Abstract
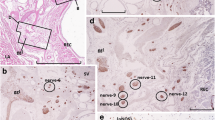
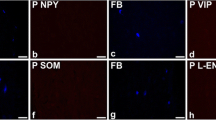
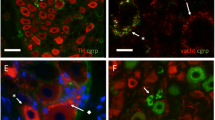
Chronic testicular pain remains an important challenge for urologists. Investigation of the innervation of male gonads thus becomes essential for deepening our understanding of their regulatory roles in male reproductive physiology and pathophysiology. Studies of testicular innervation are mainly limited to the intratesticular peptidergic nerves of the testis by immunohistochemical and acetylcholinesterase histochemical investigations in some animals. Little is known about the detailed, overall distribution in general experimental animal testis. In this study, the distribution of nerves supplying the testis, epididymis and accessory sex glands of Suncus murinus was investigated by whole mount immunohistochemistry staining using a neurofilament protein antibody. Testicular nerves arose through three routes: nerves deriving from the mesenteric and renal plexuses accompanied the testicular artery, entering into the testicular hilum through the superior ligament of the testis. The nerves originating from the hypogastric plexus then ran along the internal iliac artery, deferential artery, and passed through the mesoductus deferens or mesoepididymis, innervating the cauda and corpus of the epididymis, the vas deferens and the inferior pole of the testis. The third route arose from the pelvic plexus, distributed in the seminal vesicle and the prostate. The density of nerve fibers was higher in the cauda epididymidis than in the testis, and more abundant in the vas deferens. The different origins and distribution densities of testicular nerves in S. murinus may serve different neuronal regulatory functions, and, therefore, S. murinus may be an important model animal for understanding the different characteristics of testicular pain.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell C, McLean JR (1973) The autonomic innervation of the rat testicular capsule. J Reprod Fertil 32:253–258
Burnett AL, Ricker DD, Chamness SL, Maguire MP, Crone JK, Bredt DS, Snyder SH, Chang TS (1995) Localization of nitric oxide synthase in the reproductive organs of the male rat. Biol Reprod 52:1–7
Campbell IW, Ewing DJ, Clarke BF, Duncan LJ (1974) Testicular pain sensation in diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Br Med J 2:638–639
Chiocchio SR, Suburo AM, Vladucic E, Zhu BC, Charreau E, Décima EE, Tramezzani JH (1999) Differential effects of superior and inferior spermatic nerves on testosterone secretion and spermatic blood flow in cats. Endocrinology 140:1036–1043
Choa RG, Swami KS (1992) Testicular denervation. A new surgical procedure for intractable testicular pain. Br J Urol 70:417–419
Coujard R (1954) Contribution to the study of the sympathetic nervous pathways of the testis. Arch Anat Microsc Morphol Exp 43:321–364
de Girolamo P, Costagliola C, Lucini C, Gargiulo G, Castaldo L (2003) The autonomous innervation of the buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) testis. An immunohistochemical study. Eur J Histochem 47:159–164
Ducic I, Dellon AL (2004) Testicular pain after inguinal hernia repair: an approach to resection of the genital branch of genitofemoral nerve. J Am Coll Surg 198:181–184
Dun NJ, Dun SL, Huang RL, Dun EC, Lai CC, Wong PY, Förstermann U (1996) Distribution of origin of nitric oxide synthase-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the rat epididymis. Brain Res 738:292–300
Fowler R, Stephens FD (1959) The role of testicular vascular anatomy in the salvage of high undescended testes. Aust N Z J Surg 29:92
Gerendai I, Banczerowski P, Halász B (2005) Functional significance of the innervation of the gonads. Endocrine 28:309–318
Gong YG, Feng MM, Hu XN, Wang YQ, Gu M, Zhang W, Ge RS (2009) Peptidergic not monoaminergic fibers profusely innervate the young adult human testis. J Anat 214:330–338
Heidenreich A, Olbert P, Engelmann UH (2002) Management of chronic testalgia by microsurgical testicular denervation. Eur Urol 41:392–397
Ishigooka M, Zermann DH, Doggweiler R, Schmidt RA (2000) Similarity of distributions of spinal c-Fos and plasma extravasation after acute chemical irritation of the bladder and the prostate. J Urol 164:1751–1756
Kuntz A, Morris RE (1946) Components and distribution of the spermatic nerves and the nerves of the vas deferens. J Comp Neurol 85:33–44
Liu WC, Chen TH, Shyu JF, Chen CH, Shih C, Wang JJ, Kung SP, Lui WY, Wu CW, Liu JC (2002) Applied anatomy of the genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve in open inguinal herniorrhaphy. Eur J Surg 168:145–149
Matsushima S, Sakai Y, Hira Y (1999) Peptidergic peripheral nervous systems in the mammalian pineal gland. Microsc Res Tech 46:265–280
Mitchell GAG (1935) The innervation of the kidney, ureter, testicle and epididymis. J Anat 70:10–32
Mitchell GAG (1953) Anatomy of the autonomic nervous system: Chapter XVII, The abdominal part of the sympathetic system, 1st edn. Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp 293–296
Noordhuizen-Stassen EN, Wensing CJ (1983) The effect of transection of the main vascular and nervous supply of the testis on the development of spermatogenic epithelium in the pig. J Pediatr Surg 18:601–606
Oda S, Kondo K (1977) Usefulness of wild insectivores as laboratory animals. Exp Anim 26:273–280
