Abstract
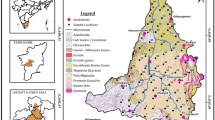
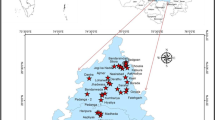
In the present study, the chemical characteristics of groundwater with respect to drinking and Irrigation water quality in upper Thirumanimuthar sub-basin, Cauvery River, have been studied. 51 groundwater samples were collected and analysed for pH, conductance, total dissolved solids, total hardness, calcium, magnesium, carbonate, bicarbonate, total alkalinity, chloride, sodium, potassium, sulphate etc. The values analyzed were evaluated in detail and compared with WHO water quality standards. It is observed that, for most of the groundwater quality parameters, the values are not potable for drinking and irrigational use. To understand the spatial distribution of unsuitable zones, ArcGIS was employed. Attributes were linked and spatial interpolation mapping was done. Inverse distance weighted interpolation technique was followed for raster and vector mapping. Finally the overlay analyses were also carried out to locate the worst quality zone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (American Public Health Association) (1996) Standard methods for the Examination of water and wastewater, 19th eds. Public Health Association, Washington, DC.
Baker Thomas, R. and Case Steven, B. (2000) Let GIS be your guide. The Science Teacher 67, no.7, pp.24–26. http://kangis.org/learning/publications/science_teacher/print/tst0010_24.pdf.
BIS. (1991) Indian standards specifications for drinking water. Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi. IS: 10500.
Durbude, D.G., Varadrajan, N. and Purandara, B.K. (2002) Mapping of ground water quality parameters in GIS environment, Proceeding of the International Conference on Hydrology and Water Management during 18–20 December, 2002, pp.568–577.
Frape, S.K., Fritz, P. and Mcnutt, R.H. (1984) Water rock interaction and chemistry of groundwaters from the Canadian Shield. Geochem. Cosmochim. Acta, v.48, pp.1617–1627.
Garrels, R.M. and Christ, C.L. (1965) Solutions, Minerals and Equilibria. Harper and Row, New York, N.Y., 450p.
Kimblin, R.T. (1995) The chemistry and origin of groundwater in Triassic sandstone and Quaternary deposits, Northwest England and some U.K. comparisons. Jour. Hydrology, v.172. pp.293–311.
Longley Paul, A. (2000) The academic success of GIS in geography: Problems and prospects. Jour. Geographical Systems, v.2, no.1, pp.37–42.
Openshaw, S.A. (1991) view on the crisis in geography, or using GIS to put humpty-dumpty back together again. Environment and Planning, v.A23, no.5, pp.621–628.
Pawar, N.J. (1993) Geochemistry of carbonate precipitation from the grounwaters in basaltic aquifers, An equilibrium thermodynamic approach. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.41, pp.119–131.
Raghunath, H.M. (1987) Ground Water. 2nd ed. New Age International (P) Limited, Publishers, New Delhi.
Raju, K.C.B. (1998) Importance of recharging depleted aquifers, State of the art of artificial recharge in India. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.51, pp.429–454.
Saraf, A.K. Gupta, R.P., Jain, R.K. and Srivastava, N.K. (1994) GIS based processing and interpretation of ground water quality data, Proceedings of Regional workshop on Environmental Aspects of Ground water Development, Oct. 17–19, Kurukshetra, India.
Som, S.K. and Bhattacharya, A.K. (1992) Groundwater geochemistry of recent weathering at Panchpatmali bauxite bearing plateau, Koraput district, Orissa. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.40, pp.453–461.
Stumm, W. and Morgan, J.J. (1970) Aquatic Chemistry. Wiley, New York, N.Y. 1022p.
Sui Daniel and Richard Morrill. (2004) Computers and geography: From automated geography to digital earth. In: D. Stanley, L. Brunn Susan, Cutter and J.W. Harrington, Jr. (Eds.), Geography and Technology, Dordrecht, Nl, Kluwer.
Swaine, S. and Schneider, P.J. (1971) The chemistry of surface water in prairie ponds. Am. Chem. Soc. Adv. Chem. Ser., v.106, pp.99–104.
Volgel, A.I. (1968) A Text Book of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis including Elementary Instrumental Analysis. 3rd Edn., ELBS/Longman, 121p.
WHO (1984) Guideline for drinking water quality. Vol.1. Recommendation, WHO, Genero, pp.1–4.
WHO (1996) Guideline for drinking water quality. Vol.2. Health criteria and other supporting information, WHO, Geneva, 973p.
Wicks, C.M. and Herman, J.S. (1994) The effect of a confining unit on the geochemical evolution of groundwater in the Upper Floridan aquifer system. Jour. Hydrology, v.153, pp.139–155.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suresh, M., Gurugnanam, B., Vasudevan, S. et al. Drinking and irrigational feasibility of groundwater, GIS spatial mapping in upper Thirumanimuthar sub-basin, Cauvery River, Tamil Nadu. J Geol Soc India 75, 518–526 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-010-0045-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-010-0045-5