Abstract
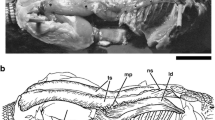
The myodural bridge (MDB) is a dense connective tissue that connects muscles with the cervical spinal dura mater via the posterior atlanto-occipital and atlato-axial interspaces. To date, the physiological function of the MDB has not been fully elucidated. Recent studies have identified the presence of the MDB in mammals, but very little information is available on the existence of the MDB in avifauna. We selected Gallus domesticus to explore the existence and the fiber property of the MDB in avifauna. We found that in this species, fibers originating from the ventral aspect of the rectus capitis dorsal minor are fused with the dorsal atlanto-occipital membrane and that numerous trabeculae connect the dorsal atlanto-occipital membrane with the cervical spinal dura mater. Furthermore, the occipital venous sinus is located between the trabeculae. The MDB is mainly composed of collagen type I fibers. Our results show that the MDB is present in G. domesticus and lead us to infer that the MDB is a highly conservative evolutionary structure which may play essential physiological roles.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cailliet R (1991) Neck; arm pain, 3rd edn. F.A. Davis Co., Philadelphia
Cramer GD, Darby SA (2013) Clinical anatomy of the spine, spinal cord and ANS, 2nd edn. Mosby Publishers, Maryland Heights
Enix ED, Frank Scali DC, Matthew E et al (2014) The cervical myodural bridge, a review of literature and clinical implications. Can Chiropr Assoc 58(2):184
Hack GD, Hallgren RC (2004) Chronic headache relief after section of suboccipital muscle dural connections: a case report. Headache 44:84–89
Hack GD, Koritzer RT, Robinson WL et al (1995) Anatomic relation between the rectus capitis posterior minor muscle and the dura mater. Spine 20(23):2484–2486
Hong J-Y, Suh S-W, Park S-Y et al (2011) Cadaver study with confocal infrared laser microscope. The Spine J 11(12):1121–1127
Kulkarni V, Chandy MJ, Babu KS (2001) Quantitative study of muscle spindles in suboccipital muscles of human fetuses. Neurol India 49(4):355–359
Liu P, Li C, Zheng N et al (2017) The myodural bridge existing in the Nephocaena phocaenoides. Sci Rep 7:8248
Lusczyk MJ, Blaisdell GY, Wiater BP et al (1982) The physiological basis of osteopathic medicine. In: Chapman JR, Agel JA, Bransford RJ (eds) Traumatic dural. Insight Publishing, New York
Lusczyk MJ, Blaisdell GY, Wiater BP et al (2014) Traumatic dural tears: what do we know and are they a problem? Spine J 14(1):49–56
Mitchell BS, Humphreys BK, Osullivan E (1998) Attachments of the ligamentum nuchae to cervical posterior spinal dura and the lateral part of the occipital bone. J Manipulative Physiol Ther 21:145–148
Nash L, Nicholson H, Lee AS et al (2005) Configuration of the connective tissue in the posterior atlanto-occipital interspace: a sheet plastination and confocal microscopy study. Spine 30:1359–1366
Palmgren PJ, Andreasson D, Eriksson M et al (2009) Cervicocephalic kinesthetic sensibility and postural balance in patients with nontraumatic chronic neck pain ¨C a pilot study. Chiropr Osteopat 17:6
Palomeque-del-Cerro L, Arráez-Aybar LA, Rodríguez-Blanco C et al (2017) A systematic review of the soft-tissue connections between neck muscles and dura mater: the myodural bridge. Spine 42:49–54
Pareja JA, Cuadrado ML, Elliott JM et al (2007) Magnetic resonance imaging study of the morphometry of cervical extensor muscles in chronic tension-type headache. Cephalalgia 27(4):355–362
Pontell ME, Scali F, Marshall E et al (2013) The obliquus capitis inferior myodural bridge. Clin Anat 26:450–454
Rutten HP, Szpak K, van Mameren H et al (1997) Letter to editor; response to anatomic relation between the rectus capitis posterior minor muscle and the dura mater. Spine 22:924–928
Scali F, Marsili ES, Pontell ME (2011) Anatomical connection between the rectus capitis posterior major and the dura mater. Spine 36:E1612–E1614
Scali F, Matthew E, Pontell ME et al (2013a) Histological analysis of the rectus capitis posterior major’s myodural bridge. Spine J 13(5):558–563
Scali F, Pontell ME, Welk AB et al (2013b) Magnetic resonance imaging investigation of the atlanto-axial interspace. Clin Anat 26(4):444–449
Shinomiya K, Dawson J, Spengler DM et al (1996) An analysis of the posterior epidural dura have passive and active functions to anchor the spinal ligament role on the cervical spinal cord. Spine 21:2081–2088
Sui HJ, Yu SB, Yuan XY et al (2013) Anatomical study on the connections between the suboccipital structures and the spinal dura mater. Chin J Clin Anat 31:489–490
Uhlig Y, Weber BR, Grob D et al (1995) Fiber with dysfunction of the cervical spine. J Orthop Res 13(2):240–249
Venne G, Rasquinha BJ et al (2017) Rectus capitis posterior minor: histological and biomechanical links tot he spinal dura mater. Spine 42(8):466–473
Xu Q, Yu SB, Zheng N et al (2016) Head movement, an important contributor to human cerebrospinal fluid circulation. Sci Rep 19(6):31787
Yuan XY, Yu SB, Li YF et al (2016) Patterns of attachment of the myodural bridge by the rectus capitis posterior minor muscle. Anatomical Sci Int 91(2):175–179
Zhang JH, Tang W, Zhang Z et al (2016) Connection of the posterior occipital muscle and dura mater of the siamese crocodile. Anat Rec 299:1402–1408
Zheng N, Yuan X, Li Y et al (2014) Definition of the to be named ligament and vertebrodural ligament and their possible effects on the circulation of CSF. PLOS One 9:e103451
Zheng N, Yuan XY, Chi YY et al (2017) The universal existence of myodural bridge in mammals: an indication of a necessary function. Sci Rep 7:1
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Ye-Xian Fan and Bing-Yi Luan in Dalian Hoffen Preservation Technique Institution for helping with preparing the sagittal sections.
Funding
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC31600972, NSFC31571234), Liaoning Province Department of Education Funds (L2016012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YRD conceived the study, performed the study, interpreted the data, prepared the figures, and wrote the manuscript. NZ supervised the research, performed the macroscopic analysis, and edited the manuscript. JG performed the scanning electron microscopy examination. TW performed the thick Sagittal section examination. OCS edited the manuscript. YZ, YZ, YXC, SYP, LCQ performed the anatomical dissections. SBY, HJS collected the research material, supervised the research, and edited the manuscript. All authors approved the last version of manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dou, YR., Zheng, N., Gong, J. et al. Existence and features of the myodural bridge in Gallus domesticus: indication of its important physiological function. Anat Sci Int 94, 184–191 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12565-018-00470-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12565-018-00470-2