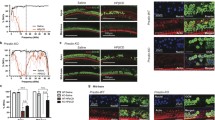
Abstract
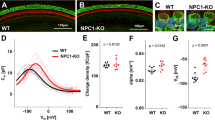
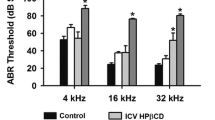
2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPβCD), a cholesterol chelator, is being used to treat diseases associated with abnormal cholesterol metabolism such as Niemann-Pick C1 (NPC1). However, the high doses of HPβCD needed to slow disease progression may cause hearing loss. Previous studies in mice have suggested that HPβCD ototoxicity results from selective outer hair cell (OHC) damage. However, it is unclear if HPβCD causes the same type of damage or is more or less toxic to other species such as rats, which are widely used in toxicity research. To address these issues, rats were given a subcutaneous injection of HPβCD between 500 and 4000 mg/kg. Distortion product otoacoustic emissions (DPOAE), the cochlear summating potential (SP), and compound action potential (CAP) were used to assess cochlear function followed by quantitative analysis of OHC and inner hair cell (IHC) loss. The 3000- and 4000-mg/kg doses abolished DPOAE and greatly reduced SP and CAP amplitudes. These functional deficits were associated with nearly complete loss of OHC as well as ~ 80% IHC loss over the basal two thirds of the cochlea. The 2000-mg/kg dose abolished DPOAE and significantly reduced SP and CAP amplitudes at the high frequencies. These deficits were linked to OHC and IHC losses in the high-frequency region of the cochlea. Little or no damage occurred with 500 or 1000 mg/kg of HPβCD. The HPβCD-induced functional and structural deficits in rats occurred suddenly, involved damage to both IHC and OHC, and were more severe than those reported in mice.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DPOAE:
-
Distortion product otoacoustic emission
- CAP:
-
Compound action potential
- HPβCD:
-
2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin
- IHC:
-
Inner hair cell
- NPC1:
-
Niemann-Pick C1
- OHC:
-
Outer hair cell
- SP:
-
Summating potential
References
Altmann SW, Davis HR Jr, Zhu LJ, Yao X, Hoos LM, Tetzloff G et al (2004) Niemann-Pick C1 like 1 protein is critical for intestinal cholesterol absorption. Science 303:1201–1204
Bellringer ME, Smith TG, Read R, Gopinath C, Olivier P (1995) Beta-cyclodextrin: 52-week toxicity studies in the rat and dog. Food and chemical Toxicology 33:367–376
Benkafadar N, Menardo J, Bourien J, Nouvian R, Francois F, Decaudin D et al (2017) Reversible p53 inhibition prevents cisplatin ototoxicity without blocking chemotherapeutic efficacy. EMBO Mol Med 9:7–26
Berry-Kravis E, Chin J, Hoffmann A, Winston A, Stoner R, LaGorio L, Friedmann K, Hernandez M, Ory DS, Porter FD, O'Keefe JA (2018) Long-term treatment of Niemann-Pick type C1 disease with intrathecal 2-hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin. Pediatr Neurol 80:24–34
Bertolla C, Rolin S, Evrard B, Pochet L, Masereel B (2008) Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of a new targeted drug carrier system: beta-cyclodextrin coupled to oxytocin. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters 18:1855–1858
Binetti R, Costamagna FM, Marcello I (2008) Exponential growth of new chemicals and evolution of information relevant to risk control. Ann Ist Super Sanita 44:13–15
Bohne BA, Kimlinger M, Harding GW (2017) Time course of organ of Corti degeneration after noise exposure. Hear Res 344:158–169
Bonnot O, Gama CS, Mengel E, Pineda M, Vanier MT, Watson L, Watissée M, Schwierin B, Patterson MC (2019) Psychiatric and neurological symptoms in patients with Niemann-Pick disease type C (NP-C): findings from the international NPC registry. World J Biol Psychiatry 20:310–319
Camilleri P, Haskins NJ, Howlett DR (1994) Beta-cyclodextrin interacts with the Alzheimer amyloid beta-A4 peptide. FEBS Letters 341:256–258
Campbell KCM, Le Prell CG (2018) Drug-induced ototoxicity: diagnosis and monitoring. Drug Saf 41:451–464
Chen GD, Kermany MH, D'Elia A, Ralli M, Tanaka C, Bielefeld EC et al (2010) Too much of a good thing: long-term treatment with salicylate strengthens outer hair cell function but impairs auditory neural activity. Hear Res 265:63–69
