Abstract
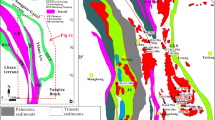
This paper presents zircon U-Pb-Hf isotopic compositions and whole-rock geochemical data for monzogranites and mafic-ultramafic complexes of the Maxingdawannan area in the western end of the east Kunlun orogenic belt, western China. The data are used to determine the ages, petrogenesis, magma sources, and geodynamic setting of the studied rocks. U-Pb zircon dating indicates that monzogranites and gabbros of the complexes were emplaced at 399 and 397 Ma, respectively. The monzogranites are shoshonitic, with high SiO 2, Al2O 3 and total-alkali contents, and low TFeO, MgO, TiO 2 and P2O5 contents. The mafic-ultramafic complexes are characterized by low SiO2 contents. The monzogranites display enrichment in light rare-earth elements (LREE) and large-ion lithophile elements (LILE), depletion in heavy REEs (HREE) and high-field-strength elements (HFSE), and negative Eu anomalies (Eu/Eu*=0.36–0.48). The mafic-ultramafic complexes are also enriched in LREEs and LILEs, and depleted in HREEs and HFSEs, with weak Eu anomalies (Eu/Eu*=0.84–1.16). Zircon εHf(t) values for the monzogranites and mafic-ultramafic complexes range from −6.68 to 1.11 and −1.81 to 6.29, with zircon model ages of 1 812–1 319 Ma (TDM2) and 1 087–769 Ma (TDM1), respectively. Hf isotopic data indicate that primary magmas of the monzogranites are originated from partial melting of ancient lower crust during the Paleo-Mesoproterozoic, with a juvenile-crust component. Primitive magmas of the mafic-ultramafic complexes are likely originated from a depleted-mantle source modified by slab-derived fluids and contaminated by crustal components. Geochemical data and the geological setting indicate that Devonian intrusions in the Maxingdawannan area are related to northward subduction of the Proto-Tethys oceanic lithosphere.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Andersen, T., 2002. Correction of Common Lead in U-Pb Analyses That do not Report 204Pb. Chemical Geology, 192(1/2): 59–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0009-2541(02)00195-x
Andersen, T., Griffin, W. L., Sylvester, A. G., 2007. Sveconorwegian Crustal Underplating in Southwestern Fennoscandia: LAM-ICPMS U-Pb and Lu-Hf Isotope Evidence from Granites and Gneisses in Telemark, Southern Norway. Lithos, 93(3/4): 273–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2006.03.068
Anderson, D. L., 1994. Komatiites and Picrites: Evidence That the ‘Plume’ Source is Depleted. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 128(3/4): 303–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-821x(94)90152-x
Campbell, I. H., 2002. Implications of Nb/U, Th/U and Sm/Nd in Plume Magmas for the Relationship between Continental and Oceanic Crust Formation and the Development of the Depleted Mantle. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 66(9): 1651–1661. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-7037(01)00856-0
Campbell, I. H., Griffiths, R. W., 1993. The Evolution of the Mantle’s Chemical Structure. Lithos, 30(3/4): 389–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/0024-4937(93)90047-g
Cao, S. T., Liu, X. K., Ma, Y. S., et al., 2011. The Discovery of Early Silurian Intrusive Rocks in Qimantage Area and Its Geological Significance. Qinghai Sci. Technol., 5: 26–30. (in Chinese)
Chen, A. X., Zhou, D., Zhang, Q. K., et al., 2018. Age, Geochemistry, and Tectonic Implications of Dulaerqiao Granite, Inner Mongolia. Journal of Earth Science, 29(1): 78–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-017-0817-6
Chen, F., Satir, M., Ji, J., et al., 2002. Nd-Sr-Pb Isotopes of Tengchong Cenozoic Volcanic Rocks from Western Yunnan, China: Evidence for an Enriched-Mantle Source. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 21(1): 39–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1367-9120(02)00007-x
Chen, N. S., He, L., Sun, M., et al., 2002. Precise Timing of the Early Paleozoic Metamorphism and Thrust Deformation in the Eastern Kunlun Orogen. Chinese Science Bulletin, 47(13): 1130–1133. (in Chinese)
Chen, S. J., Li, R. S., Ji, W. H., et al., 2008. Carboniferous Period Lithofacies Character and Tectono-Paleogeography in Kunlun Orogenic Belt. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 3: 221–233. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Chen, X. H., Gehrels, G., Yin, A., et al., 2015. Geochemical and Nd-Sr-Pb-O Isotopic Constrains on Permo–Triassic Magmatism in Eastern Qaidam Basin, Northern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: Implications for the Evolution of the Paleo-Tethys. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 114: 674–692. https://doi.org/10.13039/501100004613
Chen, H. W., Luo, Z. H., Mo, X. X., et al., 2006. SHRIMP Ages of Kayakedengtage Complex in the East Kunlun Mountains and Their Geological Implications. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 25(1): 25–32. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Chung, S. L., Wang, K. L., Crawford, A. J., et al., 2001. High-Mg Potassic Rocks from Taiwan: Implications for the Genesis of Orogenic Potassic Lavas. Lithos, 59(4): 153–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0024-4937(01)00067-6
Corfu, F., Hanchar, J. M., Hoskin, P. W., et al., 2003. Atlas of Zircon Textures. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 53: 469–500.
