Abstract
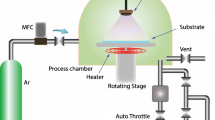
Nanocrystalline ZnO thin films have been fabricated by an RF magnetron sputtering method for the different time duration. The effect of process parameters on the structural, morphological and Optical properties of ZnO were studied by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and Photoluminescence and UV-Vis. Spectrometer. All of the films were polycrystalline, and the preferred crystal plane orientation was (101) corresponding to 2𝜃 = 36.57∘, the crystallite sizes were increased from 12 nm to 18 nm as in XRD calculations and increase from 24nm to 33 nm as in SEM image. Optical constants, such as refractive index n, were determined from the transmittance spectrum in the ultraviolet -visible. The refractive index varies in the range of 1.664 to 8.706 with an increase in deposition time. Optical energy gap estimated from the transmittance (3.304 eV) and the PL (3.44 eV) shows good agreement and increased as the time duration was increased.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tillstra L, Allen Brougton S, Robin Jelski S, French V, Zhang G, Alexander Popov K (2008) The science of nanotechnology an introductory text. Nova Science Publishers, Inc, New York
Victor Klimov I (2004) Semiconductor and metal nanocrystals synthesis and electronic and optical properties. Copyright by Marcel Dekker Inc.
George Fine F, Cavanagh LM, Afonja A, Binions R (2010) Metal oxide semi-conductor gas sensors in environmental monitoring. Sensors 10:5469–5502
Bangale SV, Bamane SR (2012) Preparation and study of h2S gas sensing behavior of ZnFe2 O 4 thick film resistors. Sensors Transd. 137:123–136
Hu Y, Zhou X, Han Q, Huang Y (2003) Sensing properties of CuO/ZnO hetrojunction gas sensors. Mater Sci Eng 99:4143
Kumar Patra S (2008) Thesis: a novel chemical approach to fabricate ZnO Nanostructures
Ellmer K (2000) Magnetron sputtering of transparent conductive zinc oxide: relation between the sputtering parameters and the electronic properties. J Phys D Appl Phys 33:R17–R32
Lee Y, Kim Y, Kim H (1998) Thickness dependence of microstructural evolution of ZnO films deposited by RF magnetron sputtering. J Mater Res 13:1260–1265
Boxman RL, Zhitomirsky V, Goldsmith S, David T, Diktyar V (2003) Society of vacuum coaters (SVC) 46th annual technical conference proceedings, pp 75–80
Misiuk A (1981) Reflection X-ray topography of ZnO thin films on non-orienting substrates. Thin Solid Films 76:83
Tewari, Bhattacharjee A (2011) Structural, electrical and optical studies on spray-deposited aluminum-doped ZnO thin films. Indian Acad Sci 76(1):53–163
Nada Saeed M, Suhail AM (2009) Preparation and propertiesof nanostructure zinc oxide thin films. Iraqi J Phys 7(8):75–81
Oǵuzer A, Aaf hassan AF, Gŭmŭş C, Gŭnerı̆ E (2011) Morphology of zinc oxide thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis. Optoelectron Adv Mater Rapid Commun 5(12):1286–1291
Ezema FI (2007) Optical properties of chemical bath deposited nickel oxide niox thin films. Superficies y Vacío 21(1):6–10
Giraldi TR, Escote MT, Bernardi MIB, Leit VR (2004) Effect of thickness on the electrical and optical properties of Sb doped SnO2(ATO) thin films. J Electr Ceram 13:159–165
Grundmann M, Wenckstern H v, Pickenhain R, Nobis Th, Rahm A, Lorenz M (2005) Super Lattices Microstruct 38:317–328
Gupta V, Bhattacharya P, Yuzuk YI, Katiyar RS, Tomar M, Sreenivas K (2004) Ferroelectric photovoltaic properties of Ce and Mn codoped BiFeO3 thin film. J Mater Res 19:2235
Wang Z, Cheeke JDN (1994) Sensitivity analysis for Love mode acoustic gravimetric sensors. Appl Phys Lett 64:2940
Keem K, Kim H, Kim GT, Lee JS, Min B, Cho K, Sung MY, Kim S (2004) Photocurrent in ZnO nanowires grown from Au electrodes. Appl Phys Lett 84:4376
Thomas DG (1960) The exciton spectrum of zinc oxide. J Phys Chem Solids 15:86
Acknowledgments
This research was reinforced by the AL-Mustansiriyah University College of science, physics department and the work crew would like to acknowledge the ministry of science and technology for providing that support through the RF-magnetron sputtering system.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, E.S., Abd, A.N. & Dawood, M.O. The Sputter Time Duration Effect on the Structural and Optical Properties of Zinc Oxide by RF Magnetron Sputtering. Silicon 10, 2901–2906 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-018-9831-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-018-9831-2