Abstract
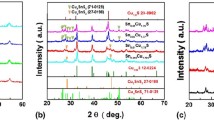
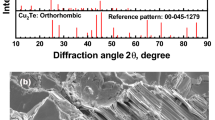
Copper sulfide Cu2S is a p-type semiconducting compound that has attracted great attentions in the thermoelectric (TE) community most recently. Considering the intrinsic ultralow lattice thermal conductivity, the enhancement of TE performance in Cu2S should be achieved through improving its electrical transport properties. To achieve this goal, lithium element was doped into Cu2S in this study. A series of Cu2−xLi x S samples with different Li contents (x = 0, 0.005, 0.010, 0.050, and 0.100) was synthesized by the melting–annealing method. When x ≤ 0.05, the Cu2−xLi x S samples are stable and pure phases, having the same monoclinic structure with the pristine Cu2S at room temperature. The electrical conductivities in the Cu2−xLi x S samples are greatly improved with the Li-doping content increasing due to the enhanced carrier concentrations. Meanwhile, doping Li into Cu2S increases the ionic activation energy and lessens the influence of mobile Cu ions on the heat-carrying phonons. Thus, the thermal conductivities of the Li-doped Cu2S samples increase. A maximal figure of merit (zT) of 0.84 at 900 K is obtained in Cu1.99Li0.01S, about 133% improvement as compared with that in Cu2S matrix.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Snyder GJ, Toberer ES. Complex thermoelectric materials. Nat Mater. 2008;7(2):105.
Li Z, Xiao C, Zhu H, Xie Y. Defect chemistry for thermoelectric materials. J Am Chem Soc. 2016;138(45):14810.
Zeier WG, Zevalkink A, Gibbs ZM, Hautier G, Kanatzids MG, Snyder GJ. Thingking like a chemist: intuition in thermoelectric materials. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2016;55(24):6826.
Shi X, Chen LD, Uher C. Recent advances in high-performance bulk thermoelectric materials. Int Mater Rev. 2016;61(6):379.
Roy P, Srivastava SK. Nanostructured copper sulfides: synthesis, properties and applications. CrystEngComm. 2015;17(41):7801.
Jiang QH, Yan HX, Khaliq J, Shen Y, Simpson K, Reece MJ. Enhancement of thermoelectric properties by atomic-scale percolation in digenite Cu x S. J Mater Chem A. 2014;2(25):9486.
Chakrabarti DJ, Laughlin DE. The Cu–S (copper–sulfur) system. Bull Alloy Phase Diagr. 1983;4(3):254.
Will G, Hinze E, Abdelrahman ARM. Crystal structure analysis and refinement of digenite, Cu1.8S, in the temperature range 10 to 500 °C under controlled sulfur partial pressure. Eur J Miner. 2002;14(3):591.
He Y, Day T, Zhang TS, Liu HL, Shi X, Chen LD, Snyder GJ. High thermoelectric performance in non-toxic earth-abundant copper sulfide. Adv Mater. 2014;26(23):397.
Zhao KP, Qiu PF, Song QF, Blichfeld AB, Eikeland E, Ren DD, Ge BH, Iversen BB, Shi X, Chen LD. Ultrahigh thermoelectric performance in Cu2−ySe0.5S0.5 liquid-like materials. Mater Today Phys. 2017;1(1):14.
Chen ZW, Jian ZZ, Li W, Chang YJ, Ge BH, Hanus R, Yang J, Chen Y, Huang MX, Snyder GJ, Pei YZ. Lattice dislocations enhancing thermoelectric PbTe in addition to band convergence. Adv Mater. 2017;29(23):1606768.
He Y, Lu P, Shi X, Xu FF, Zhang TS, Snyder GJ, Uher C, Chen L. Ultrahigh thermoelectric performance in mosaic crystals. Adv Mater. 2015;27(24):3639.
Qiu PF, Zhu YQ, Qin YT, Shi X, Chen LD. Electrical and thermal transports of binary copper sulfides Cu x S with x from 1.8 to 1.96. APL Mater. 2016;4(10):104805.
Qiu PF, Zhang TS, Qiu YT, Shi X, Chen LD. Sulfide bornite thermoelectric material: a natural mineral with ultralow thermal conductivity. Energy Environ Sci. 2014;7(12):4000.
Li XY, Hu CG, Kang XL, Len Q, Xi Y, Zhang KY, Liu H. Introducing kalium into copper sulfide for the enhancement of thermoelectric properties. J Mater Chem A. 2013;1(44):13721.
Zhang AJ, Shen XC, Zhang Z, Lu X, Yao W, Dai J, Xie DD, Guo LJ, Wang GY, Zhou XY. Large-scale colloidal synthesis of Cu5FeS4 compounds and their application in thermoelectrics. J Mater Chem C. 2017;5(2):301.