Cui, M. H., Meng, F. C., Wu, X. K., 2011. Early Ordovician Island Arc of Qimantagh Mountain, Eastern Kunlun: Evidences from Geochemistry, Sm-Nd Isotope and Geochronology of Intermediate-Basic Igneous Rocks. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27: 3365–3379. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Dai, J. G., Wang, C. S., Hourigan, J., et al., 2013. Multi-Stage Tectono-Magmatic Events of the Eastern Kunlun Range, Northern Tibet: Insights from U-Pb Geochronology and (U-Th)/He Thermochronology. Tectonophysics, 599: 97–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2013.04.005
Davidson, J. P., 1996. Deciphering Mantle and Crustal Signatures in Subduction Zone Magmatism: Subduction Top to Bottom. Geophysical Monograph Series, 96: 251–262. https://doi.org/10.1029/GM096p0251
Deng, J., Wang, C. M., Bagas, L., et al., 2015. Cretaceous-Cenozoic Tectonic History of the Jiaojia Fault and Gold Mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: Constraints from Zircon U-Pb, Illite K-Ar, and Apatite Fission Track Thermochronometry. Mineralium Deposita, 50(8): 987–1006. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-015-0584-1
Deng, J., Wang, C. M., Li, G. J., 2012. Style and Process of the Superimposed Mineralization in the Sanjiang Tethys. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28: 1349–1361. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Deng, J., Wang, Q. F., Li, G. J., et al., 2014a. Cenozoic Tectono-Magmatic and Metallogenic Processes in the Sanjiang Region, Southwestern China. Earth-Science Reviews, 138: 268–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.05.015
Deng, J., Wang, Q. F., Li, G. J., et al., 2014b. Tethys Tectonic Evolution and Its Bearing on the Distribution of Important Mineral Deposits in the Sanjiang Region, SW China. Gondwana Research, 26(2): 419–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2013.08.002
Dong, Y. P., He, D. F., Sun, S. S., et al., 2017. Subduction and Accretionary Tectonics of the East Kunlun Orogen, Western Segment of the Central China Orogenic System. Earth-Science Reviews, 186: 231–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.12.006
Eby, G. N., 1992. Chemical Subdivision of the A-Type Granitoids: Petrogenetic and Tectonic Implications. Geology, 20(7): 641–644. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0641:csotat>2.3.co;2
Feng, C. Y., Li, D. S., Wu, Z. S., et al., 2010. Major Types, Time-Space Distribution and Metallogenesis of Polymetallic Deposits in the Qimantage Metallogenic Belt, Eastern Kunlun Area. Northwestern Geology, 43(4): 10–17. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Feng, J. Y., Pei, X. Z., Yu, S. L., et al., 2010. The Discovery of the Mafic-Ultramafic Mélange in Kekesha Area of Dulan County, East Kunlun Region, and Its LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Age. Geology in China, 37: 28–38. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Feng, C. Y., Wang, S., Li, G. C., et al., 2012. Middle to Late Triassic Granitoids in the Qimantagh Area, Qinghai Province, China: Chronology, Geochemistry and Metallogenic Significances. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28: 665–678. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Furman, T. Y., Bryce, J. G., Karson, J., et al., 2004. East African Rift System (EARS) Plume Structure: Insights from Quaternary Mafic Lavas of Turkana, Kenya. Journal of Petrology, 45(5): 1069–1088. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egh004
Gao, X. F., Xiao, P. X., Xie, C. R., et al., 2010. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb Dating and Geological Significance of Bashierxi Granite in the Eastern Kunlun Area, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 29: 1001–1008. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Guo, C. L., Chen, Y. C., Zeng, Z. L., et al., 2012. Petrogenesis of the Xihuashan Granites in Southeastern China: Constraints from Geochemistry and in-situ Analyses of Zircon U-Pb-Hf-O Isotopes. Lithos, 148: 209–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2012.06.014
