Abstract
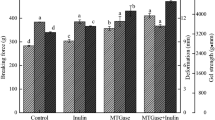
Body surface mucus was scraped off from white croaker Pennahia argentata after washing with two different procedures, suspended in cold water and filtered through a filter paper. The filtrate thus obtained was lyophilized and defined as the fish body surface substances. The relative level of the substances obtained after high-pressure water washing was 28.8% and significantly lower than those obtained after conventional washing (68.8%) and without washing (100%). The breaking strength of thermally induced gels prepared by pre-heating at 65 °C mimicking modori for 60 min after the high-pressure water washing was 3.8 N and was significantly higher than that after the conventional washing (2.6 N) and without washing (2.1 N). These results suggest that rheological properties of thermally induced gels can be improved with an extensive washing of fish material. The degradation of myosin heavy chain was recognized, when the water soluble fraction of the lyophilized powder of the fish body surface mucus was added into the ordinary muscle homogenate at around 60 °C and pH 8.15, suggesting that proteases were present in the fish body surface mucus. Such novel findings are useful for avoiding the modori phenomenon and thus improving the quality of surimi-based products.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akahane T, Chihara S, Yoshida Y, Tsuchiya T, Noguchi S, Ookami H, Matsumoto JJ (1984) Roles of constituent proteins in gel properties of cooked meat gels. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 50:1029–1033
Aranishi F (1999a) Possible role for cathepsin B and L in bacteriolysis by Japanese eel skin. Fish Shellfish Immunol 8:61–64
Aranishi F (1999b) Lysis of pathogenic bacteria by epidermal cathepsins L and B in the Japanese eel. Fish Physiol Biochem 20:37–41
Aranishi F (2000) High sensitivity of skin cathepsins L and B of European eel (Anguilla anguilla) to thermal stress. Aquaculture 182:209–213
Aranishi F, Nakane M (1997) Epidermal proteases of the Japanese eel. Fish Physiol Biochem 16:471–478
Aranishi F, Mano N, Nakane M, Hirose H (1998) Epidermal response of the Japanese eel to environmental stress. Fish Physiol Biochem 19:197–203
Busconi L, Folco EJ, Martone C, Trucco RE, Sanchez JJ (1984) Identification of two alkaline proteases and a trypsin inhibitor from muscle of white croaker (Micropogon opercularis). FEBS Lett 176:211–214
Folco EJ, Busconi L, Martone CB, Sanchez JJ (1988) Multicatalytic proteinase in fish muscle. Arch Biochem Biophys 267:599–605
Fukushima H, Yoon SH, Watabe S (2003) Differences in polymer formation through disulfide bonding of recombinant light meromyosin between white croaker and walleye pollock and their possible relation to species-specific differences in thermal unfolding. J Agric Food Chem 51:4089–4095
Fukushima H, Satoh Y, Yoon SH, Togashi M, Nakaya M, Watabe S (2005) Rheological properties of fast skeletal myosin rod and light meromyosin from walleye pollack and white croaker: contribution of myosin fragments to thermal gel formation. J Agric Food Chem 53:9193–9198
Fukushima H, Okazaki E, Fukuda Y, Watabe S (2007) Rheological properties of selected fish paste at selected temperature pertaining to shaping of surimi-based products. J Food Eng 81:492–499
Gornall AG, Bardawill CJ, David MM (1949) Determination of serum proteins by means of the biuret reaction. J Biol Chem 177:751–766
Hara K, Suzumatsu A, Ishihara T (1988) Purification and characterization of cathepsin B from carp ordinary muscle. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 54:1243–1252
Iwata K, Kobashi K, Hase J (1974) Studies on muscle alkaline protease-II. Some enzymatic properties of carp muscular alkaline protease. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 40:189–200
Iwata K, Kanna K, Okada M (1977) Kamaboko formation of mackerel and red sea bream myosins. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 43:237
Kakinuma M, Nakaya M, Hatanaka A, Hirayama Y, Watabe S, Maeda K, Ooi T, Suzuki S (1998) Thermal unfolding of three acclimation temperature-associated isoforms of carp light meromyosin expressed by recombinant DNAs. Biochemistry 37:6606–6613
Kanno G, Yamaguchi T, Kishimura H, Yamaha E, Saeki H (2010) Purification and characteristics of trypsin from masu salmon (Oncorhynchus masou) cultured in fresh-water. Fish Physiol Biochem 36:637–645
Kimura I, Sugimoto M, Toyoda K, Seki N, Arai K, Fujita T (1991) A study on the cross-linking reaction of myosin in kamaboko suwari gels. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 57:1389–1396
Kinoshita M, Toyohara H, Shimizu Y (1990) Purification and properties of a novel latent proteinase showing myosin heavy chain-degrading activity from threadfin-bream muscle. J Biochem 107:587–591
Klomklao S, Benjakul S, Visessanguan W, Kishimura H, Simpson BK (2007a) 29 kDa trypsin from the pyloric ceca of Atlantic bonito (Sarda sarda): recovery and characterization. J Agric Food Chem 55:4548–4553
Klomklao S, Benjakul S, Visessanguan W, Kishimura H, Simpson BK (2007b) Trypsin from the pyloric caeca of bluefish (Pomatomus saltatrix). Comp Biochem Physiol B: Biochem Mol Biol 148:382–389
