Abstract
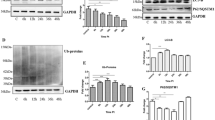
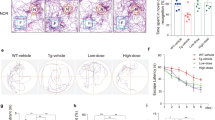
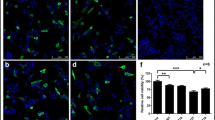
Prion protein peptide (PrP) has been associated with neurotoxicity in brain cells and progression of prion diseases due to spongiform degeneration and accumulation of the infectious scrapie prion protein (PrPSc). Autophagy has been shown to provide protective functions for neurodegenerative diseases, including prion disease. Thymosin beta 4 (Tβ4) plays a key role in the nervous system, providing a neuronal growth effect that includes motility, neurite outgrowth, and proliferation. However, the effect of Tβ4 on autophagy in prion disease has not been investigated. In this study, we investigated the neuroprotective effects of Tβ4, an activator of autophagy, in cholinergic signaling activation in PrP (106–126)-treated HT22 cells. We found that Tβ4-induced autophagy markers, LC3A/B and Beclin1, were protective against PrP-induced neurotoxicity. Interestingly, a balance between autophagy markers and autophagy pathway factors (AKT, p-AKT, mTOR, and p-mTOR) was maintained by Tβ4 competitively against each protein factors reacted to PrP (106–126). The cholinergic signaling markers ChTp and AChE, which play an important role in the brain, were maintained by Tβ4 competitively against each protein factors reacted to PrP (106–126). However, these results were reversed by 3-MA, an autophagy inhibitor. Taken together, our results indicate that Tβ4 has cholinergic signaling activities through the induction of autophagy. Thus, Tβ4 may be to a potential therapeutic agent for preventing neurodegenerative diseases.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aizawa S, Yamamuro Y (2010) Involvement of histone acetylation in the regulation of choline acetyltransferase gene in NG108-15 neuronal cells. Neurochem Int 56:627–633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2010.01.007
Bales KR, Tzavara ET, Wu S, Wade MR, Bymaster FP, Paul SM, Nomikos GG (2006) Cholinergic dysfunction in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease is reversed by an anti-A beta antibody. J Clin Invest 116:825–832. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci27120
Boellaard JW, Kao M, Schlote W, Diringer H (1991) Neuronal autophagy in experimental scrapie. Acta Neuropathol 82:225–228
Boya P, Reggiori F, Codogno P (2013) Emerging regulation and functions of autophagy. Nat Cell Biol 15:713–720. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2788
Cherra SJ III, Chu CT (2008) Autophagy in neuroprotection and neurodegeneration: a question of balance. Future Neurol 3:309–323. https://doi.org/10.2217/14796708.3.3.309
Contestabile A, Ciani E, Contestabile A (2008) The place of choline acetyltransferase activity measurement in the “cholinergic hypothesis” of neurodegenerative diseases. Neurochem Res 33:318–327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9497-4
Deretic V, Saitoh T, Akira S (2013) Autophagy in infection, inflammation and immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 13:722–737. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3532
Eisenberg-Lerner A, Bialik S, Simon HU, Kimchi A (2009) Life and death partners: apoptosis, autophagy and the cross-talk between them. Cell Death Differ 16:966–975. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2009.33
Hay N (2005) The Akt-mTOR tango and its relevance to cancer. Cancer Cell 8:179–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2005.08.008
Heiseke A, Aguib Y, Schatzl HM (2010) Autophagy, prion infection and their mutual interactions. Curr Issues Mol Biol 12:87–97
Hubbi ME, Semenza GL (2015) An essential role for chaperone-mediated autophagy in cell cycle progression. Autophagy 11:850–851. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2015.1037063
Kiriyama Y, Nochi H (2015) The function of autophagy in neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci 16:26797–26812. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161125990
Larsen KE, Sulzer D (2002) Autophagy in neurons: a review. Histol Histopathol 17:897–908. https://doi.org/10.14670/hh-17.897
Malinda KM, Sidhu GS, Mani H, Banaudha K, Maheshwari RK, Goldstein AL, Kleinman HK (1999) Thymosin beta4 accelerates wound healing. J Invest Dermatol 113:364–368. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1747.1999.00708.x
Melo JB, Agostinho P, Oliveira CR (2007) Prion protein aggregation and neurotoxicity in cortical neurons. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1096:220–229. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1397.088