Hanyu, T., Tatsumi, Y., Nakai, S., et al., 2006. Contribution of Slab Melting and Slab Dehydration to Magmatism in the NE Japan Arc for the Last 25 Myr: Constraints from Geochemistry. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 7(8): 1–29. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005gc001220
Hao, J., Liu, X. H., Sang, H. Q., 2003. Geochemical Characteristics and 40Ar/39Ar Age of the Ayak Adamellite and Its Tectonic Significance in the East Kunlun, Xinjiang. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 19: 517–522. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Hao, N. N., Yuan, W. M., Zhang, A. K., et al., 2015. Evolution Process of the Late Silurian-Late Devonian Tectonic Environment in Qimantagh in the Western Portion of East Kunlun, China: Evidence from the Geochronology and Geochemistry of Granitoids. Journal of Earth System Science, 124(1): 171–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-014-0531-z
Hofmann, A. W., 1988. Chemical Differentiation of the Earth: The Relationship between Mantle, Continental Crust, and Oceanic Crust. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 90(3): 297–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-821x(88)90132-x
Hoskin, P. W. O., Schaltegger, U., 2003. The Composition of Zircon and Igneous and Metamorphic Petrogenesis. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 53(1): 27–62. https://doi.org/10.2113/0530027
Irvine, T. N., Baragar, W. R. A., 1971. A Guide to the Chemical Classification of the Common Volcanic Rocks. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 8(5): 523–548. https://doi.org/10.1139/e71-055
Jiang, C. F., Yang, J. S., Feng, B. G., 1992. Opening-Closing Evolution of the Kunlun Mountains. In: Jiang, C. F., Yang, J. S., Feng, B. G., eds. Opening Closing Tectonics of Kunlun Mountain. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese)
Jiang, Y. H., Jia, R. Y., Liu, Z., et al., 2013. Origin of Middle Triassic High-K Calc-Alkaline Granitoids and Their Potassic Microgranular Enclaves from the Western Kunlun Orogen, Northwest China: A Record of the Closure of Paleo-Tethys. Lithos, 156–159: 13–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2012.10.004
Ju, Y. J., Zhang, X. L., Lai, S. C., et al., 2017. Permian-Triassic Highly-Fractionated I-Type Granites from the Southwestern Qaidam Basin (NW China): Implications for the Evolution of the Paleo-Tethys in the Eastern Kunlun Orogenic Belt. Journal of Earth Science, 28(1): 51–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-017-0745-5
Kong, H. L., Li, J. C., Li, Y. Z., et al., 2017. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb Dating and Its Geological Significance of the Halongxiuma Pyroxene Peridotite in East Kunlun, Qinghai Province. Geological Science and Technology Information, 36: 41–47. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Li, S. J., Sun, F. Y., Gao, Y. W., et al., 2012. The Theoretical Guidance and the Practice of Small Intrusions Forming Large Deposits: The Enlightenment and Significance for Searching Breakthrough of Cu-Ni Sulfide Deposit in Xiarihamu, East Kunlun, Qinghai. Northwestern Geology, 45(4): 185–191. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Li, H. K., Lu, S. N., Xiang, Z. Q., et al., 2006. SHRIMP U-Pb Zircon Age of the Granulite from the Qingshuiquan Area, Central Eastern Kunlun Suture Zone. Earth Science Frontiers, 13: 311–321. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Li, R. S., Ji, W. H., Yang, Y. C., et al., 2008. Kunlun Mountains and Geology of Adjacent Areas. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Li, X. T., Yan, D. P., Qiu, L., 2018. Early Cretaceous Post-Collisional Collapse of the Yidun Terrane: Geochronological and Geochemical Constraints from Calc-Alkaline to Alkaline Basalts in Xiqiu Area, Southwest China. Journal of Earth Science, 29(1): 57–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-018-0825-1
Li, Z. X., Bogdanova, S. V., Collins, A. S., et al., 2008. Assembly, Configuration, and Break-Up History of Rodinia: A Synthesis. Precambrian Research, 160: 179–210.
