Abstract
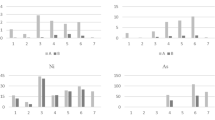
The micromorphology and physicochemical properties of hydrophobic blasting dust (HBD) from an iron mine were comprehensively analyzed by laser particle size analysis (LPSA), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The results show that the HBD particles can be classified into three types based on their particle size (PS): larger particles (PS > 10 µm), medium particles (1 µm ≤ PS ≤ 10 µm), and nanoparticles (PS > 1 µm). The cumulative volume of respirable dust (PS > 10 µm) was 84.45%. In addition, three shapes of HBD were observed by SEM: prism, flake, and bulk. In particular, the small particles were mostly flaky, with a greater possibility of being inhaled. Furthermore, the body and surface chemical compounds of HBD were determined by XRD and XPS, respectively. Ammonium adipate (C6H16N2O4) was the only organic compound in the body of HBD, but its mass fraction was only 13.4%. However, the content of organic C on the surface of HBD was 85.35%. This study demonstrated that the small-particle size and large amount of organic matter on the surface of HBD are the main reasons for its hydrophobicity, which can provide important guidance for controlling respirable dust in iron mines.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
X.T. Feng, J.P Liu, B.R Chen, Y.X Xiao, G.L Feng, and F.P Zhang, Monitoring, warning, and control of rockburst in deep metal mines, Engineering, 3(2017), No. 4, p. 538.
M.F. Cai, Prediction and prevention of rockburst in metal mines-A case study of Sanshandao gold mine, J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 8(2016), No. 2, p. 204.
G.Y. Zhao, M.A. Ju, L.J. Dong, X.B. Li, G.H. Chen, and C.X. Zhang, Classification of mine blasts and microseismic events using starting-up features in seismograms, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 25(2015), No. 10, p. 3410.
T. Norgate and N. Haque, Energy and greenhouse gas impacts of mining and mineral processing operations, J. Cleaner Prod., 18(2010), No. 3, p. 266.
M.I. Greenberg, J. Waksman, and J. Curtis, Silicosis: A review, Disease-a-Month, 53(2007), No. 8, p. 394.
X.Z. Wang, Z.A. Jiang, S.W. Wang, and Y. Liu, Numerical simulation of distribution regularities of dust concentration during the ventilation process of coal roadway driving, J. China Coal Soc., 32(2007), No. 4, p. 386.
J. Toraño, S. Torno, M. Menéndez, and M. Gent, Auxiliary ventilation in mining roadways driven with roadheaders: Validated CFD modelling of dust behaviour, Tunnelling Underground Space Technol., 26(2011), No. 1, p. 201.
H.T. Wang, D.M. Wang, W.X. Ren, X.X. Lu, F.W. Han, and Y.K. Zhang, Application of foam to suppress rock dust in a large cross-section rock roadway driven with roadheader, Adv. Powder Technol., 24(2013), No. 1, p. 257.
H.T. Wang, D.M. Wang, Y. Tang, B.T. Qin, and H.H. Xin, Experimental investigation of the performance of a novel foam generator for dust suppression in underground coal mines, Adv. Powder Technol., 25(2014), No. 3, p. 1053.
X.X. Lu, D.M. Wang, C.H. Xu, C.B. Zhu, and W. Shen, Experimental investigation and field application of foam used for suppressing roadheader cutting hard rock in underground tunneling, Tunnelling Underground Space Technol., 49(2015), p. 1.
S.P. Ma and Z.M. Kou, Study on mechanism of reducing dust by spray, J. China Coal Soc., 30(2005), No. 3, p. 297.
E.A. Almuhanna, R.G. Maghirang, J.P. Murphy, and L.E. Erickson, Effectiveness of electrostatically charged water spray in reducing dust concentration in enclosed spaces, Trans. ASABE, 51(2008), No. 1, p. 279.
J. Yang., X.K. Wu, J.G. Gao, and G.P. Li, Surface characteristics and wetting mechanism of respirable coal dust, Min. Sci. Technol., 20(2010), No. 3, p. 365.
L.Z. Jin, J.M. Zhu, Z.G. Ren, and W. Wei, Research on an antifreezing dust depressor used to the road in open-pit mine, J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing, 26(2004), No. 1, p. 4.
L.Z. Jin, J.X. Yang, and S.N. Ou, Experimental study of wetting chemical dust-depressor, J. Saf. Environ., 7(2007), No. 6, p. 109.
H.H. Tang, L.H. Zhao, W. Sun, Y.H. Hu, and H.S. Han, Surface characteristics and wettability enhancement of respirable sintering dust by nonionic surfactant, Colloids Surf. A, 509(2016), p. 323.
X.F. Liu and B.S. Nie, Fractal characteristics of coal samples utilizing image analysis and gas adsorption, Fuel, 182(2016), p. 314.
X.F. Liu, D.Z. Song, X.Q. He, Z.P. Wang, M.R. Zeng, and L.K. Wang, Quantitative analysis of coal nanopore characteristics using atomic force microscopy, Powder Technol., 346(2019), p. 332.
X.Q. He, X.F. Liu, D.Z. Song, and B.S. Nie, Effect of microstructure on electrical property of coal surface, Appl. Surf. Sci., 483(2019), p. 713.
