Abstract
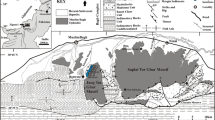
Basaltic pillow lavas near the Kazhaba village in Balochistan are found in the tectonic slivers of the Bagh complex: the melange zone beneath the Muslim Bagh ophiolite complex. These vol-canics are mainly represented by alkali basalts. The petrography and chemistry suggest that these volcanic rocks belong to mildly to strongly alkaline, intra-plate volcanic rock series. Their low Mg# and low Cr, Ni and Co contents suggest that the parent magma of these volcanics was not directly derived from a partially melted mantle source, but resulted fractionation in an upper level magma chamber, en-route to eruption. Their LILE and HFSE, enriched primordial mantle-normalized patterns with marked positive Nb anomalies further confirm their within-plate geochemical signatures and are consistent with an enriched mantle source. Their highly enriched LREE patterns and high (La/Yb)N and (Ce/Yb)N ratios suggest a partially melted garnet-lherzolite parent magma source. The Zr versus Zr/Y studies suggest that these volcanics were derived from about 15% partially melted enriched mantle source. It is suggested that these Late Cretaceous intra-plate volcanics may represent the mantle plume activity of the Reunion hotspot, and were erupted during the passage of Ceno-Tethys Ocean floor prior to the passage of Indian Plate over it.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Baker, B. H., 1987. Outline of the Petrology of the Kenya Rift Alkaline Province. In: Fitten, J. G. and Upton, B. G. J. eds., Alkaline Igneous Rocks, Balckwell, Oxford. 30(1): 293–312. doi: 10.1144/gsl.sp.1987.030.01.14
Backmann, J., Duncan, R. A., 1989. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, 115 Initial Reports. 1085
Basaltic Volcanism Study Project 1981. Basaltic Volcanism on the Terrestrial Planets. New York: Pergamon Press. 1286.
Boulin, J., 1990. Neocimmerian Events in Central and Western Afghanistan. Tectonophysics, 175(4): 285–315. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(90)90177-a
Brookfield, M. E., 1993. The Himalayan Passive Margin from Precambrian to Cretaceous Times. Sedimentary Geology, 84(1–4): 1–35. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(93)90042-4
Caroff, M., Maury, R. C., Guille, G., Cotten, J., 1997. Partial Melting below Tubuai (Austral Islands, French Polynesia). Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 127(4): 369–382.doi: 10.1007/s004100050286
Chen, J. J., Fu, L. B., Wei, J. H., et al., 2016. Geochemical Characteristics of Late Ordovician Granodiorite in Gouli Area, Eastern Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Qinghai Province: Implications on the Evolution of Proto-Tethys Ocean. Earth Science, 41(11): 1863–1882
Deitz R. S., Holden J. C., 1970, The Breakup of Pangaea. Scientific American 223: 30–41
Duncan, R. A., Pyle, D. G., 1988. Rapid Eruption of Deccan Flood Basalt at the Cretaceous/Tertary Boundary. Nature, 333(6176): 841–843. doi: 10.1038/333841a0
Dewey, J. F., Bird, J. M., 1970. Mountain Belts and the New Global Tectonics. Journal of Geophysical Research, 75(14): 2625–2647.doi: 10.1029/jb075i014p02625
Fisk, M. R., Upton, B. G. J. Ford, C.E., 1988. Geochemical and Experimental Study of the Genesis of Magmas of Reunion Island, Indian Ocean. Journal of Geophysical Research, 93(B5): 4933–4950. doi: 10.1029/jb093ib05p04933
Floyd, P. A. and Winchester, J. A., 1975. Magma Types and Tectonic Setting Discrimination Using Immobile Elements. Earth and Planetary Science Letter, 27(2): 211–218.doi: 10.1016/0012-821x(75)90031-x
Floyd, P. A., 1991. Oceanic Islands and Seamounts. In: Foyd, P. A. ed., Blackie, Glasgow and London. 455
Frey, F. A., Green, D. H. Roy, S. D., 1978. Integrated Model for Basalt Petrogenesis: A Study of Quartz Tholeiites to Olivine Melilite from Southeastern Australia, Utilizing Geochemical and Experimental Petrological Data. Journal of Petrolology, 19(3): 463–513. doi: 10.1093/petrology/19.3.463
Fyfe, W. S., 1976. Hydrosphere and Continental Crust. Geoscience, 3(2): 255–268
Gansser, A., 1979. Reconnaissance Visit to the Ophiolites in Baluchistan. In: Farah, A., DeJong, K. A. eds., Geodynamics of Pakistan. 193–213
Gill, J. B., 1981, Orogenic Andesites and Plate Tectonics: Springer, Berlin, 189.
