Abstract
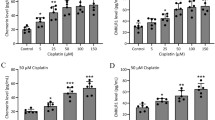
Sodium salicylate (SS) is one of the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and widely used in clinical practice. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the potential ototoxicity mechanism of sodium salicylate: the influence of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (Ca2+/CaMKII) in interaction between NMDA receptors (NMDAR) and GABAA receptors (GABAAR) in rat cochlear spiral ganglion neurons (SGNs). After treatment with SS, NMDA, and an NMDAR inhibitor (APV), the changes of GABAAR β3 (GABR β3) mRNA, surface and total protein, and GABAAR currents in SGNs were assessed by quantitative PCR, Western blot, and whole-cell patch clamp. Mechanistically, SS and/or NMDA increased the GABR β3 mRNA expression, while decreased GABR β3 surface protein levels and GABAAR-mediated currents. Moreover, application of SS and/or NMDA showed promotion in phosphorylation levels at S383 of GABR β3. Collectively, Ca2+ chelator (BAPTA) or Ca2+/CaMKII inhibitor (KN-93) reversed the effects of SS and/or NMDA on GABAAR. Therefore, we hypothesize that the interaction between NMDAR and GABAAR is involved in the SGNs damage induced by SS. In addition, the underlying molecular mechanism is related to Ca2+/CaMKII-mediated signaling pathway, which suggests that the interaction between calcium signal-regulated receptors mediates SS ototoxicity.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SGNs:
-
Spiral ganglion neurons
- GABAAR:
-
γ-Aminobutyric acid-A receptor
- NMDAR:
-
N-Methyl-d-aspartate receptor
- SS:
-
Sodium salicylate
- APV:
-
NMDAR inhibitor
- KN93:
-
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II inhibitor
- BAPTA:
-
Ca2+ chelator
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- TBST:
-
Tris-buffered saline tween
References
Bauer CA, Brozoski TJ, Holder TM, Caspary DM (2000) Effects of chronic salicylate on GABAergic activity in rat inferior colliculus. Hear Res 147(1–2):175–182
Chen QX, Wong RK (1995) Suppression of GABAA receptor responses by NMDA application in hippocampal neurones acutely isolated from the adult guinea-pig. J Physiol 482(Pt 2):353–362
Chen G, Kittler JT, Moss SJ, Yan Z (2006) Dopamine D3 receptors regulate GABAA receptor function through a phospho-dependent endocytosis mechanism in nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci 26(9):2513–2521. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4712-05.2006
Chen GD, Stolzberg D, Lobarinas E, Sun W, Ding D, Salvi R (2013) Salicylate-induced cochlear impairments, cortical hyperactivity and re-tuning, and tinnitus. Hear Res 295:100–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heares.2012.11.016
Chen H, Zeng Q, Yao C, Cai Z, Wei T, Huang Z, Su J (2016) Src family tyrosine kinase inhibitors suppress Nav1.1 expression in cultured rat spiral ganglion neurons. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol 202(3):185–193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-016-1066-3
Cheng Q, Yeh HH (2003) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor attenuates mouse cerebellar granule cell GABA(A) receptor-mediated responses via postsynaptic mechanisms. J Physiol 548(Pt 3):711–721. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2002.037846
Comenencia-Ortiz E, Moss SJ, Davies PA (2014) Phosphorylation of GABAA receptors influences receptor trafficking and neurosteroid actions. Psychopharmacology 231(17):3453–3465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3617-z
Cong D, Tang Z, Li L, Huang Y, Wang J, Chen L (2011) Cross-talk between NMDA and GABA(A) receptors in cultured neurons of the rat inferior colliculus. Sci China Life Sci 54(6):560–566. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-011-4178-6
Coultrap SJ, Bayer KU (2012) CaMKII regulation in information processing and storage. Trends Neurosci 35(10):607–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2012.05.003
Deng L, Ding D, Su J, Manohar S, Salvi R (2013) Salicylate selectively kills cochlear spiral ganglion neurons by paradoxically up-regulating superoxide. Neurotox Res 24(3):307–319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-013-9384-5
Drescher DG, Green GE, Khan KM, Hajela K, Beisel KW, Morley BJ, Gupta AK (1993) Analysis of gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor subunits in the mouse cochlea by means of the polymerase chain reaction. J Neurochem 61(3):1167–1170
