Abstract
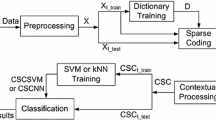
In this paper, we propose a new sparsity-based approach for the spectral–spatial classification of hyperspectral imagery. The proposed approach exploits the sparse representations of the spectral and spatial information contained in the data to generate an accurate classification map; specifically, we use all the spectral information (reflectance registered in the bands) and extended multiattribute profiles to extract spatial features. Hyperspectral image classification with sparse representations is based on the study that a pixel can be sparsely represented by a linear combination of a few learning examples from a structured dictionary. Then, by giving the set of training samples, any given sample may be sparsely represented by solving a sparsity-constrained optimization problem and thus classified in the class that minimizes a residual function. In this paper, we propose a new residual function which combines the sparse representations of the spectral features and the sparse representations of the spatial features to determine the class label of the test sample. Experiments are conducted on the familiar AVIRIS “Indian Pines” data set. It was found that the proposed method provided more accurate classification results than SVM with composite kernel.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Available at: http://engineering.purdue.edu/~biehl/MultiSpec/.
References
Ben Salem, R., Saheb, E. K., & Hamdi, M. A. (2016). Spectral–spatial classification of hyperspectral image based on oversampling and multi-feature kernels. Graphics, Vision and Image Processing Journal, 16(2), 31–40.
Benediktsson, J. A., Palmason, J. A., & Sveinsson, J. R. (2005). Classification of hyperspectral data from urban areas based on extended morphological profiles. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 43(3), 480–491.
Chen, Y., Nasrabadi, N., & Tran, T. (2011a). Hyperspectral image classification using dictionary-based sparse representation. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 49(10), 3973–3985.
Chen, Y., Nasrabadi, N. & Tran, T. (2011b). Hyperspectral image classification via kernel sparse representation. In Proceedings of ICIP, pp. 1233–1236.
Cui, M., & Prasad, S. (2015). Class-dependent sparse representation classifier for robust hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Society, 53(5), 2683–2695.
Datt, B., McVicar, T. R., Van Niel, T. G., Jupp, D., & Pearlman, J. (2003). Preprocessing eo-1 hyperion hyperspectral data to support the application of agricultural indexes. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 41(6), 1246–1259.
Davis, G., Mallat, S., & Avellaneda, M. (1997). Adaptive greedy approximations. Constructive Approximation, 13(1), 57–98.
Elad, M., & Aharon, M. (2006). Image denoising via sparse and redundant representations over learned dictionaries. IEEE Transaction on Image Processing, 15(12), 3736–3745.
Fang, L., Li, S., Kang, X., & Benediktsson, J. A. (2014). Spectral–spatial hyperspectral image classification via multiscale adaptive sparse representation. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Society, 52(12), 7738–7749.
Goel, P. K., Prasher, S. O., Patel, R. M., Landry, J. A., Bonnell, R. B., & Viau, A. A. (2003). Classification of hyperspectral data by decision trees and artificial neural networks to identify weed stress and nitrogen status of corn. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 39(2), 67–93.
Krishnapuram, B., Carin, L., Figueiredo, M., & Hartemink, A. (2005). Sparse multinomial logistic regression: fast algorithms and generalization bounds. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 27(6), 957–968.
Li, J., Marpu, P. R., Plaza, A., Bioucas-Dias, J. M., & Benediktsson, J. A. (2013). Generalized composite kernel framework for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Society, 51(9), 4816–4829.
Liu, J., Wu, Z., Wei, Z., Xiao, L., & Sun, L. (2013). Spatial-spectral kernel sparse representation for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Geoscience & Remote Sensing Society, 6(6), 2462–2471.
Manolakis, D., & Shaw, G. (2002). Detection algorithms for hyperspectral imaging applications. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 19(1), 29–43.
Mura, M. D., Benediktsson, J. A., Waske, B., & Bruzzone, L. (2010). Extended profiles with morphological attribute filters for the analyses of hyperspectral data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 31(22), 5975–5991.
Palmason, J. A., Benediktsson, J. A., Sveinsson, J. R. & Chanussot, J. (2005). Classification of hyperspectral data from urban areas using morphological preprocessing and independent component analysis. In Proceedings of IGARSS, pp. 25–29.
Pan, L., Li, H., Meng, H., Li, W., Du, Q., & Emery, W. J. (2017). Hyperspectral image classification via low-rank and sparse representation with spectral consistency constraint. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Society, 14(11), 2117–2121.
Patel, N., Patnaik, C., Dutta, S., Shekh, A., & Dave, A. (2001). Study of crop growth parameters using airborne imaging spectrometer data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 22(12), 2401–2411.
Song, B., Li, J., Mura, M. D., Li, P., Plaza, A., Bioucas-Dias, J. M., et al. (2014). Remotely sensed image classification using sparse representations of morphological attribute profiles. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 52(8), 5122–5136.
Stein, D., Beaven, S., Hoff, L., Winter, E., Schaum, A., & Stocker, A. (2002). Anomaly detection from hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 19(1), 58–69.
Tan, M., Tsang, I. W., Wang, L. & Zhang, X. (2012). Convex matching pursuit for large-scale sparse coding and subset selection. In Proceedings of AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp. 1119–1125.
Tang, Y. Y., Yuan, H., & Li, L. (2014). Manifold-based sparse representation for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Society, 52(12), 7606–7618.
Wright, J., Yang, A., Ganesh, A., Sastry, S., & Ma, Y. (2009). Robust face recognition via sparse representation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 31(2), 210–227.
Zhang, H., Li, J., Huang, Y., & Zhang, L. (2014). A nonlocal weighted joint sparse representation classification method for hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 7(6), 2056–2065.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Hamdi, M.A., Ben Salem, R. Sparse Representations for the Spectral–Spatial Classification of Hyperspectral Image. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 47, 923–929 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-018-0908-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-018-0908-6