Coisne C, Tilloy S, Monflier E, Wils D, Fenart L, Gosselet F (2016) Cyclodextrins as emerging therapeutic tools in the treatment of cholesterol-associated vascular and neurodegenerative diseases. Molecules;21
Crini G (2014) Review: a history of cyclodextrins. Chem Rev 114:10940–10975
Cronin S, Lin A, Thompson K, Hoenerhoff M, Duncan RK (2015) Hearing loss and otopathology following systemic and intracerebroventricular delivery of 2-hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 16:599–611
Crumling MA, King KA, Duncan RK (2017) Cyclodextrins and iatrogenic hearing loss: new drugs with significant risk. Front Cell Neurosci 11:355
Crumling MA, Liu L, Thomas PV, Benson J, Kanicki A, Kabara L, Hälsey K, Dolan D, Duncan RK (2012) Hearing loss and hair cell death in mice given the cholesterol-chelating agent hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin. PLoS One 7:e53280
Dallos P, Harris D (1978) Properties of auditory nerve responses in absence of outer hair cells. J Neurophysiol 41:365–383
Davidson CD, Ali NF, Micsenyi MC, Stephney G, Renault S, Dobrenis K, Ory DS, Vanier MT, Walkley SU (2009) Chronic cyclodextrin treatment of murine Niemann-Pick C disease ameliorates neuronal cholesterol and glycosphingolipid storage and disease progression. PLoS One 4:e6951
di Cagno M, Terndrup Nielsen T, Lambertsen Larsen K, Kuntsche J, Bauer-Brandl A (2014) Beta-cyclodextrin-dextran polymers for the solubilization of poorly soluble drugs. Int J Pharm 468:258–263
Dike CR, Bernat J, Bishop W, DeGeeter C (2019) Niemann-Pick disease type C presenting as very early onset inflammatory bowel disease. BMJ Case Reports:12
Ding D, Allman BL, Salvi R (2012) Review: ototoxic characteristics of platinum antitumor drugs. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 295:1851–1867
Ding D, Jiang H, Chen GD, Longo-Guess C, Muthaiah VP, Tian C et al (2016) N-Acetyl-cysteine prevents age-related hearing loss and the progressive loss of inner hair cells in gamma-glutamyl transferase 1 deficient mice. Aging (Albany NY) 8:730–750
Ding D, McFadden S, Salvi RJ (2001) Cochlear hair cell densities and inner ear staining techniques. In: Willott JF (ed) The auditory psychobiology of the mouse. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp 189–204
Duan X, Chen S, Chen J, Wu J (2013) Enhancing the cyclodextrin production by synchronous utilization of isoamylase and alpha-CGTase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:3467–3474
Durrant JD, Wang J, Ding DL, Salvi RJ (1998) Are inner or outer hair cells the source of summating potentials recorded from the round window? J Acoust Soc Am 104:370–377
Fenyvesi E, Vikmon M, Szente L (2016) Cyclodextrins in food technology and human nutrition: benefits and limitations. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 56:1981–2004
Forge A (1991) Structural features of the lateral walls in mammalian cochlear outer hair cells. Cell Tissue Res 265:473–483
Forge A, Schacht J (2000) Aminoglycoside antibiotics. Audiol Neurootol 5:3–22
Fu Y, Ding D, Jiang H, Salvi R (2012) Ouabain-induced cochlear degeneration in rat. Neurotox Res 22:158–169
Funfschilling U, Jockusch WJ, Sivakumar N, Mobius W, Corthals K, Li S, Quintes S, Kim Y, Schaap IAT, Rhee JS, Nave KA, Saher G (2012) Critical time window of neuronal cholesterol synthesis during neurite outgrowth. J Neurosci 32:7632–7645
Glueckert R, Bitsche M, Miller JM, Zhu Y, Prieskorn DM, Altschuler RA, Schrott-Fischer A (2008) Deafferentation-associated changes in afferent and efferent processes in the guinea pig cochlea and afferent regeneration with chronic intrascalar brain-derived neurotrophic factor and acidic fibroblast growth factor. J Comp Neurol 507:1602–1621
Gomes LM, Petito N, Costa VG, Falcao DQ, de Lima Araujo KG (2014) Inclusion complexes of red bell pepper pigments with beta-cyclodextrin: preparation, characterisation and application as natural colorant in yogurt. Food Chem 148:428–436
Gould S, Scott RC (2005) 2-Hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin (HP-beta-CD): a toxicology review. Food Chem Toxicol 43:1451–1459