Govindaraju, K., 1989. Working Group on Analytical Standards of Minerals, Ores and Rocks. Geostandards Newsletter, Special Issue, France, 114
Green, D. H., 1973. Experimental Studies on a Modal Upper Mantle Composition at High Pressure under Water Saturated and Water Undersaturated Condtions. Canadian Mineralogist, 19(1): 37–53
Hanson, G. N. and Langmuir, C. H., 1978. Modelling of Major Elements in Mantle-Melts Systems Using Trace Element Approaches. Geochimca et Cosmochem Acta, 42(6): 725–742. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(78)90090-x
Humphris, S. E., Thompson, G., Schilling, J. G. et al., 1985, Petrological and Geochemical Variation along the Mid Atlantic Ridge between 46º S and 32º S: Influence of Tristen da Cunha Mantle Plume. Geochem. Acta, 49(6): 1445–1464. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(85)90294-7
Khan, W., McCormick, G. R. Reagen, M. K., 1999, Parh Group Basalts of Northeastern Balochistan, Pakistan: Precursors to the Deccan Traps. Special Paper–Geological Society of America, 2(9): 1916–1923
Kimura, K., Mengal, J. M., Siddiqui, M. R.H., et al., 1993. Geology of the Muslim Bagh Ophiolite and Associated Bagh Complex in Northwestern Balochistan, Pakistan. Proceedings of Geoscience Colloquium. 5: 36
Kojima, S., Naka, T., Kimura, K., et al., 1993. Mesozoic Radiolarians from the Bagh Complex in the Muslim Bagh Area Pakistan: Their Significance in Reconstructing the Geologic History of Ophiolites along the Neo Tethys Suture Zone. Bulletin Geological Survey of Japan, 45(2): 63–97
Le Bas, M. J., Le Maitre, R. W., Streckeisen, A. and Zanettin, B., 1986. A Chemical Classification of Volcanic Rocks Based on the Total Alkali Silica Diagram. Journal of Petrology, 27(3): 745–750.doi: 10.1093/petrology/27.3.745
Le Maitre, R. W., Bateman, P., Dudek, A., et al., 1989. A Classification of Igneous Rocks and Glossary of Terms. In: Le Maitre, R. W., ed., Recommendations of the International Union of Geological Sciences Subcommissionon the Systematics of Igneous Rocks: Blackwell Sciety. Publication. 193
Luhr, J. F., Aranda–Gómez, J. J., Housh, T.B., 1995. San Quintín Volcanic Field, Baja California Norte, México: Geology, Petrology, and Geochemistry. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 100(B6): 10353–10380. doi: 10.1029/95jb00037
California Norte, México. Geology, Petrology and Geochemistry. Journal of Geophysical Research, 100(B7): 10353–10380
McCormick, G. R., 1985. Preliminary Study of the Volcanic Rocks of the South Tethyan, Suture in Baluchistan, Pakistan. Acta Mineralogica, 1: 1–29
McCormick, G. R., 1991. Origin of Volcanics in the Tethyan Zone of Pakistan. In: Peters, T. J., Niwlas, A., Coleman, R. G., et al., eds., Ophiolite Genesis and Evolution of the Oceanic Lithosphere. Ministry of Petroleum and Minerals Sultanate of Oman, Muscat 715–722
Mengal, J. M. Siddiqui, R. H., 1993. Geological Map of Bagh Quadrangle, Killa Safullah District, Balochistan, Pakistan. Geol, Survey of Pakistan Map Series.
