Abstract
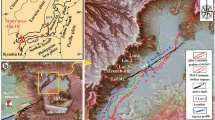
The two eastern segments of the Sertengshan piedmont fault have moved considerably since the Holocene. Several paleoseismic events have occurred along the fault since 30 ka BP. Paleoearthquake studies have been advanced by digging new trenches and combining the results with the findings of previous studies. Comprehensive analyses of the trenches revealed that 6 paleoseismic events have occurred on the Kuoluebulong segment since approximately 30 ka BP within the following successive time periods: 19.01–37.56, 18.73, 15.03–15.86, 10.96, 5.77–6.48, and 2.32 ka BP. The analyses also revealed that 6 paleoseismic events have occurred on the Dashetai segment since approximately 30 ka BP, and the successive occurrence times are 29.07, 19.12–28.23, 13.92–15.22, 9.38–9.83, 6.08–8.36, and 3.59 ka BP. The results indicate that quasi-periodic recurrences occurred along the two segments with an approximate 4 000 a mean recurrence interval. The consistent timing of the 6 events between the two segments indicates that the segments might conform to the cascade rupturing model between the two segments. As recorded by a large number of Chinese historical texts, the latest event on the Kuoluebulong segment is the historical M 8.0 earthquake occurred on November 11, 7 BC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Aitken, M. J., 1998. An Introduction to Optical Dating. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Anonymous, 1986. Han Shu (Volume 27) Wuxingzhi. Shanhai Ancient Literature Press, Shanghai. 507 (in Chinese)
Ban, G., 1962. Han Shu (Volume 27) Wuxingzhi. Zhonghua Book Company, Beijing. 1454–1455 (in Chinese)
Cao, Z. X., 1987. Historical Earthquake References of Beijing Area. Forbidden City Press, Beijing. 1 (in Chinese)
Chen, G. Y., 1986. The List of Natural and Man-Made Disaster of China’s Past Dynasties. Shanghai Bookstore Publishing House, Shanghai. 57 (in Chinese)
Chen, L. C., Ran, Y. K., Chang, Z. P., 2003b. Characteristics of Late Quaternary Faulting and Paleoseismic Events on the East of Delingshan Segment of the Sertengshan Piedmont Fault. Seismology and Geology, 25: 556–565 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Chen, L. C., Ran, Y. K., Yang, X. P., 2003a. Late Quarternary Activity and Segmentation Model of the Sertengshan Piedmong Fault. Earthquake Research in China, 19(3): 255–265 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Deng, Q. D., Zhang, P. Z., 1995. Principles and Methods for Segmentation of Active Faults. In: Institute of Geology, State Seismlolgical Bureau, ed., Research on Recent Crustal Movement (6). Seismological Press, Beijing. 196–207 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Ding, G. Y., Tian, Q. J., Kong, F. C. et al., 1993. Segmentation of Active Fault: Principle, Method and Application. Seismological Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Du, W., Jiang, Z. X., Li, Q., et al., 2016. Sedimentary Characterization of the Upper Paleozoic Coal-Bearing Tight Sand Strata, Daniudi Gas Field, Ordos Basin, China. Journal of Earth Science, 27(5): 823–834. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-016-0705-5
He, Z. T., Ma, B. Q., 2015. Holocene Paleoearthquakes of the Daqingshan Fault Detected from Knickpoint Identification and Alluvial Soil Profile. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 98: 261–271. https://doi.org/10.13039/501100001809
Hong, H., 1802. Jiaqing Reversed ‘Yananfu Records’, Vol. 4. Phoenix Publishing House, Hongkong. 27 (in Chinese)
Institute of Geophysics, SSB, Institute of Historical Geography of Fudan University, 1990. Atlas of Historical Earthquakes in China. China Cartographic Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese)
Jiang, T. X., 1934. The Compendium of Works of Past and Present. Zhonghua Book Company, Beijing (in Chinese)
Jiang, W. L., Wang, X., Tian, T., et al., 2014. Detailed Crustal Structure of the North China and Its Implication for Seismicity. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 81: 53–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.11.021
Li, F., 1960. Imperial Readings of the Taiping Era. Zhonghua Book Company, Beijing (in Chinese)
Liang, M. H., 1992. Qingyangfu Records, Vol. 18. Zhonghua Book Company, Beijing. 529 (in Chinese)
Lu, Y. C., Wang, X. L., Wintle, A. G., 2007. A New OSL Chronology for Dust Accumulation in the last 130 000 yr for the Chinese Loess Plateau. Quaternary Research, 67(1): 152–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yqres.2006.08.003
Mao, F. Y., Zhang, P. Z., 1995. Progressive Constraining Method in Paleoseismic Study and Paleoearthquakes along the Major Active Faults in Northern Xinjinag, In: Institute of Geology, SSB, eds., Research on Acvive Fault (4). Seismological Press, Beijing. 153–164 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Murray, A. S., Wintle, A. G., 2000. Luminescence Dating of Quartz Using an Improved Single-Aliquot Regenerative-Dose Protocol. Radiation Measurements, 32(1): 57–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1350-4487(99)00253-x