Liu, B., Ma, C. Q., Jiang, H. A., et al., 2013a. Early Paleozoic Tectonic Transition from Ocean Subduction to Collisional Orogeny in the Eastern Kunlun Region: Evidence from Huxiaoqin Mafic Rocks. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29: 2093–2106. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Liu, B., Ma, C. Q., Guo, P., et al., 2013b. Discovery of the Middle Devonian A-Type Granite from the Eastern Kunlun Orogen and Its Tectonic Implications. Earth Science, 38(5): 947–962. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Liu, B., Ma, C. Q., Zhang, J. Y., et al., 2012. Petrogenesis of Early Devonian Intrusive Rocks in the East Part of Eastern Kunlun Orogen and Implication for Early Paleozoic Orogenic Processes. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28: 1785–1807. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Liu, Y. H., Mo, X. X., Yu, X. H., et al., 2006. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb Dating of the Jingren Granite, Yemaquan Region of the East Kunlun and Its Geological Significance. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22: 2457–2463. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Liu, Y. S., Hu, Z. C., Gao, S., et al., 2008. In-situ Analysis of Major and Trace Elements of Anhydrous Minerals by LA-ICP-MS without Applying an Internal Standard. Chemical Geology, 257(1/2): 34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004
Liu, Z. Q., Pei, X. Z., Li, R. B., et al., 2011. LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Geochronology of the Two Suites of Ophiolites at the Buqingshan Area of the A’nyemaqen Orogennic Belt in the Southern Margin of East Kunlun and Its Tectonic Implication. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85: 185–194. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Lu, J. P., Dai, M. F., Li, J., et al., 2006. Geochemical Characteristics and Its Tectonic Setting of Xiremangya Late Carboniferous Granite in the Qimantagh Mountains, East Kunlun. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 4: 1–8. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Lu, S. N., 2002. Precambrian Geology of the Northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese)
Lu, S. N., 2001. From Rodinia to Gondwanaland Supercontinents-Thinking about Problems of Researching Neoproterozoic Supercontinents. Earth Science Frontiers, 8(4): 441–448. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Ludwig, K. R., 2003. User’s Manual for Isoplot/Ex v30: A Geochronology Toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronological Center Special Publications, 4: 25–31.
Ma, Y. S., Bai, Y. S., He, J., et al., 2010. Discovery of Erchang Granite in Qimantagh Region in Pan-African Period and Its Significance. Journal of Qinghai University, 28: 56–60 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
MacDonald, R., 2001. Plume-Lithosphere Interactions in the Generation of the Basalts of the Kenya Rift, East Africa. Journal of Petrology, 42(5): 877–900. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/42.5.877
McDonough, W. F., Sun, S. S., 1995. The Composition of the Earth. Chemical Geology, 120(3/4): 223–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(94)00140-4
McKenzie, D., 1989. Some Remarks on the Movement of Small Melt Fractions in the Mantle. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 95(1/2): 53–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-821x(89)90167-2
Meng, F. C., Zhang, J. X., Cui, M. H., 2013. Discovery of Early Paleozoic Eclogite from the East Kunlun, Western China and Its Tectonic Significance. Gondwana Research, 23(2): 825–836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2012.06.007
Mo, X. X., Luo, Z. H., Deng, J. F., et al., 2007. Granitoids and Crustal Growth in the East-Kunlun Orogenic Belt. Geological Journal of China Universities, 13: 403–414. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Neal, C. R., 2002. Mantle Sources and the Highly Variable Role of Continental Lithosphere in Basalt Petrogenesis of the Kerguelen Plateau and Broken Ridge LIP: Results from ODP Leg 183. Journal of Petrology, 43(7): 1177–1205. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/43.7.1177
Pan, Y. S., Zhou, W. M., Xu, R. H., et al., 1996. Geological Characteristics and Evolution of the Kunlun Mountains Region during the Early Paleozoic. Science in China: Earth Sciences, 4: 302–307. (in Chinese)
Pearce, J. A., Peate, D. W., 1995. Tectonic Implications of the Composition of Volcanic Arc Magmas. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 23(1): 251–285. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ea.23.050195.001343
