Abstract
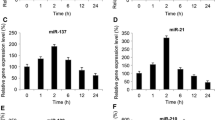
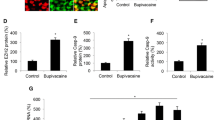
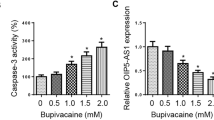
In this work, we evaluated the functional role of microRNA-33-5p (miR-33-5p) in regulating bupivacaine (Bv)-induced neural apoptosis in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) cells. DRG was extracted from adult mice and treated with BV in vitro. A TUNEL assay was applied to assess neural apoptosis among DRG cells. A qRT-PCR assay was applied to assess miR-33-5p expression among BV-treated DRG cells. MiR-33-5p was genetically knocked down in DRG cells. Its effect on BV-induced neural apoptosis was further evaluated by TUNEL assay. Correlation between miR-33-5p and its putative downstream target gene, glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), was assessed by dual-luciferase activity and qRT-PCR assays, respectively. GDNF was then inhibited in miR-33-5p-downregulated DRG cells to further assess its functional regulation in BV-induced neural apoptosis. BV induced significant neural apoptosis, in a dose-dependent manner, in DRG cells in vitro. MiR-33-5p was upregulated by BV treatment, also in a dose-dependent manner in DRG cells. On the other hand, downregulation of miR-33-5p protected BV-induced DRG neural apoptosis. GDNF was shown to be inversely correlated with miR-33-5p in BV-treated DRG cells. Moreover, inhibiting GDNF was able to reverse the protection of miR-33-5p-downregulation on BV-induced DRG neural apoptosis. MiR-33-5p, through its inverse regulation on DGNF gene, modulates anesthesia-induced neural apoptosis in DRG cells.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Averill S, Michael GJ, Shortland PJ, Leavesley RC, King VR, Bradbury EJ, McMahon SB, Priestley JV (2004) NGF and GDNF ameliorate the increase in ATF3 expression which occurs in dorsal root ganglion cells in response to peripheral nerve injury. Eur J Neurosci 19:1437–1445
Bar KJ, Saldanha GJ, Kennedy AJ, Facer P, Birch R, Carlstedt T, Anand P (1998) GDNF and its receptor component Ret in injured human nerves and dorsal root ganglia. Neuroreport 9:43–47
Brull R, McCartney CJ, Chan VW, El-Beheiry H (2007) Neurological complications after regional anesthesia: contemporary estimates of risk. Anesth Analg 104:965–974
Cui C, Xu G, Qiu J, Fan X (2015) Up-regulation of miR-26a promotes neurite outgrowth and ameliorates apoptosis by inhibiting PTEN in bupivacaine injured mouse dorsal root ganglia. Cell Biol Int 39:933–942
Graham MR (2017) Clinical update regarding general anesthesia-associated neurotoxicity in infants and children. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 30:682–687
Jan A, Karasinska JM, Kang MH, de Haan W, Ruddle P, Kaur A, Connolly C, Leavitt BR, Sorensen PH, Hayden MR (2015) Direct intracerebral delivery of a miR-33 antisense oligonucleotide into mouse brain increases brain ABCA1 expression. [Corrected]. Neurosci Lett 598:66–72
Jevtovic-Todorovic V (2011) Pediatric anesthesia neurotoxicity: an overview of the 2011 SmartTots panel. Anesth Analg 113:965–968
Jovasevic V, Corcoran KA, Leaderbrand K, Yamawaki N, Guedea AL, Chen HJ, Shepherd GM, Radulovic J (2015) GABAergic mechanisms regulated by miR-33 encode state-dependent fear. Nat Neurosci 18:1265–1271
Lin LF, Doherty DH, Lile JD, Bektesh S, Collins F (1993) GDNF: a glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor for midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Science 260:1130–1132
Meng F, You Y, Liu Z, Liu J, Ding H, Xu R (2015) Neuronal calcium signaling pathways are associated with the development of epilepsy. Mol Med Rep 11:196–202
Moore MW, Klein RD, Farinas I, Sauer H, Armanini M, Phillips H, Reichardt LF, Ryan AM, Carver-Moore K, Rosenthal A (1996) Renal and neuronal abnormalities in mice lacking GDNF. Nature 382:76–79
Radwan IA, Saito S, Goto F (2002) The neurotoxicity of local anesthetics on growing neurons: a comparative study of lidocaine, bupivacaine, mepivacaine, and ropivacaine. Anesth Analg 94:319–324 table of contents
Shi H, Luo X (2016) 7, 8, 3′-Trihydroxyflavone promotes neurite outgrowth and protects against bupivacaine-induced neurotoxicity in mouse dorsal root ganglion neurons. Med Sci Monit 22:2301–2308
Vutskits L, Davidson A (2017) Update on developmental anesthesia neurotoxicity. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 30:337–342
Wang R, Guo W, Ossipov MH, Vanderah TW, Porreca F, Lai J (2003) Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor normalizes neurochemical changes in injured dorsal root ganglion neurons and prevents the expression of experimental neuropathic pain. Neuroscience 121:815–824
Xie X, Peng L, Zhu J, Zhou Y, Li L, Chen Y, Yu S, Zhao Y (2017) miR-145-5p/Nurr1/TNF-alpha signaling-induced microglia activation regulates neuron injury of acute cerebral ischemic/reperfusion in rats. Front Mol Neurosci 10:383
Yan Q, Matheson C, Lopez OT (1995) In vivo neurotrophic effects of GDNF on neonatal and adult facial motor neurons. Nature 373:341–344
Yu T, Lin W (2016) Small-molecule GSK-3 inhibitor rescued apoptosis and neurodegeneration in anesthetics-injured dorsal root ganglion neurons. Biomed Pharmacother 84:395–402
Yu XJ, Zhao W, Li YJ, Li FX, Liu ZJ, Xu HL, Lai LY, Xu R, Xu SY (2017) Neurotoxicity comparison of two types of local anaesthetics: amide-bupivacaine versus ester-procaine. Sci Rep 7:45316
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Wang, K. Downregulation of MicroRNA-33-5p Protected Bupivacaine-Induced Apoptosis in Murine Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons Through GDNF. Neurotox Res 35, 860–866 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-018-9994-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-018-9994-z