Erondu NE, Kennedy MB (1985) Regional distribution of type II Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase in rat brain. J Neurosci 5(12):3270–3277
Feng S, Pflueger M, Lin SX, Groveman BR, Su J, Yu XM (2012) Regulation of voltage-gated sodium current by endogenous Src family kinases in cochlear spiral ganglion neurons in culture. Pflugers Arch 463(4):571–584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-012-1072-4
Fritschy JM, Panzanelli P (2014) GABAA receptors and plasticity of inhibitory neurotransmission in the central nervous system. Eur J Neurosci 39(11):1845–1865. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.12534
Gao M, Fang X, Fen S, Wang R, Deng L, Su J (2012) Salicylate enhances expression and function of NMDA receptors in cochlear spiral ganglion neurons. J Otol 7(1):9–14
Gong N, Zhang M, Zhang XB, Chen L, Sun GC, Xu TL (2008) The aspirin metabolite salicylate enhances neuronal excitation in rat hippocampal CA1 area through reducing GABAergic inhibition. Neuropharmacology 54(2):454–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.10.017
Guetg N, Abdel Aziz S, Holbro N, Turecek R, Rose T, Seddik R, Gassmann M, Moes S, Jenoe P, Oertner TG, Casanova E, Bettler B (2010) NMDA receptor-dependent GABAB receptor internalization via CaMKII phosphorylation of serine 867 in GABAB1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(31):13924–13929. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1000909107
Guitton MJ, Pujol R, Puel JL (2005) m-Chlorophenylpiperazine exacerbates perception of salicylate-induced tinnitus in rats. Eur J Neurosci 22(10):2675–2678. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04436.x
Gutierrez ML, Ferreri MC, Gravielle MC (2014) GABA-induced uncoupling of GABA/benzodiazepine site interactions is mediated by increased GABAA receptor internalization and associated with a change in subunit composition. Neuroscience 257:119–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.10.077
Honkura N, Matsuzaki M, Noguchi J, Ellis-Davies GC, Kasai H (2008) The subspine organization of actin fibers regulates the structure and plasticity of dendritic spines. Neuron 57(5):719–729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2008.01.013
Houston CM, Smart TG (2006) CaMK-II modulation of GABA(A) receptors expressed in HEK293, NG108-15 and rat cerebellar granule neurons. Eur J Neurosci 24(9):2504–2514. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.05145.x
Houston CM, Lee HH, Hosie AM, Moss SJ, Smart TG (2007) Identification of the sites for CaMK-II-dependent phosphorylation of GABA(A) receptors. J Biol Chem 282(24):17855–17865. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M611533200
Huang X, Chen HY, Wei TJ, Qin DX, Liu PQ, Ye WH, Su JP (2017) The sodium salicylate affects the expression of NMDA receptor and GABAa receptor subunits in spiral ganglion neurons of the cochlea through DA receptor. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 31(20):1593–1598. https://doi.org/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2017.20.012
Hudmon A, Schulman H (2002) Neuronal CA2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II: the role of structure and autoregulation in cellular function. Annu Rev Biochem 71:473–510. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.71.110601.135410
Hwang JH, Chen JC, Yang SY, Wang MF, Liu TC, Chan YC (2011) Expression of COX-2 and NMDA receptor genes at the cochlea and midbrain in salicylate-induced tinnitus. Laryngoscope 121(2):361–364. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.21283
Kittler JT, Chen G, Honing S, Bogdanov Y, McAinsh K, Arancibia-Carcamo IL, Jovanovic JN, Pangalos MN, Haucke V, Yan Z, Moss SJ (2005) Phospho-dependent binding of the clathrin AP2 adaptor complex to GABAA receptors regulates the efficacy of inhibitory synaptic transmission. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(41):14871–14876. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0506653102
Lee HH, Deeb TZ, Walker JA, Davies PA, Moss SJ (2011) NMDA receptor activity downregulates KCC2 resulting in depolarizing GABAA receptor-mediated currents. Nat Neurosci 14(6):736–743. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2806
