Abstract
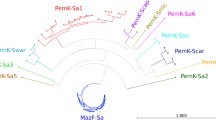
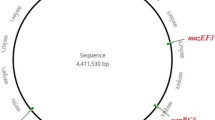
Klebsiella pneumoniae is an increasingly important bacterial pathogen to human. This Gram-negative bacterium species has become a serious concern due to its dramatic increase in the levels of multiple antibiotic resistances, particularly to carbapenems. The toxin-antitoxin (TA) system has recently been reported to be involved in the formation of drug-tolerant persister cells. The type II TA system is composed of a stable toxin protein and a relatively unstable antitoxin protein that is able to inhibit the toxin. Here, we examine the type II TA locus distribution and compare the TA diversity throughout ten completely sequenced K. pneumoniae genomes by using bioinformatics approaches. Two hundred and twelve putative type II TA loci were identified in 30 replicons of these K. pneumoniae strains. The amino acid sequence similarity-based grouping shows that these loci distribute differently not only among different K. pneumoniae strains isolated from diverse sources, but also between their chromosomes and plasmids.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nordmann P, Cuzon G, Naas T (2009) The real threat of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase-producing bacteria. Lancet Infect Dis 9(4):228–236
Liu P, Li P, Jiang X, Bi D, Xie Y, Tai C, Deng Z, Rajakumar K, Ou HY (2012) Complete genome sequence of Klebsiella pneumoniae subsp. pneumoniae HS11286, a multidrug-resistant strain isolated from human sputum. J Bacteriol 194(7):1841–1842
Zhang J, van Aartsen JJ, Jiang X, Shao Y, Tai C, He X, Tan Z, Deng Z, Jia S, Rajakumar K, Ou HY (2011) Expansion of the known Klebsiella pneumoniae species gene pool by characterization of novel alien DNA islands integrated into tmRNA gene sites. J Microbiol Methods 84(2):283–289
Yamaguchi Y, Park JH, Inouye M (2011) Toxin-antitoxin systems in bacteria and archaea. Annu Rev Genet 45:61–79
Ghafourian S, Raftari M, Nourkhoda S, Sekawi Z. (2013) Toxin-antitoxin systems: classification, biological function and application in biotechnology. Horizon Scientific Press, New York, vol 16, no Biol, pp 9–14
Wang X, Wood TK (2011) Toxin-antitoxin systems influence biofilm and persister cell formation and the general stress response. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(16):5577–5583
Maisonneuve E, Gerdes K (2014) Molecular mechanisms underlying bacterial persisters. Cell 157(3):539–548
Masuda H, Tan Q, Awano N, Wu KP, Inouye M (2012) YeeU enhances the bundling of cytoskeletal polymers of MreB and FtsZ, antagonizing the CbtA (YeeV) toxicity in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 84(5):979–989
Wang X, Lord DM, Cheng HY, Osbourne DO, Hong SH, Sanchez-Torres V, Quiroga C, Zheng K, Herrmann T, Peti W, Benedik MJ, Page R, Wood TK (2012) A new type V toxin-antitoxin system where mRNA for toxin GhoT is cleaved by antitoxin GhoS. Nat Chem Biol 8(10):855–861
Pandey DP, Gerdes K (2005) Toxin-antitoxin loci are highly abundant in free-living but lost from host-associated prokaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res 33(3):966–976
Ou HY, Wei Y, Bi D (2013) Type II toxin-antitoxin loci: phylogeny. In: Prokaryotic toxin-antitoxins. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 239–247
Sala A, Bordes P, Genevaux P (2014) Multiple toxin-antitoxin systems in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Toxins (Basel) 6(3):1002–1020
Sevin EW, Barloy-Hubler F (2007) RASTA-Bacteria: a web-based tool for identifying toxin-antitoxin loci in prokaryotes. Genome Biol 8(8):R155
Hyatt D, Chen GL, Locascio PF, Land ML, Larimer FW, Hauser LJ (2010) Prodigal: prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinform 11:119
Shao Y, Harrison EM, Bi D, Tai C, He X, Ou HY, Rajakumar K, Deng Z (2011) TADB: a web-based resource for type 2 toxin-antitoxin loci in bacteria and archaea, Nucleic Acids Res 39(Database issue):D606–D611
Finn RD, Clements J, Eddy SR (2011) HMMER web server: interactive sequence similarity searching. Nucleic Acids Res 39(Web Server issue):W29–W37
Wozniak RA, Waldor MK (2009) A toxin-antitoxin system promotes the maintenance of an integrative conjugative element. PLoS Genet 5(3):e1000439
Black DS, Kelly AJ, Mardis MJ, Moyed HS (1991) Structure and organization of hip, an operon that affects lethality due to inhibition of peptidoglycan or DNA synthesis. J Bacteriol 173(18):5732–5739
Van Melderen L, Saavedra De Bast M (2009) Bacterial toxin-antitoxin systems: more than selfish entities? PLoS Genet 5(3):e1000437
Boggild A, Sofos N, Andersen KR, Feddersen A, Easter AD, Passmore LA, Brodersen DE (2012) The crystal structure of the intact E. coli RelBE toxin-antitoxin complex provides the structural basis for conditional cooperativity. Structure 20(10):1641–1648
Tashiro Y, Kawata K, Taniuchi A, Kakinuma K, May T, Okabe S (2012) RelE-mediated dormancy is enhanced at high cell density in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 194(5):1169–1176
Makarova KS, Wolf YI, Koonin EV (2009) Comprehensive comparative-genomic analysis of type 2 toxin-antitoxin systems and related mobile stress response systems in prokaryotes. Biol Direct 4:19
Jurenaite M, Markuckas A, Suziedeliene E (2013) Identification and characterization of type II toxin-antitoxin systems in the opportunistic pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii. J Bacteriol 195(14):3165–3172
Castro-Roa D, Garcia-Pino A, De Gieter S, van Nuland NA, Loris R, Zenkin N (2013) The Fic protein Doc uses an inverted substrate to phosphorylate and inactivate EF-Tu. Nat Chem Biol 9(12):811–817
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by partial funding from the 973 program, Ministry of Science and Technology, China (2015CB554202, 2012CB721000); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31170082); the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education, China (20130073110062).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, YQ., Bi, DX., Wei, DQ. et al. Prediction of Type II Toxin-Antitoxin Loci in Klebsiella pneumoniae Genome Sequences. Interdiscip Sci Comput Life Sci 8, 143–149 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-015-0135-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-015-0135-6