X.F. Liu, D.Z. Song, X.Q. He, B.S. Nie, and L.K. Wang, Insight into the macromolecular structural differences between hard coal and deformed soft coal, Fuel, 245(2019), p. 188.
X.F. Liu, D.Z. Song, X.Q. He, Z.P. Wang, M.R. Zeng, and K. Deng, Nanopore structure of deep-burial coals explored by AFM, Fuel, 246(2019), p. 9.
V.K. Kollipara, Y.P. Chugh, and K. Mondal, Physical, mineralogical and wetting characteristics of dusts from Interior Basin coal mines, Int. J. Coal Geol., 127(2014), p. 75.
C.H. Xu, D.M. Wang, H.T. Wang, H.H. Xin, L.Y. Ma, X.L. Zhu, Y. Zhang, and Q.G. Wang, Effects of chemical properties of coal dust on its wettability, Powder Technol., 318(2017), p. 33.
H.T. Wang, L. Zhang, D.M. Wang, and X.X. He, Experimental investigation on the wettability of respirable coal dust based on infrared spectroscopy and contact angle analysis, Adv. Powder Technol., 28(2017), No. 12, p. 3130.
G. Zhou, C.C. Xu, W.M. Cheng, Q. Zhang, and W. Nie, Effects of oxygen element and oxygen-containing functional groups on surface wettability of coal dust with various metamorphic degrees based on XPS experiment, J. Anal. Methods Chem., 2015(2015), art. No. 467242.
S.S. Lu, H.F. Liu, X.L. Guo, X. Liu, and X. Gong, Determination method of particle size and distribution of coal by laser size analyzer, China Powder Sci. Technol., 16(2010), No. 4, p. 5.
Å. Gustafsson, A.M. Krais, A. Gorzsás, T. Lundh, and P. Gerde, Isolation and characterization of a respirable particle fraction from residential house-dust, Environ. Res., 161(2018), p. 284.
Z.G. Cao, G. Yu, Y.S. Chen, C. Liu, K. Liu, T.T. Zhang, B. Wang, S.B. Deng, and J. Huang, Mechanisms influencing the BFR distribution patterns in office dust and implications for estimating human exposure, J. Hazard. Mater., 252(2013), p. 11.
C.C. Negrila, C. Logofatu, R.V. Ghita, C. Cotirlan, F. Ungureanu, A.S. Manea, and M.F. Lazarescu, Angle-resolved XPS structural investigation of GaAs surfaces, J. Cryst. Growth, 310(2008), No. 7–9, p. 1576.
T. Takahagi and A. Ishitani, XPS studies by use of the digital difference spectrum technique of functional groups on the surface of carbon fiber, Carbon, 22(1984), No. 1, p. 43.
Y. Taki and O. Takai, XPS structural characterization of hydrogenated amorphous carbon thin films prepared by shielded arc ion plating, Thin Solid Films, 316(1998), No. 1–2, p. 45.
M. Devillers, O. Dupuis, A. Janosi, and J.P. Soumillion, Coordination compounds as precursors for laser deposition of nickel-based conducting films, Appl. Surf. Sci., 81(1994), No. 1, p. 83.
J.L. Jordan, C.A. Kovac, J.F. Morar, and R.A. Pollak, High-resolution photoemission study of the interfacial reaction of Cr with polyimide and model polymers, Phys. Rev. B, 36(1987), No. 3, p. 1369.
E.Z. Kurmaev, V.V. Fedorenko, V.R. Galakhov, S. Bartkowski, S. Uhlenbrock, M. Neumann, P.R. Slater, C. Greaves, and Y. Miyazaki, Analysis of oxyanion (BO 3−3 , CO 2−3 , SO 2−4 , PO 3−4 , SeO 4−4 ) substitution in Y123 compounds studied by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, J. Supercond., 9(1996), No. 1, p. 97.
A.B. Christie, J. Lee, I. Sutherland, and J.M. Walls, An XPS study of ion-induced compositional changes with group II and group IV compounds, Appl. Surf. Sci., 15(1983), No. 1–4, p. 224.
E. Paparazzo, XPS and auger spectroscopy studies on mixtures of the oxides SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3 and Cr2O3, J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom., 43(1987), No. 2, p. 97.
M.I. Sosulnikov and Y.A. Teterin, X-ray photoelectron study of calcium, strontium, barium and their oxides, Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 317(1991), No. 2, p. 418.
D. Sprenger, H. Bach, W. Meisel, and P. Gütlich, XPS study of leached glass surfaces, J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 126(1990), No. 1–2, p. 111.
L.P. Buchwalter and C. Czornyj, Poly(methyl methacrylate) degradation during x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A, 8(1990), No. 2, p. 781.
D. Briggs and G. Beamson, Primary and secondary oxygen-induced C1s binding energy shifts in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of polymers, Anal. Chem., 64(1992), No. 15, p. 1729.
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. SQ2017YFSF060069) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51574017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Jg., Jin, Lz., Wang, Jy. et al. Micromorphology and physicochemical properties of hydrophobic blasting dust in iron mines. Int J Miner Metall Mater 26, 665–672 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-019-1793-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-019-1793-x