Gu FG, Cui FD, Gao YL (2005) Preparation of prostaglandin E1-hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin complex and its nasal delivery in rats. Int J Pharm 290:101–108
Katabuchi AU, Godoy V, Shil P, Moser A, Maegawa GHB (2018) Serendipitous effects of beta-cyclodextrin on murine model of Krabbe disease. Mol Genet Metab Rep 15:98–99
Kelly JB, Masterton B (1977) Auditory sensitivity of the albino rat. Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology 91:930–936
Kim H, Han J, Park JH (2020) Cyclodextrin polymer improves atherosclerosis therapy and reduces ototoxicity. J Control Release 319:77–86
Kim HJ, Oh GS, Lee JH, Lyu AR, Ji HM, Lee SH, Song J, Park SJ, You YO, Sul JD, Park C, Chung SY, Moon SK, Lim DJ, So HS, Park R (2011) Cisplatin ototoxicity involves cytokines and STAT6 signaling network. Cell Res 21:944–956
Kim SJ, Jeong HJ, Myung NY, Kim MC, Lee JH, So HS, Park RK, Kim HM, Um JY, Hong SH (2008) The protective mechanism of antioxidants in cadmium-induced ototoxicity in vitro and in vivo. Environ Health Perspect 116:854–862
King KA, Gordon-Salant S, Yanjanin N, Zalewski C, Houser A, Porter FD, Brewer CC (2014) Auditory phenotype of Niemann-Pick disease, type C1. Ear Hear 35:110–117
Kujawa SG, Liberman MC (2015) Synaptopathy in the noise-exposed and aging cochlea: primary neural degeneration in acquired sensorineural hearing loss. Hear Res 330:191–199
Lawner BE, Harding GW, Bohne BA (1997) Time course of nerve-fiber regeneration in the noise-damaged mammalian cochlea. Int J Dev Neurosci 15:601–617
Li J, Loh XJ (2008) Cyclodextrin-based supramolecular architectures: syntheses, structures, and applications for drug and gene delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 60:1000–1017
Liberman MC, Gao J, He DZ, Wu X, Jia S, Zuo J (2002) Prestin is required for electromotility of the outer hair cell and for the cochlear amplifier. Nature 419:300–304
Liberman MC, Kujawa SG (2017) Cochlear synaptopathy in acquired sensorineural hearing loss: manifestations and mechanisms. Hear Res 349:138–147
Liu B, Turley SD, Burns DK, Miller AM, Repa JJ, Dietschy JM (2009) Reversal of defective lysosomal transport in NPC disease ameliorates liver dysfunction and neurodegeneration in the npc1−/− mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:2377–2382
Liu X, Li L, Chen GD, Salvi R (2020) How low must you go? Effects of low-level noise on cochlear neural response. Hear Res 392:107980
Maarup TJ, Chen AH, Porter FD, Farhat NY, Ory DS, Sidhu R, Jiang X, Dickson PI (2015) Intrathecal 2-hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin in a single patient with Niemann-Pick C1. Mol Genet Metab 116:75–79
Majumder P, Duchen MR, Gale JE (2015) Cellular glutathione content in the organ of Corti and its role during ototoxicity. Front Cell Neurosci 9:143
Manna S, Gray ML, Kaul VF, Wanna G (2019) Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5) inhibitors and ototoxicity: a systematic review. Otol Neurotol 40:276–283
Marttin E, Verhoef JC, Merkus FW (1998) Efficacy, safety and mechanism of cyclodextrins as absorption enhancers in nasal delivery of peptide and protein drugs. J Drug Target 6:17–36
Matsuo M, Togawa M, Hirabaru K, Mochinaga S, Narita A, Adachi M, Egashira M, Irie T, Ohno K (2013) Effects of cyclodextrin in two patients with Niemann-Pick type C disease. Mol Genet Metab 108:76–81
McFadden SL, Ding D, Jiang H, Salvi RJ (2004) Time course of efferent fiber and spiral ganglion cell degeneration following complete hair cell loss in the chinchilla. Brain Res 997:40–51
Miller JM, Le Prell CG, Prieskorn DM, Wys NL, Altschuler RA (2007) Delayed neurotrophin treatment following deafness rescues spiral ganglion cells from death and promotes regrowth of auditory nerve peripheral processes: effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and fibroblast growth factor. J Neurosci Res 85:1959–1969
Mukherjea D, Jajoo S, Whitworth C, Bunch JR, Turner JG, Rybak LP, Ramkumar V (2008) Short interfering RNA against transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 attenuates cisplatin-induced hearing loss in the rat. J Neurosci 28:13056–13065