Meyer G, Czompa A, Reboul C, Csepanyi E, Czegledi A, Bak I, Balla G, Balla J, Tosaki A, Lekli I (2013) The cellular autophagy markers Beclin-1 and LC3B-II are increased during reperfusion in fibrillated mouse hearts. Curr Pharm Des 19:6912–6918
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM, Klionsky DJ (2008) Autophagy fights disease through cellular self-digestion. Nature 451:1069–1075. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06639
Na JY, Kim S, Song K, Kwon J (2014) Rutin alleviates prion peptide-induced cell death through inhibiting apoptotic pathway activation in dopaminergic neuronal cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 34:1071–1079. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-014-0084-3
Nakagaki T, Satoh K, Ishibashi D, Fuse T, Sano K, Kamatari YO, Kuwata K, Shigematsu K, Iwamaru Y, Takenouchi T, Kitani H, Nishida N, Atarashi R (2013) FK506 reduces abnormal prion protein through the activation of autolysosomal degradation and prolongs survival in prion-infected mice. Autophagy 9:1386–1394. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.25381
Noda T, Ohsumi Y (1998) Tor, a phosphatidylinositol kinase homologue, controls autophagy in yeast. J Biol Chem 273:3963–3966
Perry EK, Irving D, Kerwin JM, McKeith IG, Thompson P, Collerton D, Fairbairn AF, Ince PG, Morris CM, Cheng AV, Perry RH (1993) Cholinergic transmitter and neurotrophic activities in Lewy body dementia: similarity to Parkinson’s and distinction from Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 7:69–79
Philp D, Goldstein AL, Kleinman HK (2004) Thymosin beta4 promotes angiogenesis, wound healing, and hair follicle development. Mech Ageing Dev 125:113–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2003.11.005
Pirkkala L, Nykanen P, Sistonen L (2001) Roles of the heat shock transcription factors in regulation of the heat shock response and beyond. FASEB J 15:1118–1131
Pollard TD, Borisy GG (2003) Cellular motility driven by assembly and disassembly of actin filaments. Cell 112:453–465
Prusiner SB (1982) Novel proteinaceous infectious particles cause scrapie. Science (New York, NY) 216:136–144
Rosenfeldt MT, Ryan KM (2011) The multiple roles of autophagy in cancer. Carcinogenesis 32:955–963. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgr031
Rubinsztein DC (2006) The roles of intracellular protein-degradation pathways in neurodegeneration. Nature 443:780–786. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05291
Schatzl HM et al (1997) A hypothalamic neuronal cell line persistently infected with scrapie prions exhibits apoptosis. J Virol 71:8821–8831
Schmelzle T, Hall MN (2000) TOR, a central controller of cell growth. Cell 103:253–262
Sikorska B, Liberski PP, Brown P (2007) Neuronal autophagy and aggresomes constitute a consistent part of neurodegeneration in experimental scrapie. Folia Neuropathol 45:170–178
Singh BN, Kumar D, Shankar S, Srivastava RK (2012) Rottlerin induces autophagy which leads to apoptotic cell death through inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in human pancreatic cancer stem cells. Biochem Pharmacol 84:1154–1163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2012.08.007
Sosne G, Chan CC, Thai K, Kennedy M, Szliter EA, Hazlett LD, Kleinman HK (2001) Thymosin beta 4 promotes corneal wound healing and modulates inflammatory mediators in vivo. Exp Eye Res 72:605–608. https://doi.org/10.1006/exer.2000.0985
Yang H, Cheng X, Yao Q, Li J, Ju G (2008) The promotive effects of thymosin beta4 on neuronal survival and neurite outgrowth by upregulating L1 expression. Neurochem Res 33:2269–2280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-008-9712-y
Yu FX, Lin SC, Morrison-Bogorad M, Atkinson MA, Yin HL (1993) Thymosin beta 10 and thymosin beta 4 are both actin monomer sequestering proteins. J Biol Chem 268:502–509
Zhao RR, Xu F, Xu XC, Tan GJ, Liu LM, Wu N, Zhang WZ, Liu JX (2015) Effects of alpha-lipoic acid on spatial learning and memory, oxidative stress, and central cholinergic system in a rat model of vascular dementia. Neurosci Lett 587:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2014.12.037
Zhong Z, Sanchez-Lopez E, Karin M (2016) Autophagy, inflammation, and immunity: a troika governing cancer and its treatment. Cell 166:288–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.051
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the National Research Foundation of Korea, funded by the Korean government (NRF-2015R1D1A1A01057696).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, HJ., Kim, S. & Kwon, J. Thymosin beta 4-Induced Autophagy Increases Cholinergic Signaling in PrP (106–126)-Treated HT22 Cells. Neurotox Res 36, 58–65 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-018-9985-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-018-9985-0