Oda S, Koyasu K, Shrestha K (1992) Breeding of the house musk shrew, Suncus murinus, originating from a wild population in Kathmandu, Nepal. Ann Res Inst Environ Med 43:239–240
Oliveira RG, Camara C, Alves Jde M, Coelho RF, Lucon AM, Srougi M (2009) Microsurgical testicular denervation for the treatment of chronic testicular pain initial results. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 64:393–396
Qin C, Foreman RD (2004) Viscerovisceral convergence of urinary bladder and colorectal inputs to lumbosacral spinal neurons in rats. NeuroReport 15:467–471
Rauchenwald M, Steers WD, Desjardins C (1995) Efferent innervation of the rat testis. Biol Reprod 52:1136–1143
Ren K, Kinoshita M, Dai Y, Wang H, Yi K, Itoh M, Yi SQ (2016) A new model for localized pancreatitis, ventral pancreatic duct ligation in the adult house musk shrew, Suncus murinus. Acad J Biotechnol 4(2):055–061. https://doi.org/10.15413/ajb.2015.0242
Ren K, Dai Y, Yi K, Kinoshita M, Itoh M, Sakata I, Skai T, Yi SQ (2017) Using a whole-mount immunohistochemical method to study the innervation of the biliary tract in Suncus murinus. J Vis Exp. https://doi.org/10.3791/55483
Saleh AM, Alameldin MA, Abdelmoniem ME, Hassouna EM, Wrobel KH (2002) Immunohistochemical investigations of the autonomous nerve distribution in the testis of the camel (Camelus dromedarius). Ann Anat 184:209–220
Setchell BP, Maddock S, Brook DE (1994) Anatomy, vasculature, innervation, and fluids of the male reproductive tract. In: Knobil E, Neill D (eds) The physiology of reproduction, vol 1, 2nd edn. Raven, New York, pp 1063–1175
Soyer T, Tosun A, Somuncu S, Aydin G, Akman H, Inal E, Kanmaz T, Cakmak M (2007) Electrophysiological evaluation of cremasteric reflex in experimental testicular torsion. Eur J Pediatr Surg 17:261–265
Suburo AM, Chiocchio SR, Cantó Soler MV, Nieponice A, Tramezzani JH (2002) Peptidergic innervation of blood vessels and interstitial cells in the testis of the cat. J Androl 23:121–134
Tamura R, Mizumura K, Sato J, Kitoh J, Kumazawa T (1996) Segmental distribution of afferent neurons innervating the canine testis. J Auton Nerv Syst 58:101–107
Tilki D, Kilic E, Tauber R, Pfeiffer D, Stief CG, Tauber R, Ergün S (2007) The complex structure of the smooth muscle layer of spermatic veins and its potential role in the development of varicocele testis. Eur Urol 51:1402–1409
Tsutsui C, Kajihara K, Yanaka T, Sakata I, Itoh Z, Oda S, Sakai T (2009) House musk shrew (Suncus murinus, order: Insectivora) as a new model animal for motilin study. Peptides 30:318–329
Vera PL, Meyer-Siegler KL (2004) Inflammation of the rat prostate evokes release of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in the bladder: evidence for a viscerovisceral reflex. J Urol 172:2440–2445
Wrobel KH, Brandl B (1998) The autonomous innervation of the porcine testis in the period from birth to adulthood. Ann Anat 180:145–156
Wrobel KH, Moustafa MN (2000) On the innervation of the donkey testis. Ann Anat 182:13–22
Wrobel KH, Schenk E (2003) Immunohistochemical investigations of the autonomous innervation of the corvine testis. Ann Anat 185:493–506
Yamamoto M, Hibi H, Katsuno S, Miyake K (1995) Management of chronic orchialgia of unknown etiology. Int J Urol 2:47–49
Yi SQ, Shimokawa T, Akita K, Ohta T, Kayahara M, Miwa K, Tanaka S (2003) Anatomical study of the pancreas in the house musk shrew, Suncus murinus, with special reference to the blood supply and innervation. Anat Rec 273:630–635
Yi SQ, Ohta T, Miwa K, Shimokawa T, Akita K, Itoh M, Miyamoto K, Tanaka S (2005) Surgical anatomy of the innervation of the major duodenal papilla in humans and Suncus murinus, from the perspective of preserving innervation in organ-saving procedures. Pancreas 30:211–217
Yi SQ, Ru F, Ohta T, Terayama H, Naito M, Hayashi S, Buhe S, Yi N, Miyaki T, Tanaka S, Itoh M (2006) Surgical anatomy of the innervation of the pylorus in humans and Suncus murinus, in relation to the surgical technique for pylorus-preserving pancreatoduodenectomy. World J Gastroenterol 12:2209–2216
Yi SQ, Ohta T, Tsuchida A, Terayama H, Naito M, Li J, Wang HX, Yi N, Tanaka S, Itoh M (2007) Surgical anatomy of innervation of the gallbladder in humans and Suncus murinus with special reference to morphological understanding of gallstone formation after gastrectomy. World J Gastroenterol 13:2066–2071
Yi SQ, Ren K, Kinoshita M, Takano N, Itoh M, Ozaki N (2016) Innervation of extrahepatic biliary tract, with special reference to the direct bidirectional neural connections of the gall bladder, sphincter of Oddi and duodenum in Suncus murinus, in whole-mount immunohistochemical study. Anat Histol Embryol 45:184–188
Yoshioka K, Tanahashi M, Uchida W (2010) Behavioral and urological evaluation of a testicular pain model. Urology 75:943–948
Zhu BC, Chiocchio SR, Suburo AM, Tramezzani JH (1995) Monoaminergic and peptidergic contributions of the superior and the inferior spermatic nerves to the innervation of the testis in the rat. J Androl 16:248–258
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, Y., Ren, K., Kurosawa, K. et al. The distribution of nerves supplying the testis, epididymis and accessory sex glands of Suncus murinus. Anat Sci Int 94, 128–135 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12565-018-0459-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12565-018-0459-5