Lo FS, Blue ME, Erzurumlu RS (2016) Enhancement of postsynaptic GABAA and extrasynaptic NMDA receptor-mediated responses in the barrel cortex of Mecp2-null mice. J Neurophysiol 115(3):1298–1306. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00944.2015
Lu J, Cui Y, Cai R, Mao Y, Zhang J, Sun X (2008) Early auditory deprivation alters expression of NMDA receptor subunit NR1 mRNA in the rat auditory cortex. J Neurosci Res 86(6):1290–1296. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.21577
Luscher B, Fuchs T, Kilpatrick CL (2011) GABAA receptor trafficking-mediated plasticity of inhibitory synapses. Neuron 70(3):385–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2011.03.024
Maison SF, Rosahl TW, Homanics GE, Liberman MC (2006) Functional role of GABAergic innervation of the cochlea: phenotypic analysis of mice lacking GABA(A) receptor subunits alpha 1, alpha 2, alpha 5, alpha 6, beta 2, beta 3, or delta. J Neurosci 26(40):10315–10326. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2395-06.2006
Malgrange B, Rigo JM, Lefebvre PP, Coucke P, Goffin F, Xhauflaire G, Belachew S, Van de Water TR, Moonen G (1997) Diazepam-insensitive GABAA receptors on postnatal spiral ganglion neurones in culture. Neuroreport 8(3):591–596
Milbrandt JC, Holder TM, Wilson MC, Salvi RJ, Caspary DM (2000) GAD levels and muscimol binding in rat inferior colliculus following acoustic trauma. Hear Res 147(1–2):251–260
Mou L, Dias BG, Gosnell H, Ressler KJ (2013) Gephyrin plays a key role in BDNF-dependent regulation of amygdala surface GABAARs. Neuroscience 255:33–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.09.051
Muir J, Arancibia-Carcamo IL, MacAskill AF, Smith KR, Griffin LD, Kittler JT (2010) NMDA receptors regulate GABAA receptor lateral mobility and clustering at inhibitory synapses through serine 327 on the gamma2 subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(38):16679–16684. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1000589107
Murashita H, Tabuchi K, Sakai S, Uemaetomari I, Tsuji S, Hara A (2007) The effect of a GABAA agonist muscimol on acoustic injury of the mouse cochlea. Neurosci Lett 418(1):18–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2007.02.060
Nakagawa T, Yamashita M, Hisashi K, Usami SI, Kakazu Y, Shibata S, Nakashima T, Koike K, Kubo K, Komune S (2005) GABA-induced response in spiral ganglion cells acutely isolated from guinea pig cochlea. Neurosci Res 53(4):396–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2005.08.011
Pougnet JT, Compans B, Martinez A, Choquet D, Hosy E, Boue-Grabot E (2016) P2X-mediated AMPA receptor internalization and synaptic depression is controlled by two CaMKII phosphorylation sites on GluA1 in hippocampal neurons. Sci Rep 6:31836. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep31836
Robello M, Amico C, Cupello A (1997) A dual mechanism for impairment of GABAA receptor activity by NMDA receptor activation in rat cerebellum granule cells. Eur Biophys J 25(3):181–187
Sahley TL, Hammonds MD, Musiek FE (2013) Endogenous dynorphins, glutamate and N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors may participate in a stress-mediated type-I auditory neural exacerbation of tinnitus. Brain Res 1499:80–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2013.01.006
Sakai S, Tabuchi K, Murashita H, Hara A (2008) Activation of the GABA(A) receptor ameliorates the cochlear excitotoxicity caused by kainic acid in the guinea pig. Tohoku J Exp Med 215(3):279–285
Saliba RS, Kretschmannova K, Moss SJ (2012) Activity-dependent phosphorylation of GABAA receptors regulates receptor insertion and tonic current. EMBO J 31(13):2937–2951. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2012.109
Sheppard A, Hayes SH, Chen GD, Ralli M, Salvi R (2014) Review of salicylate-induced hearing loss, neurotoxicity, tinnitus and neuropathophysiology. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 34(2):79–93
Sigel E, Steinmann ME (2012) Structure, function, and modulation of GABA(A) receptors. J Biol Chem 287(48):40224–40231. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R112.386664
Szabadits E, Cserep C, Szonyi A, Fukazawa Y, Shigemoto R, Watanabe M, Itohara S, Freund TF, Nyiri G (2011) NMDA receptors in hippocampal GABAergic synapses and their role in nitric oxide signaling. J Neurosci 31(16):5893–5904. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.5938-10.2011