Murray, A. S., Wintle, A. G., 2003. The Single Aliquot Regenerative Dose Protocol: Potential for Improvements in Reliability. Radiation Measurements, 37(4/5): 377–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1350-4487(03)00053-2
Nie, Z. S., 2013. Preliminary Investigation on the Historical M 8 Earthquake Occurred in 7 BC at Baotou, Inner Mongolia. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 35: 584–603 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Nulay, P., Chonglakmani, C., Feng, Q. L., 2016. Petrography, Geochemistry and U-Pb Detrital Zircon Dating of the Clastic Phu Khat Formation in the Nakhon Thai Region, Thailand: Implications for Provenance and Geotectonic Setting. Journal of Earth Science, 27(3): 329–349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-016-0667-7
Ran, Y. K., Chen, L. C., Yang, X. P., et al., 2003. Recurrence Characteristics of Late Quaternary Strong Earthquakes on the Major Faults along the Northern Border of Ordos Block. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 46: 189–200 (in Chinese)
Ran, Y. K., Zhang, P. Z., Hu, B., et al., 2002. Paleoseismic Activity on the Hohhot Segment of Daqingshan Piedmont Fault in the Late Quaternary History. Earthquake Research in China, 18: 15–27 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Research Group on ‘Active Fault System around Ordos Massif’, SSB, (1988). Active Fault System around Ordos Massif. Seismological Press, Beijing. 39–76 (in Chinese)
Seismic History Work Committee of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 1956. Chronology of Chinese Earthquakes. Science Press, Bejjing. 1, 181–182, 303, 359, 440 (in Chinese)
Shen, R., 1968. Jinzhou Records 1(2). Taiwan Students Bookstore, Taipei. 323 (in Chinese)
Si, M. G., 1992. Comprehensive Mirror for Aid in Government. Zhonghua Book Company, Beijing. 1063 (in Chinese)
Sun, J. L., 1985. The Probability of Strong Earthquakes in the Northern Margin of the Ordos Block. Northwestern Seismological Journal, (S1): 13–23 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Wheeler, R. L., 1989. Persistent Segment Boundaries on Basin-Range Normal Faults. In: Schwartz, D. P., Sibson, R. H., eds., Proceedings of the of Workshop XL V-Fault Segmentation and Controls of Rupture Initiation and Termination. U.S. Geol. Surv. Open-file Rep., 89(315): 432–444
Wu, W. M., Nie, Z. S., Xu, G. L., 1996. Research on the West Segment of the Serteng Piedmont fault. Research on Active Faults (5). Seismological Press, Beijing. 113–123 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Xie, Y. S., Cai, M. B., Wang, H. A., et al., 1983. Compilation of Historical Materials of Chinese Earthquake (Vol. 1). Science Press, Beijing. 12–13 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Xun, Y., 1996. Annals of the Han Dynasty China. Kangxi Bingzi Year Block-Printed Edition 2. Beijing (in Chinese)
Yang, X. P., Ran, Y. K., Hu, B., et al., 2002. Active Fault and Paleoearthquakes of the Piedmont Fault (Wujumengkou-Dongfeng Village) for Serteng Mountain, Inner Mongolia. Earthquake Research in China, 18: 127–140 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Yang, X. P., Ran, Y. K., Hu, B., et al., 2003. Paleoseismic Activity on Wujiahe Segment of Serteng Piedmont Fault, Inner Mongolia. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 16(1): 67–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11589-003-0008-7
Yuan, Z. L., 2009. The General History of China’s Disaster (Qin and Han Dynasties Volume). Zhengzhou University Press, Zhengzhou. 82 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhang, P. Z., Deng, Q. D., 1995. Principles and Methods for Segmentation of Active Faults. In: State Seismlolgical Bureau, eds., Institute of Geology. Research on Recent Crustal Movement (6). Seismological Press, Beijing. 208–215 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhang, P. Z., Mao, F. Y., Chang, X. D., 1998. The Criteria for Active Fault Segmentation in Seismic Safety Assessment of Major Engineering. Seismology and Geology, 20: 289–301 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhe, Y. L., 2005. Zhengning County Records, Vol. 13. Gansu Culture Press, Lanzhou. 162 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Institute of Crustal Dynamics, China Earthquake Administration (No. ZDJ2016-11), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41602221) and the 1 : 50 000 Geological Mapping of the Sertengshan Piedmont Fault (No. 201408023). The OSL samples were analyzed by Dr. Junxiang Zhao at the Key Laboratory of Crustal Dynamics, Institute of Crustal Dynamics, China Earthquake Administration. We thank the anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments on the manuscript. The final publication is available at Springer via https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-017-0937-z
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Z., Ma, B., Long, J. et al. New Progress in Paleoearthquake Studies of the East Sertengshan Piedmont Fault, Inner Mongolia, China. J. Earth Sci. 29, 441–451 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-017-0937-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-017-0937-z