Balapanov MK, Gafurov IG, Mukhamed’yanov UK, Yakshibaev RA, Ishembetov RK. Ionic conductivity and chemical diffusion in superionic Li x Cu2−xS (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.25). Phys Status Solidi B. 2004;241(1):114.
Kang SD, Pöhls JH, Aydemir U, Qiu PF, Stoumpos CC, Hanus R, White MA, Shi X, Chen LD, Kanatzidis MG, Snyder GJ. Enhanced stability and thermoelectric figure-of-merit in copper selenide by lithium doping. Mater Today Phys. 2017;1(1):7.
Potter RW. An electrochemical investigation of the system copper–sulfur. Econ Geol. 1977;72(8):1524.
Shannon RD. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. 1976;A32(5):751.
Kowalczyk SP, Ley L, McFeely FR, Pollak RA, Shirley DA. X-ray photoemission from sodium and lithium. Phys Rev B. 1973;8(8):3583.
Duan B, Yang J, Salvador JR, He Y, Zhao B, Wang SY, Wei P, Ohuchi FS, Zhang WQ, Hermann RP, Gourdon O, Mao SX, Cheng YW, Wang CM, Liu J, Zhai PC, Tang XF, Zhang QJ, Yang JH. Electronegative guests in CoSb3. Energy Environ Sci. 2016;9(6):2090.
Marshall R, Mitra SS. Optical properties of cuprous sulfide. J Appl Phys. 1965;36(12):3882.
Jiang BB, Qiu PF, Eikeland E, Chen HY, Song QF, Ren DD, Zhang TS, Yang J, Iversen BB, Shi X, Chen LD. Cu8GeSe6-based thermoelectric materials with an argyrodite structure. J Mater Chem C. 2017;5(4):943.
Zhao KP, Duan HZ, Raghavendra N, Qiu PF, Zeng Y, Zhang WQ, Yang JH, Shi X, Chen LD. Solid-state explosive reaction for nanoporous bulk thermoelectric materials. Adv Mater. 2017;29(42):1701148.
He Y, Zhang TS, Shi X, Wei SH, Chen LD. High thermoelectric performance in copper telluride. NPG Asia Mater. 2015;7(8):e210.
Zhao LL, Wang XL, Fei FY, Wang JY, Cheng ZX, Dou SX, Wang J, Snyder GJ. High thermoelectric and mechanical performance in highly dense Cu2−xS bulks prepared by a melt-solidification technique. J Mater Chem A. 2015;3(18):9432.
Ge ZH, Zhao LD, Wu D, Liu X, Zhang BP, Li JF, He JQ. Low-cost, abundant binary sulfides as promising thermoelectric materials. Mater Today. 2016;19(4):227.
Zhao KP, Blichfeld AB, Chen HY, Song QF, Zhang TS, Zhu CX, Ren DD, Hanus R, Qiu PF, Iversen B, Xu FF, Snyder GJ, Shi X, Chen LD. Enhanced thermoelectric performance through tuning bonding energy in Cu2Se1−xS x liquid-like materials. Chem Mater. 2017;29:6367.
Lukashev P, Lambrecht WRL, Kotani T, van Schilfgaarde M. Electronic and crystal structure of Cu2−xS: full-potential electronic structure calculations. Phys Rev B. 2007;76(19):195202.
Sun YX, Xi LL, Yang J, Wu LH, Shi X, Chen LD, Snyder GJ, Yang JH, Zhang WQ. The “electron crystal” behavior in copper chalcogenides Cu2X (X = Se, S). J Mater Chem A. 2017;5(10):5098.
May AF, Fleurial JP, Snyder GJ. Thermoelectric performance of lanthanum telluride produced via mechanical alloying. Phys Rev B. 2008;78(12):125205.
Zhao KP, Blichfeld AB, Eikeland E, Qiu PF, Ren DD, Iversen BB, Shi X, Chen LD. Extremely low thermal conductivity and high thermoelectric performance in liquid-like Cu2Se1−xS x polymorphic materials. J Mater Chem A. 2017;5(34):18148.
Chen YX, Ge ZH, Yin MJ, Feng D, Huang XQ, Zhao WY, He JQ. Understanding of the extremely low thermal conductivity in high-performance polycrystalline SnSe through potassium doping. Adv Funct Mater. 2016;26(37):6836.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51472262 and 51625205), the Key Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. KFZD-SW-421) and the Shanghai Government (No. 15JC1400301).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, MJ., Qiu, PF., Song, QF. et al. Improved electrical transport properties and optimized thermoelectric figure of merit in lithium-doped copper sulfides. Rare Met. 37, 282–289 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-018-1007-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-018-1007-0