Melson, W. T., Thompson, G. Van Andel, T. H., 1968. Volcanism and Metamorphism in the Mid-Atlantic Ridge 22° N Latitude. Journal of Geophysical Research, 73(18): 5925–5941. doi: 10.1029/jb073i018p05925
Meschede, M., 1986. A Method of Discriminating between Different Types of Mid–Oceanic Ridge Basalts and Continental Tholeiites with the Nb-Zr-Y Diagram. Chemical Geology, 56(3): 207–218.doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(86)90004-5
Metcalfe, I., 1995. Gondwana Dispersion and Asian Accretion. Journal of Geology, B: 223–266.doi: 10.1016/s0899-5362(99)90074-x
Naka, T., Kimura, K., Mengal J. M., Siddiqui, R. H., Kojima, S., Sawada, Y., 1996, Mesozoic Sedimentary–Igneous Complex, Bagh Complex in Muslim Bagh Area, Pakistan. Proceedings of Geoscience Colloquium. 16: 47–94
Otsuki, K., Anwar, M., Mengal, J. M., et al., 1989. Breakup of Gondwanaland and Emplacement of Ophiolite Complex in Muslim Bagh Area Balochistan, Pakistan. Hiroshima University Special. Publication. 33–57
Pearce, J. A. Cann, J. R., 1973. Tectonic Setting of Basic Volcanic Rocks Determined Using Trace Elements Analysis. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 19(2): 290–300. doi: 10.1016/0012-821x(73)90129-5
Pearce, J. A., Norry, M., 1979. Petrogenetic Implications of Ti, Zr, Y and Nb Variation in Volcanic Rocks. Contribution to Mineralogy and Petrology, 69(1): 33–47. doi: 10.1007/bf00375192
Pearce, J. A., 1982. Trace Elements Characteristics of Lavas from Destructive Plate Boundaries. In: Throp, R. S., ed., Andesites: Orogenic Andesites and Related Rocks. John Wiley and Sons, New York. 525–548
Pearce, J. A., 1983. The Role of Subcontinental Lithosphere in the Magma Genesis at Destructive Plate Margin, In: Hawkesworth, C. J., Norry, M. J. eds., Continental Basalts and Mantle Xenoliths. Natwich Shiva, 230–249
Perfit, M. R., Gust, D. A., Bence, A. E., et al., 1980. Chemical Characteristics of Island Arc Basalts: Implications for Mantle Sources. Chemical Geology, 30(3): 227–256. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(80)90107-2
Price, R, C., Johnson, R. W., Gray, C. M., et al., 1985. Geochemistry of Phonolites and Trachytes from the Summit Region of Mt. Kenya. Contribution to Mineralogy and Petrology, 89(4): 394–409. doi: 10.1007/bf00381560
Saunders, A. D. Tarney, J., 1991. Back-Arc Basins. In: Floyd. P.A. ed., Oceanic Basalts, Blackie, London. 219–263
Schawarzer, R. R. Roger, J. J. W., 1974. A Worldwide Comparison of Alkaline-Olivine Basalt and Their Differentiation Trends. Earth and Planetary Science Letter, 23(3): 286–296. doi: 10.1016/0012-821x(74)90117-4
Sawada, Y., Nagao, K., Siddiqui, R.H. et al., 1995. K-Ar Ages of Mesozoic Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks from the Muslim Bagh Area, Pakistan. Proc.Geosc. Coll. 12: 73–90
Sengör, A. M. C., Altinar, D., Cin, A., et al., 1988. Origin and Assembly of Tethyside Orogenic Collage at the Expence of Gondwanaland, 37(1): 119–181. doi: 10.1144/gsl.sp.1988.037.01.09
Shervais, J. W., 1982. Ti Versus V Plots and the Petogenesis of Modern and Ophiolitic Lavas. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 59(1): 101–108. doi: 10.1016/0012-821x(82)90120-0
Siddiqui, R. H., Brohi, I. A. Haidar, N. 2010. Geochemistry, Petrogenesis and Crustal Contamination of Hotspot Related Volcanism on the North Western Margin of Indian Plate. Sindh University Research Journal, 42(2): 15–34
Siddiqui, R.H., Mengal, J. M., Hoshino, K., et al., 2011, Back-Arc Basin Signatures from the Sheeted Dykes of Muslim Bagh Ophiolite Complex, Balochistan, Pakistan. Sindh University Research Journal, 43(1): 51–62