Peccerillo, A., Taylor, S. R., 1976. Geochemistry of Eocene Calc-Alkaline Volcanic Rocks from the Kastamonu Area, Northern Turkey. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 58(1): 63–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00384745
Peng, B., Sun, F. Y., Li, B. L., et al., 2016. The Geochemistry and Geochronology of the Xiarihamu II Mafic-Ultramafic Complex, Eastern Kunlun, Qinghai Province, China: Implications for the Genesis of Magmatic Ni-Cu Sulfide Deposits. Ore Geology Reviews, 73: 13–28. https://doi.org/10.13039/501100004613
Regelous, M., Collerson, K. D., Ewart, A., et al., 1997. Trace Element Transport Rates in Subduction Zones: Evidence from Th, Sr and Pb Isotope Data for Tonga-Kermadec Arc Lavas. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 150(3/4): 291–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0012-821x(97)00107-6
Rudnick, R. L., Fountain, D. M., 1995. Nature and Composition of the Continental Crust: A Lower Crustal Perspective. Reviews of Geophysics, 33(3): 267–309. https://doi.org/10.1029/95rg01302
Sang, J. Z., Pei, X. Z., Li, R. B., et al., 2016. LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Dating and Geochemical Characteristics of Gabbro in Qingshuiquan, East Section of East Kunlun, and Its Tectonic Significance. Geological Bulletin of China, 35: 700–710. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Shen, Y. C., Yang, J. Z., Wang, Y. J., et al., 1999. Petrologic Characteristics and Tectonic Setting of Volcanic Rocks Upper Triassic System in the Qimantagh Region in East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Xinjiang. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 79: 50–58. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Song, X. Y., Yi, J. N., Chen, L. M., et al., 2016. The Giant Xiarihamu Ni-Co Sulfide Deposit in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Northern Tibet Plateau, China. Economic Geology, 111(1): 29–55. https://doi.org/10.2113/econgeo.111.1.29
Song, X. Y., Yi, J. N., Chen, L. M., et al., 2016. The giant Xiarihamu Ni-Co Sulfide Deposit in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Northern Tibet Plateau, China. Economic Geology, 111(1): 29–55. https://doi.org/10.2113/econgeo.111.1.29
Sun, F. Y., Li, B. L., Ding, Q. F., et al., 2009. Research on the Key Problems of Ore Prospecting in the Eastern Kunlun Metallogenic Belt. Geological Survey Institute of Jilin University, Changchun (in Chinese)
Sun, S. S., McDonough, W. F., 1989. Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts: Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1): 313–345. https://doi.org/10.1144/gsl.sp.1989.042.01.19
Tan, S. X., Bai, Y. S., Chang, G. H., et al., 2004. Discovery and Geological Significance of Metamorphic and Intrusive Rock (System) of Qimantagh Region in Jinning Epoch. Northwestern Geology, 37: 69–73. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Wang, B. Z., Luo, Z. H., Li, H. Y., et al., 2009. Petrotectonic Assemblages and Temporal-Spatial Framework of the Late Paleozoic-Early Mesozoic Intrusions in the Qimantagh Corridor of the East Kunlun Belt. Geology in China, 36: 769–782. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Wang, B. Z., Luo, Z. H., Pan, T., et al., 2012. Petrotectonic Assemblages and LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Age of Early Paleozoic Volcanic Rocks in Qimantagh Area, Tibetan Plateau. Geological Bulletin of China, 31: 860–874. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Wang, G., Sun, F. Y., Li, B. L., et al., 2014. Petrography, Zircon U-Pb Geochronology and Geochemistry of the Mafic-Ultramafic Intrusion in Xiarihamu Cu-Ni Deposit from East Kunlun, with Implications for Geodynamic Setting. Earth Science Frontiers, 21(6): 381–401. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Wang, G., Sun, F. Y., Li, B. L., et al., 2013. Zircon U-Pb Geochronology and Geochemistry of the Early Devonian Syenogranite in the Xiarihamu Ore District from East Kunlun, with Implications for the Geodynamic Setting. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 37(4): 685–697401. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Wang, G. C., Wei, Q. R., Jia, C. X., et al., 2007. Some Ideas of Precambrian Geology in the East Kunlun, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 26(8): 929–937. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Watson, E. B., 1979. Zircon Saturation in Felsic Liquids: Experimental Results and Applications to Trace Element Geochemistry. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 70(4): 407–419. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00371047
Watson, E. B., Harrison, T. M., 1983. Zircon Saturation Revisited: Temperature and Composition Effects in a Variety of Crustal Magma Types. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 64(2): 295–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-821x(83)90211-x