Tang X, Gao M, Fen S, Su J (2010) Gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit expression in rat spiral ganglion neurons. Neural Regen Res 5(13):1020–1024. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374
Terunuma M, Xu J, Vithlani M, Sieghart W, Kittler J, Pangalos M, Haydon PG, Coulter DA, Moss SJ (2008) Deficits in phosphorylation of GABA(A) receptors by intimately associated protein kinase C activity underlie compromised synaptic inhibition during status epilepticus. J Neurosci 28(2):376–384. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4346-07.2008
Wang D, Lu H, Xu T (2000) Mediation by calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II of suppression of GABA(A) receptors by NMDA. Sci China C Life Sci 43(6):655–662. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02882287
Wang HT, Luo B, Zhou KQ, Xu TL, Chen L (2006) Sodium salicylate reduces inhibitory postsynaptic currents in neurons of rat auditory cortex. Hear Res 215(1–2):77–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heares.2006.03.004
Wei L, Ding D, Salvi R (2010) Salicylate-induced degeneration of cochlea spiral ganglion neurons-apoptosis signaling. Neuroscience 168(1):288–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.03.015
Xu H, Gong N, Chen L, Xu TL (2005) Sodium salicylate reduces gamma aminobutyric acid-induced current in rat spinal dorsal horn neurons. Neuroreport 16(8):813–816
Yang K, Huang ZW, Huang J, Zhang XJ, Xiao BK (2008) Expression of the neuron-specific potassium chloride cotransporter KCC2 in adult rat cochlear. Neurosci Lett 441(2):205–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2008.06.038
Yao C, Cai Z, Wang R, Chen H, Huang Z, Qin J, Su J (2015) The effect of sodium salicylate on the expression of GABAa receptor subunits in cochlear spiral ganglion neurons. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 29(11):1024–1029
Zarate S, Jaita G, Ferraris J, Eijo G, Magri ML, Pisera D, Seilicovich A (2012) Estrogens induce expression of membrane-associated estrogen receptor alpha isoforms in lactotropes. PLoS One 7(7):e41299. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0041299
Zhu J, Apparsundaram S, Dwoskin LP (2009) Nicotinic receptor activation increases [3H]dopamine uptake and cell surface expression of dopamine transporters in rat prefrontal cortex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 328(3):931–939. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.108.147025
Zou QZ, Shang XL (2012) Effect of salicylate on the large GABAergic neurons in the inferior colliculus of rats. Acta Neurol Belg 112(4):367–374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-012-0090-5
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (81360157, 81560174), the Life Sciences Research Institute of Guangxi Medical University, and the Experimental Animal Center of Guangxi Medical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Danxue Qin performed cell culture, immunofluorescence, and Western Blot detection, which were used in the present study, and completed data analysis; paper writing was under the guidance of Huiying Chen and Jiping Su. Peiqiang Liu performed quantitative PCR and whole-cell patch clamp technique, which were used in the present study. Wenhua Ye, Xiaoyu Lin, and Weifang Yu made effort for cell culture. All the experimental technology were under the guidance of Huiying Chen and Xi Huang. Jiping Su conceived, designed, and directed this project. All authors contributed to and have approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The experimental animals were provided by the Experimental Animal Center of Guangxi Medical University, and the animal experiments were approved and governed by the Animal Ethics Committee of Guangxi Medical University. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the NSFC guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals; every effort was made to relieve any pain felt by the experimental animals.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, D., Liu, P., Chen, H. et al. Salicylate-Induced Ototoxicity of Spiral Ganglion Neurons: Ca2+/CaMKII-Mediated Interaction Between NMDA Receptor and GABAA Receptor. Neurotox Res 35, 838–847 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-0006-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-0006-8