Abstract
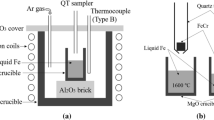
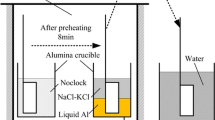
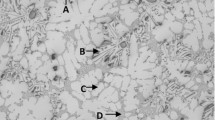
The present study aims to clarify the formation mechanism of the interfacial layer between solid CaO and molten iron through SEM–EDS analysis. The interfacial layer formed between CaO and molten iron is observed by SEM–EDS for different compositions of molten iron (CaO/Fe–C–S interface: CaS layer; CaO/Fe–C–Si–S interface: CaS and Ca2SiO4 layers; CaO/Fe–C–Si interface: no interfacial layer; CaO/Fe–S–Si interface: Ca2SiO4 and CaS layers). The effect of S and Si concentrations on layer formation is discussed using the following proposed mechanism.
In the case of the Fe–C–Si–Al–S/CaO interface, CaS and Ca3Al2O6 layers are observed. The formation mechanism of a reaction layer for Al-containing iron melts is also proposed as below.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Niedringhaus, R. Fruehan, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 19, 261 (1988)
F. Oeters, Metallurgie der Stahlherstellung (Springer, Berlin, 2012)
D. Boyd, W. Phelps, M. Hepworth, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 6, 87 (1975)
E. Turkdogan, L. Msartonik, Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 23, 1038 (1983)
Y. Kawai, K. Mori, Y. San-nomiya, Tetsu-to-Hagané 61, 29 (1975)
T. Mitsuo, T. Shoji, Y. Hatta, H. Ono, H. Mori, T. Kai, Trans. Jpn. Inst. Met. 23, 768 (1982)
H.-J. Visser, R. Boom, ISIJ Int. 46, 1771 (2006)
D. Lindström, P. Nortier, D. Sichen, Steel Res. Int. 85, 76 (2014)
E.T. Turkdogan, Physical Chemistry of High Temperature Technology (Academic Press, New York, NY, 1980)
Q. Han, X. Zhang, D. Chen, P. Wang, MTB 19, 617 (1988)
S.R. Simeonov, I.N. Ivanchev, A.V. Hainadjiev, ISIJ Int. 31, 1396 (1991)
N.G.S.S.D. Iinkai, Steelmaking Data Sourcebook (Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, New York, 1998)
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by the Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology project no. 10076604.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S., Min, D.J. A Study on the Formation Mechanism of the Interfacial Layer Between Solid CaO and Molten Iron Alloys. Met. Mater. Int. 25, 248–256 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-018-0162-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-018-0162-z