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Makinodan Y, Ikeda S (1969) Studies on fish muscle protease-II. Purification and properties of a proteinase active in slightly alkaline pH range. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 35:749–757
Matsuoka Y, Wan J, Ushio H, Watabe S (2013) Thermal gelation properties of white croaker, walleye pollack and deepsea bonefish surimi after suwari treatment at various temperatures. Fish Sci 79:715–724
Nakaya M, Watabe S, Ooi T (1995) Differences in the thermal stability of acclimation temperature-associated carp myosin and its rod isoforms on differential scanning calorimetry. Biochemistry 34:3114–3120
Nakaya M, Kakinuma M, Watabe S, Ooi T (1997) Differential scanning calorimetry and CD spectrometry of acclimation temperature-associated types of carp light meromyosin. Biochemistry 36:9179–9184
Ni S, Nozawa H, Seki N (1999) The combined effect of transglutaminase and protease inhibitors on the thermal gelation of actomyosin sol from carp and salmon muscles. Fish Sci 65:606–612
Ni S, Nozawa H, Seki N (2001) Effect of pH on the gelation of walleye pollock surimi and carp actomyosin pastes. Fish Sci 67:920–927
Nishimoto S, Hashimoto A, Seki N, Kimura I, Toyoda K, Fujita T, Arai K (1987) Influencing factors on changes in myosin heavy chain and jelly strength of salted meat paste from Alaska pollack during setting. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 53:2011–2020 (in Japanese with English abstract)
Nishioka F, Shimizu Y (1983) Recovery of proteins from washings of minced fish meat by pH-shifting method. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 49:795–800 (in Japanese with English abstract)
Niwa E, Nakayama T, Hamada I (1983) Effect of setting on the network structure of protein in fish flesh gel. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 49:245–249 (in Japanese with English abstract)
Numakura T, Seki N, Kimura I, Toyoda K, Fujita T, Takama K, Arai K (1985) Cross-linking reaction of myosin in the fish paste during setting (suwari). Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 51:1559–1565 (in Japanese with English abstract)
Numakura T, Seki N, Kimura I, Toyoda K, Fujita T, Takama K, Arai K (1987) Effect of quality of surimi on cross-linking reaction of myosin heavy chain during setting. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 53:633–639 (in Japanese with English abstract)
Numakura T, Mizoguchi R, Kimura I, Toyoda K, Fujita T, Seki N, Arai K (1989) Changes in gel forming ability and cross-linking ability of myosin heavy chain of Alaska pollack surimi denatured by heat treatment. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 55:1083–1090 (in Japanese with English abstract)
Sano T, Noguchi FS, Matsumoto JJ, Tsuchiya T (1989) Role of F-actin in thermal gelation of fish actomyosin. J Food Sci 54:800–804
Satoh Y, Nakaya M, Ochiai Y, Watabe S (2006) Characterization of fast skeletal myosin from white croaker in comparison with that from walleye pollack. Fish Sci 72:646–655
Schneider C, Rasband W, Eliceiri K (2012) NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9:671–675
Shimizu Y, Machida R, Takenami S (1981) Species variations in the gel-forming characteristics of fish meat paste. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 47:95–104
Takahashi Y, Kajiwaki T, Itami T, Okamoto T (1987) Enzymatic properties of the bacteriolytic substances in the skin mucus of yellowtail. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 53:425–431
Ueki N, Wan J, Watebe S (2014) The pepsin digestibility of thermal gel products made from white croaker (Pennahia argentata) muscle in associating with myosin polymerization levels. J Food Sci 79:C2427–C2433
Ueki N, Wan J, Watabe S (2016a) Deterioration of white croaker (Pennahia argentata) meat thermally-induced gel products caused by proteolytic enzymes in the contaminated intestine and kidney. Food Chem 199:416–422
Ueki N, Wan J, Watabe S (2016b) Proteolytic profiles of walleye pollack (Theragra calcogramma) and white croaker (Pennahia argentata) meats in the presence of intestinal extracts from their own or different fish species. Food Sci Technol Res 22:787–792
Ueki N, Matsuoka Y, Wan J, Watabe S (2018) The effects of endogenous proteases within abdominal muscle parts on the rheological properties of thermally induced gels from white croaker (Pennahia argentata). Food Chem 268:498–503
Yanagihara S, Nakaoka H, Hara K, Ishihara T (1991) Purification and characterization of serine proteinase from white croaker skeletal muscle. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 57:133–142
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ueki, N., Matsuoka, Y., Wan, J. et al. Quality improvement of thermally induced surimi gels by extensive washing for dressed white croaker to remove contamination by body surface mucus proteases. Fish Sci 85, 883–893 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-019-01335-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-019-01335-x