Whalen, J. B., Currie, K. L., Chappell, B. W., 1987. A-Type Granites: Geochemical Characteristics, Discrimination and Petrogenesis. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 95(4): 407–419. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00402202
Wu, F. Y., Jahn, B. M., Wilde, S., et al., 2000. Phanerozoic Crustal Growth: U-Pb and Sr-Nd Isotopic Evidence from the Granites in Northeastern China. Tectonophysics, 328(1/2): 89–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0040-1951(00)00179-7
Wu, F. Y., Wilde, S. A., Zhang, G. L., et al., 2004. Geochronology and Petrogenesis of the Post-Orogenic Cu-Ni Sulfide-Bearing Mafic-Ultramafic Complexes in Jilin Province, NE China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 23(5): 781–797. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1367-9120(03)00114-7
Wu, F. Y., Yang, Y. H., Xie, L. W., et al., 2006. Hf Isotopic Compositions of the Standard Zircons and Baddeleyites Used in U-Pb Geochronology. Chemical Geology, 234(1/2): 105–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.05.003
Wu, F. Y., Li, X. H., Yang, J. H., et al., 2007. Discussions on the Petrogenesis of Granites. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 23(6): 1217–1238. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Yan, W., Qiu, D. M., Ding, Q. F., et al., 2016. Geochronology, Petrogenesis, Source and Its Structural Significance of Houtougou Monzogranite of Wulonggou Area in Eastern Kunlun Orogen. Journal of Jilin University, 46(2): 443–460. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Yang, J. S., Robinson, P. T., Jiang, C. F., et al., 1996. Ophiolites of the Kunlun Mountains, China and Their Tectonic Implications. Tectonophysics, 258(1–4): 215–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1951(95)00199-9
Yuan, H. L., Gao, S., Liu, X. M., et al., 2004. Accurate U-Pb Age and Trace Element Determinations of Zircon by Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 28(3): 353–370. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-908x.2004.tb00755.x
Zhang, Y. L., Hu, D. G., Shi, Y. R., et al., 2010. SHIRMP Zircon U-Pb Ages and Tectonic Significance of Maoniushan Formation Volcanic Rocks in East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 29: 1614–1618. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhao, X., Fu, L. B., Wei, J. H., et al., 2018. Geochemical Characteristics of An’nage Hornblende Gabbro from East Kunlun Orogenic Belt and Its Constraints on Evolution of Paleo-Tethys Ocean. Earth Science, 43(2): 354–370. (in Chinese with English Abstract). https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2018.020
Zhao, Z. M., Ma, H. D., Wang, B. Z., et al., 2008. The Evidence of Intrusive Rocks about Collision-Orogeny during Early Devonian in Eastern Kunlun Area. Geological Review, 54: 47–56. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhu, C. B., Sun, F. F., Yuan, W. M., et al., 2018. Apatite Fission Track Thermochronology and Tectonic Significance in Yemaquan Area, East Kunlun. Earth Science, 43(6): 2019–2028. (in Chinese with English Abstract). https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2018.598
Zhu, Y. H., Lin, Q. X., Jia, C. X., et al., 2006. SHRIMP Zircon U-Pb Age and Significance of Early Paleozoic Volcanic Rocks in East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Qinghai Province, China. Science China Earth Sciences, 49(1): 88–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-004-5317-8
Zhu, Y. H., Lin, Q. X., Jia, C. X., et al., 2005. Early Paleozoic Volcanic Zircon SHRIMP Age and Its Geological Significance of East Kunlun Orogenic Belt. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 35: 1112–1119. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Acknowledgements
We thank the staff of the Yanduzhongshi Geological Analysis Laboratories Ltd., Institute of Mineral Resources, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, for helping in the analysis. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41272093), and China Geological Survey (No. 12120114080901). The final publication is available at Springer via https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-018-1203-8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, J., Sun, G., Sun, F. et al. Geochronology, Geochemistry, and Hf Isotopic Compositions of Monzogranites and Mafic-Ultramafic Complexes in the Maxingdawannan Area, Eastern Kunlun Orogen, Western China: Implications for Magma Sources, Geodynamic Setting, and Petrogenesis. J. Earth Sci. 30, 335–347 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-018-1203-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-018-1203-8