Abstract
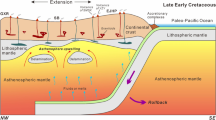
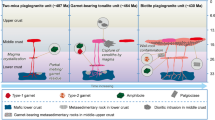
The extensive Eshan granites of Yunnan are made up of three intrusive units distinguished by their field contact relations; in descending order of age they are the Pojiao Unit, the Lüzicun Unit and the Mokela Unit. The Pojiao Unit and Lüzicun Unit contain petrographically and geochemically similar rocks but contact relationships show that the latter is younger. The Mokela Unit mainly consists of dykes intruding the other two and has petrographic and geochemical differences. Zircon U/Pb dating and zircon crystallization temperature measurements confirm the sequence of intrusions. Major and trace element analyses suggest that the magmas of the Pojiao Unit granites derived by partial melting of a clay-poor source from the upper crust; the magmas of the Lüzicun Unit granites derived by partial melting of upper crust with a small proportion of middle crust accompanied by crystallization of albite which triggered strength reduction. Both magmas mixed and underwent with crustal contamination, assimilation and fractional crystallization. The magmas of the Mokela Unit derived from residual melts and assimilation of argillaceous rocks. A time sequence of melting, intrusion and deformation events is derived from these results and compared with other published tectonic models for the evolution of the SW margin of the Yangtze Plate. Magmatism was initiated by exhumation of upper continental crust during which strongly peraluminous porphyritic biotite monzogranite granites were produced at ca. 854–852 Ma, and the genesis of two-mica granite reflected a later batch of exhumed melts with crustal contamination, assimilation and fractional crystallization at ca. 842 Ma. Finally biotite alkali-feldspar granite and tourmaline granite magmas experienced strong fractional crystallization, emplaced in the cooling stage at ca. 823 Ma, indicating the end of exhumation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Boehnke, P., Watson, E. B., Trail, D., et al., 2013. Zircon Saturation Re-Revisited. Chemical Geology, 351: 324–334. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.05.028
Chen, Y. X., Song, S. G., Niu, Y. L., et al., 2014. Melting of Continental Crust during Subduction Initiation: A Case Study from the Chaidanuo Peraluminous Granite in the North Qilian Suture Zone. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 132: 311–336. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2014.02.011
Deng, H., Kusky, T. M., Wang, L., et al., 2012. Discovery of a Sheeted Dike Complex in the Northern Yangtze Craton and its Implications for Craton Evolution. Journal of Earth Science, 23(5): 676–695. doi:10.1007/s12583-012-0287-9
Du, L. L., Guo, J. H., Geng, Y. S., et al., 2013. Age and Tectonic Setting of the Yanbian Group in the Southwestern Yangtze Block: Constraints from Clastic Sedimentary Rocks. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(2): 641–672 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Johannes, W., Holtz, F., 1996. Petrogenesis and Experimental Petrology of Granitic Rocks. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg. 335
Labrousse, L., Prouteau, G., Ganzhorn, A. C., 2011. Continental Exhumation Triggered by Partial Melting at Ultrahigh Pressure. Geology, 39(12): 1171–1174. doi:10.1130/g32316.1
Li, X. H., Li, W. X., He, B., 2012. Building of the South China Block and Its Relevance to Assembly and Breakup of Rodinia Supercontinent: Observations, Interpretations and Tests. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 31(6): 543–559. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2012.06.002
Li, X. H., Li, Z. X., Ge, W. C., et al., 2003. Neoproterozoic Granitoids in South China: Crustal Melting above a Mantle Plume at ca. 825 Ma?. Precambrian Research, 122(1–4): 45–83. doi:10.1016/S0301-9268(02)00207-3
Li, Z. X., Bogdanova, S. V., Collins, A. S., 2008. Assembly, Configuration, and Break-Up History of Rodinia: A Synthesis Original Research Article. Precambrian Research, 160(1/2): 179–210. doi:10.1016/j.precamres.2007.04.021
Ling, W. L., Gao, S., Zhang, B. R., et al., 2003. Neoproterozoic Tectonic Evolution of the Northwestern Yangtze Craton, South China: Implications for Amalgamation and Break-Up of the Rodinia Supercontinent. Precambrian Research, 122(1/2/3/4): 111–140. doi:10.1016/s0301-9268(02)00222-x
Liu, S. B., 2016. Zircon U-Pb Geochronology, Geochemistry and TectonicSetting of the Eshan Granite with Mo Mineralization inYunnan Province: [Dissertation]. China University of Geosciences, Beijing (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Ma, G. G., 1991. Isotopic Age of the Eshan Granite in Yunnan Province and Its Geological Significance. Bull. Yichang Inst. Geol. Miner. Res., 16: 121–129 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Patiño Douce, A. E., Harris, N., 1998. Experimental Constraints on Himalayan Anatexis. Journal of Petrology, 39(4): 689–710. doi:10.1093/petroj/39.4.689
Petö, P., 1976. An Experimental Investigation of Melting Relations Involving Muscovite and Paragonite in The Silica-Saturated Portion of The System K2O-Na2O-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O To 15 kb Total Pressure. In: Progress in Experimental Petrology. NERC, London. 41–45
Rudnick, R. L., Gao, S., 2014. Composition of the Continental Crust. In: Holland, H., Turekian, K., eds., Treatise on Geochemistry (Second Edition). Elsevier, [S.l.]. 1–64
Schmidt, M. W., Poli, S., 2014. Devolatilization during Subduction. Treatise Geochem., 4: 669–701
