influence of exhalation, ventilation and deposition processes upon the concentration of radon (222Rn), thoron (220Rn) and their decay products in room air, Health Phys., 34 (1978) 419–477.
A. Katase, Y. Matsumoto, T. Sakae and K. Ishibashi, Indoor concentrations of 220Rn and its decay products, Health Phys., 54 (1988) 249–344.
T. Yamasaki, Q. Guo and T. Iida, Distributions of thoron progeny concentrations in Dwellings, Radiat. Prot. Dosim., 59 (1995) 135–140.
H.M. Mok, Perturbative method in the indoor radon/thoron concentration study, Radiat. Prot. Dosim., 67 (1996) 65–70.
S. Kato, Appliance of CFDS technique for designing room air distribution—Part 1. Overview of CFD for analyzing indoor climate, Soci. Heat. Air Condi. & Sani. Eng. Jap., 71 (1997) 533–542.
W. Zhuo, T. Iida, J. Moriizumi, T. Aoyagi and I. Takahashi, Simulation of the concentrations and distributions of indoor radon and thoron, Radiat. Prot. Dosim., 93 (2001) 357–367.
V. Urosevic, D. Nikezic and S. Vulovic, A theoretical approach to indoor radon and thoron distribution, J. Enviro. Radioact., 99 (2008) 1829–1833.
L. Oufni and M.A. Misdaq, Radon emanation in a limestone cave using CR-39 and LR-115 solid state nuclear track detectors, J. Radio. Anal. Nucl. Chem., 250 (2001) 309–313.
L. Oufni, M.A. Misdaq, M. Amrane, Radon level and radon effective dose rate determination in Moroccan dwellings using SSNTDs, Rad. Meas., 40 (2005) 118–123.
L. Oufni, Determination of the radon diffusion coefficient and radon exhalation rate in Moroccan quaternary samples using the SSNTD technique, J.Radio. Anal. Nucl. Chem, 256 (2003) 581–586.
L. Oufni, S. Taj, B. Manaut and M. Eddouks, Transfer of uranium and thorium from soil to different parts of medicinal plants using SSNTD, J. Radio. Anal. Nucl. Chem., 287 (2011) 403–410.
G. de With and P. de Jong, CFD modelling of thoron and thoron progeny in the indoor environment, Radiat. Prot. Dosim., 145 (2011) 138–144.
N. Chauhan, R.P. Chauhan, M. Joshi, T.K. Agarwal, P. Aggarwal and B.K.J. Sahoo, Study of indoor radon distribution using measurements and CFD modeling, Enviro. Radioact., 136 (2014) 105–111.
K. Akbari, J. Mahmoudi and M. Ghanbari, Influence of indoor air conditions on radon concentration in a detached house, J. Enviro. Radioact., 116 (2013) 166–173.
H. Elharfi, M. Naïmi, M. Lamsaadi, A. Raji and M. Hasnaoui, Inter. Schol. Res. Net., 2012 (2012) 16.
R. Rabi, L. Oufni,. A theoretical investigation of the distribution of indoor radon concentrations, Indian J. Phys., 91 (2017) 471–479.
J.A. Rabi and A.A. Mohamad, Parametric modelling and numerical simulation of natural-convective transport of radon-222 from a phosphogypsum stack into open air, Appl. Math. Mod., 30 (2006) 1546–1560.
A. Kumar, R.P. Chauhan, J. Manish and B.K. Sahoo, Modeling of indoor radon concentration from radon exhalation rates of building materials and validation through measurements, J. Enviro. Radioact., 127 (2014) 50–55.
J. Porestendorfer, Properties and behaviour of radon and thoron and their decay products in the air, J. Aerosol. Sci., 25 (1994) 219–263.
UNSCEAR. United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation. Report to the General Assembly with Scientific Annexes. United Nations Publication, New York, USA, (2000).
(ICRP) (International Commission on Radiological Protection) (1993) Protection against radon at home and at work. ICRP Publication 65, Ann ICRP 23(2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rabi, R., Oufni, L. A theoretical and experimental investigation of spatial distribution of radon in a typical ventilated room. MAPAN 33, 123–130 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12647-017-0238-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12647-017-0238-0