Müller M (1991) Frequency representation in the rat cochlea. Hear Res 51:247–254
Nguyen T, Jeyakumar A (2019) Genetic susceptibility to aminoglycoside ototoxicity. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 120:15–19
Ory DS, Ottinger EA, Farhat NY, King KA, Jiang X, Weissfeld L, Berry-Kravis E, Davidson CD, Bianconi S, Keener LA, Rao R, Soldatos A, Sidhu R, Walters KA, Xu X, Thurm A, Solomon B, Pavan WJ, Machielse BN, Kao M, Silber SA, McKew JC, Brewer CC, Vite CH, Walkley SU, Austin CP, Porter FD (2017) Intrathecal 2-hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin decreases neurological disease progression in Niemann-Pick disease, type C1: a non-randomised, open-label, phase 1-2 trial. Lancet 390:1758–1768
Otero-Espinar FJ, Luzardo-Alvarez A, Blanco-Mendez J (2010) Cyclodextrins: more than pharmaceutical excipients. Mini Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry 10:715–725
Paken J, Govender CD, Pillay M, Sewram V (2019) A review of cisplatin-associated ototoxicity. Semin Hear 40:108–121
Patterson MC, Mengel E, Wijburg FA, Muller A, Schwierin B, Drevon H, Vanier MT, Pineda M (2013) Disease and patient characteristics in NP-C patients: findings from an international disease registry. Orphanet J Rare Dis 8:12
Patterson MC, Walkley SU (2017) Niemann-Pick disease, type C and Roscoe Brady. Mol Genet Metab 120:34–37
Prakash Krishnan Muthaiah V, Ding D, Salvi R, Roth JA (2017) Carbaryl-induced ototoxicity in rat postnatal cochlear organotypic cultures. Environ Toxicol 32:956–969
Quitschke WW, Steinhauff N, Rooney J (2013) The effect of cyclodextrin-solubilized curcuminoids on amyloid plaques in Alzheimer transgenic mice: brain uptake and metabolism after intravenous and subcutaneous injection. Alzheimers Res Ther 5:16
Raileanu M, Todan L, Voicescu M, Ciuculescu C, Maganu M (2013) A way for improving the stability of the essential oils in an environmental friendly formulation. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 33:3281–3288
Ramirez CM, Liu B, Taylor AM, Repa JJ, Burns DK, Weinberg AG, Turley SD, Dietschy JM (2010) Weekly cyclodextrin administration normalizes cholesterol metabolism in nearly every organ of the Niemann-Pick type C1 mouse and markedly prolongs life. Pediatr Res 68:309–315
Ross CJ, Katzov-Eckert H, Dube MP, Brooks B, Rassekh SR, Barhdadi A et al (2009) Genetic variants in TPMT and COMT are associated with hearing loss in children receiving cisplatin chemotherapy. Nat Genet 41:1345–1349
Roth JA, Salvi R (2016) Ototoxicity of divalent metals. Neurotox Res 30:268–282
Ryan A, Dallos P (1975) Effect of absence of cochlear outer hair cells on behavioural auditory threshold. Nature 253:44–46
Rybak LP (1986) Drug ototoxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 26:79–99
Salvi R, Sun W, Ding D, Chen GD, Lobarinas E, Wang J et al (2016) Inner hair cell loss disrupts hearing and cochlear function leading to sensory deprivation and enhanced central auditory gain. Front Neurosci 10:621
Samperio C, Boyer R, Eigel WN 3rd, Holland KW, McKinney JS, O'Keefe SF et al (2010) Enhancement of plant essential oils’ aqueous solubility and stability using alpha and beta cyclodextrin. J Agric Food Chem 58:12950–12956
Sanchez SA, Gunther G, Tricerri MA, Gratton E (2011) Methyl-beta-cyclodextrins preferentially remove cholesterol from the liquid disordered phase in giant unilamellar vesicles. J Membr Biol 241:1–10
Schweitzer SO, Lu ZJ (2018) Pharmaceutical economics and policy: perspectives, promises, and problems, Third edition. edn. Oxford University Press, New York, NY
Sheppard AM, Chen GD, Manohar S, Ding D, Hu BH, Sun W, Zhao J, Salvi R (2017) Prolonged low-level noise-induced plasticity in the peripheral and central auditory system of rats. Neuroscience 359:159–171
Takahashi S, Homma K, Zhou Y, Nishimura S, Duan C, Chen J, Ahmad A, Cheatham MA, Zheng J (2016) Susceptibility of outer hair cells to cholesterol chelator 2-hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrine is prestin-dependent. Sci Rep 6:21973