Shen, W. Z., Ling, H. F., Xu, S. J., et al., 2000. Geochemical Characteristics and Genesis of Some Neoproterozoic Granitoids in the Northern Part of the Western Margin of the Yangtze Block. Geological Review, 46(5): 512–519 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Song, S. G., Wang, M. J., Wang, C., Niu, Y. L. 2015. Magmatism during Continental Collision, Subduction, Exhumation and Mountain Collapse in Collisional Orogenic Belts and Continental Net Growth: A Perspective. Science China: Earth Sciences, 58: 1284–1304. doi:10.1007/s11430-015-5102-x
Stevens, G., Clemens, J. D., Droop, G. T. R., 1997. Melt Production during Granulite-Facies Anatexis: Experimental Data from “Primitive” Metasedimentary Protoliths. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 128(4): 352–370. doi:10.1007/s004100050314
Sun, S. S., McDonough, W. F., 1989. Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts: Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1): 313–345. doi:10.1144/gsl.sp.1989.042.01.19
Sylvester, P. J., 1998. Post-Collisional Strongly Peraluminous Granites. Lithos, 45(1/2/3/4): 29–44. doi:10.1016/s0024-4937(98)00024-3
Wang, J., 2000. Neoproterozoic Rifting History of South China: Significance to Rodinia Breakup: [Dissertation]. Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Wang, X., Erdtmann, B. D., Mao, X., 1996. 30th IGC Field Trip Guide T106/T340: Geology of the Yangtze Gorges Area. Geology Publishing House, Beijing. 73
Watson, E. B., Harrison, T. M., 1983. Zircon Saturation Revisited: Temperature and Composition Effects in a Variety of Crustal Magma Types. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 64(2): 295–304. doi:10.1016/0012-821x(83)90211-x
Weber, M. B. I., Tarney, J., Kempton, P. D., et al., 2002. Crustal Make-Up of the Northern Andes: Evidence Based on Deep Crustal Xenolith Suites, Mercaderes, SW Colombia. Tectonophysics, 345(1/2/3/4): 49–82. doi:10.1016/s0040-1951(01)00206-2
Wei, C. J., Zhu, W. P., 2016. Granulite Facies Metamorphism and Petrogenesis of Granite (I): Metamorphic Phase Equilibria for HT-UHT Metapelites/Greywackes. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(6): 1611–1624 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Wu, F. Y., Liu, Z. C., Liu, X. C., et al., 2015. Himalayan Leucogranite: Petrogenesis and Implications to Orogenesis and Plateau Uplift. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(1): 1–36 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Xue, X. H., Cai, Z. B., Xiong, J. Y., 1986. The Main Characteristics and Age Determination of E-Shan Granite in Yunnan Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2(1): 50–58 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhang, C. H., Gao, L. Z., Wu, Z. J., 2007. Tuff Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb Age of the Kunyang Group in Central Yunnan: Evidence of Greenwill Orogenic in Southern China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52(7): 818–824 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhao, Z. F., Zheng, Y. F., Dai, L. Q., 2013. Origin of Residual Zircon and the Nature of Magma Source for Postcollisional Granite in Continental Collision Zone. Chinese Science Bulletin, 58(23): 2285–2289. doi:10.1360/972013-636
Zheng, Y. F., Yang, J. H., Song, S. G., et al., 2013a. Progress in the Study of Chemical Geodynamics. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 32(1): 1–24. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2013.01.001
Zheng, Y. F., Zhang, L.F., Liu, L., 2013b. Progress in the Study of Continental Deep Subduction and Ultrahigh Pressure Metamorphism. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 32(2): 135–158. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2013.02.001.
Zheng, Y. F., Zhao, Z. F., Chen, Y. X., 2013c. Continental Subduction Channel Processes: Plate Interface Interaction during Continental Collision. Chinese Science Bulletin, 58(35): 4371–4377. doi:10.1007/s11434-013-6066-x
Zheng, Y. F., Zhang, S. B., Zhao, Z. F., et al., 2007. Contrasting Zircon Hf and O Isotopes in the Two Episodes of Neoproterozoic Granitoids in South China: Implications for Growth and Reworking of Continental Crust. Lithos, 96(1/2): 127–150. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2006.10.003
Zhou, J. C., Wang, X. L., Qiu, J. S., 2005. The Characters of Magmatism in the Western Section of the Jiangnan Orogenic Belt. Geological Journal of China Universities, 11(4): 527–533. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2005.04.008 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhou, M. F., Yan, D. P., Kennedy, A. K., et al., 2002. SHRIMP U-Pb Zircon Geochronological and Geochemical Evidence for Neoproterozoic Arc-Magmatism along the Western Margin of the Yangtze Block, South China. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 196(1/2): 51–67. doi:10.1016/s0012-821x(01)00595-7
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Yunnan Nonferrous Geological Bureau 313 Team. Besides, we acknowledge the facility support from the State Key Laboratory of Continental Dynamics, Northwest University as well as helpful comments by reviewers and editors. Roger Mason has revised the final version. The final publication is available at Springer via https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-017-0747-3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, J., Zhang, S., Zhang, G. et al. Geochemistry and Tectonic Setting of the Eshan Granites in the Southwestern Margin of the Yangtze Plate, Yunnan. J. Earth Sci. 29, 130–143 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-017-0747-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-017-0747-3