Siddiqui, R. H., Jan, M. Q., Kakar M. I., et al., 2017. Petrogenesis of Middle Triassic Volcaniclastic Rocks from Balochistan, Pakistan: Implications for the Break-Up of Gondwanaland. Journal of Earth Science, 28(2): 218–228. doi: 10.1007/s12583-016-0911-x
Sinha, A. K. Mishra, M., 1992. Plume Activity and Seamounts in Neo-Tethys: Evidence Supported by Geochemical and Geochronological Data. Jour. Hima. Geol. 3(1): 91–96
Stocklin, J., 1989. Tethys Evolution in the Afghanistan-Pamir-Pakistan Region. In: Sengör, ed., Tectonic Evolution of Tethys Region. Kluwer Academic Publishers, 241–264
Sun, S. S. McDonough, W. F., 1989. Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Ocean Basalt, Implication for Mantle Composition and Processes. In: Saunders, A. D., Tarny, M. J., eds., Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geol. Soc. London, Spec. Pub., 42: 313–345. doi: 10.1144/gsl.sp.1989.042.01.19
Tatsumi, Y. Eggins, S., 1995. Subduction Zone Magmatism. Blackwell Science, Oxford, England. 211
Veevers, J. J., 1995. Emergent Long Lived Gondwanaland Vs, Submergent, Short Lived Laurasia: Supercontinentaland Pan-African Heat Imparts Long-Term Buoyancy by Mafic under Plating. Geology, 23(12): 1133–1138. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<1131:ellgvs>2.3.co;2
Weaver, B. L., Tarney, J., Windley, B., 1981. Geochemistry and Petrogenesis of the Fiskenaesset Anorthosite Complex Southern West Greenland: Nature of the Parent Magma. Geochem. Cosmochem. Acta, 45(5): 711–725. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(81)90044-2
Weaver, B.L., Wood, D. A., Tarney, J. et al., 1987. Geochemistry of Ocean Island Basalt from the South Atlantic, Ascension, Bouvet, St. Helena, Gongh and Tristen da Cunha. Geol. Soc. London, Spec. Pub., 568: 253–268. doi: 10.1144/gsl.sp.1987.030.01.11
Whitemarsh, R. B., 1974. Summary of General Features of Arabian Sea and Red Sea Cenozoic History. Based on Leg 23 Cores. Init. Rep. DSDP, 23: 115–1123
Wilkinson, J. F. G., Le Maitre, R. W., 1987. Upper Mantle Amphiboles and Micas and TiO2, K2O and P2O5 Abundances and 100×Mg/(Mg+Fe+2) Ratios of Common Basalts and Undeleted Mantle Compositions. Journal of Petrology, 28(1): 37–73. doi: 10.1093/petrology/28.1.37
Wilson, M., 1989. Igneous Petrogenesis. Unwin and Hyman, London, 466.
Winchester, J. A., Floyd, P. A., 1977. Geochemical Discrimination of Different Magma Series and Their Differentiation Products Using Immobile Elements. Chemical Geology, 20(C): 325–343. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(77)90057-2
Zaman, H., Torii, M., 1999. Paleomagnetic Study of Cretaceous Red Beds from the Eastern Hindukush Ranges, Northern Pakistan, Paleoarc Construction of the Kohistan-Karakoram Composite Unit before the India-Asia Collision. Geophysical Journal International, 136(3): 719–738. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246x.1999.00757.x
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to S. Hassan Gauhar, Former Director General, Geological Survey of Pakistan, for the arrangement of funds for field and laboratory research. The final publication is available at Springer via http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12583-017-0758-0
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Rehanul Haq Siddiqui: http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7710-0999
Changqian Ma: http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1778-0547
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siddiqui, R.H., Ma, C. Petrogenesis of Late Cretaceous Volcanism in Kazhaba Area and its relationship with mantle plume activity of Reunion hotspot. J. Earth Sci. 28, 229–240 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-017-0758-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-017-0758-0