Toyoda K, Shoda T, Uneyama C, Takada K, Takahashi M (1997) Carcinogenicity study of beta-cyclodextrin in F344 rats. Food Chem Toxicol 35:331–336
Trautwein P, Hofstetter P, Wang J, Salvi R, Nostrant A (1996) Selective inner hair cell loss does not alter distortion product otoacoustic emissions. Hear Res 96:71–82
Tsutsui K (2012) Neurosteroid biosynthesis and action during cerebellar development. Cerebellum 11:414–415
Vite CH, Bagel JH, Swain GP, Prociuk M, Sikora TU, Stein VM et al (2015) Intracisternal cyclodextrin prevents cerebellar dysfunction and Purkinje cell death in feline Niemann-Pick type C1 disease. Sci Transl med 7:276ra26
Waalkens-Berendsen DH, Bar A (2004) Embryotoxicity and teratogenicity study with alpha-cyclodextrin in rats. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 39(Suppl 1):S34–S39
Waalkens-Berendsen DH, Smits-Van Prooije AE, Bar A (2004) Embryotoxicity and teratogenicity study with alpha-cyclodextrin in rabbits. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 39(Suppl 1):S40–S46
Waalkens-Berendsen DH, Verhagen FJ, Bar A (1998) Embryotoxicity and teratogenicity study with gamma-cyclodextrin in rats. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 27:166–171
Wang D, Xiong B, Xiong F, Chen GD, Hu BH, Sun W (2016) Apical hair cell degeneration causes the increase in the amplitude of summating potential. Acta Otolaryngol 136:1255–1260
Wang H, Zhang X, Yu B, Peng X, Liu Y, Wang A et al (2019) Cyclodextrin ameliorates the progression of atherosclerosis via increasing high-density lipoprotein cholesterol plasma levels and anti-inflammatory effects in rabbits. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 73:334–342
Wang J, Powers NL, Hofstetter P, Trautwein P, Ding D, Salvi R (1997) Effects of selective inner hair cell loss on auditory nerve fiber threshold, tuning and spontaneous and driven discharge rate. Hear Res 107:67–82
Ward S, O'Donnell P, Fernandez S, Vite CH (2010) 2-Hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin raises hearing threshold in normal cats and in cats with Niemann-Pick type C disease. Pediatr Res 68:52–56
Wu WJ, Sha SH, McLaren JD, Kawamoto K, Raphael Y, Schacht J (2001) Aminoglycoside ototoxicity in adult CBA, C57BL and BALB mice and the Sprague-Dawley rat. Hear Res 158:165–178
Youn CK, Kim J, Park JH, Do NY, Cho SI (2015) Role of autophagy in cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 79:1814–1819
Young OA, Gupta RB, Sadooghy-Saraby S (2012) Effects of cyclodextrins on the flavor of goat milk and its yogurt. J Food Sci 77:S122–S127
Yu D, Ding D, Jiang H, Stolzberg D, Salvi R (2011) Mefloquine damage vestibular hair cells in organotypic cultures. Neurotox Res 20:51–58
Zhang J, Sun H, Salvi R, Ding D (2018) Paraquat initially damages cochlear support cells leading to anoikis-like hair cell death. Hear Res 364:129–141
Zheng XY, Wang J, Salvi RJ, Henderson D (1996) Effects of kainic acid on the cochlear potentials and distortion product otoacoustic emissions in chinchilla. Hear Res 95:161–167
Zhou Y, Takahashi S, Homma K, Duan C, Zheng J, Cheatham MA, Zheng J (2018) The susceptibility of cochlear outer hair cells to cyclodextrin is not related to their electromotile activity. Acta Neuropathol Commun 6:98
Zidovetzki R, Levitan I (2007) Use of cyclodextrins to manipulate plasma membrane cholesterol content: evidence, misconceptions and control strategies. Biochim Biophys Acta 1768:1311–1324
Funding
This research was supported by NIH grant (R01DC014693).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interest related to this manuscript and research. Dr. Salvi is a consultant for Auris Medical and CilCare.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Ding, D., Chen, GD. et al. 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin Ototoxicity in Adult Rats: Rapid Onset and Massive Destruction of Both Inner and Outer Hair Cells Above a Critical Dose. Neurotox Res 38, 808–823 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00252-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00252-7