Abstract
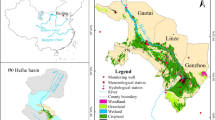
Constant alterations of oasis landscape pattern, triggered by specific natural and human driving forces, have aroused some heated discussions in the field of regional environmental change research especially in arid areas. In this study, the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index and the Soil Brightness Index have been selected to successfully identify discrete land cover classes derived from a series of Landsat satellite images of Manas River watershed in 1989, 1998, and 2014. FRAGSTATS and principal components analysis were used to recognize independent components of landscape structure. Nine land cover classes combined with ten landscape metrics indicated variations in the composition and configuration of landscape pattern. Results related to historical data were analyzed to identify driving forces, mainly including population growth, agricultural modernization, urbanization, and water resource provision. The results revealed a trend toward less landscape fragmentation, as indicated by a steady decrease in the number of patches as well as an increase in mean patch size and contagion. To be more specific, we found substantial increases in cropland (72.3%) as well as built-up land (43.7%) with larger and more compact patches, while water (64.1%), snow cover (52.0%), and saline–alkali soil (48.5%) dropped sharply. Our findings suggested that population influx and reclamation of saline–alkali soil were two major driving forces critical to those landscape pattern changes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Botequilha Leitão, A., & Ahern, J. (2002). Applying landscape ecological concepts and metrics in sustainable landscape planning. Landscape and Urban Planning, 59(2), 65–93.
Brink, A. B., & Eva, H. D. (2009). Monitoring 25 years of land cover change dynamics in Africa: A sample-based remote sensing approach. Applied Geography, 29(4), 501–512.
Buyantuyev, A., Wu, J., & Gries, C. (2007). Estimating vegetation cover in an urban environment based on Landsat ETM+ imagery: A case study in Phoenix, USA. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 28(2), 269–291.
Buyantuyev, A., Wu, J., & Gries, C. (2010). Multiscale analysis of the urbanization pattern of the Phoenix metropolitan landscape of USA: Time, space and thematic resolution. Landscape and Urban Planning, 94(3–4), 206–217.
Chen, M. J., Wang, H., & Wang, F. (2004). Water-driven ecological evolution mechanism in an inland arid region. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24(10), 2108–2114.
Cheng, W. M., Zhou, C., Liu, H., Zhang, Y., & Jiang, Y. (2006). The oasis expansion and eco-environment change over the last 50 years in Manas River Watershed, Xinjiang. Science in China, 49(2), 163–175. (In Chinese).
China Forestry. (2002). Some opinions of the state council on further improving the policy and measures for “Grain to Green”.
China Forestry. (2015). Notice on the expansion of a new round of “Grain to Green”, Financiers [2015] no. 258.
Cushman, S. A., McGarigal, K., & Neel, M. C. (2008). Parsimony in landscape metrics: Strength, universality, and consistency. Ecological Indicators, 8, 691–703.
Defries, R. S., Foley, J. A., & Asner, G. P. (2004). Land-use choices: Balancing human needs and ecosystem function. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 2, 249–257.
Fan, W. B., Zhou, H. F., & Li, J. F. (2010). The composition of ecological water requirement and estimation of ecological water demand of Manas River Valley. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 17(6), 242–251. (In Chinese).
Fan, Z. L., Ma, Y. J., Wang, R. H., Ji, F., & Zhang, L. Y. (2000). Ecosystem types in the continental river watershed of arid area and the management approaches. Journal of Desert Research, 12(4), 293–296. (In Chinese).
Feng, Y. X., Luo, G. P., Lu, L., Zhou, D. C., Han, Q. F., Xu, W. Q., et al. (2011). Effects of land use change on landscape pattern of the Manas River watershed in Xinjiang, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 64(8), 2067–2077.
Frondoni, R., Mollo, B., & Capotorti, G. (2011). A landscape analysis of land cover change in the Municipality of Rome (Italy): Spatio-temporal characteristics and ecological implications of land cover transitions from 1954 to 2001. Landscape and Urban Planning, 100, 117–128.
GB/T 21010-2007 Current Land Use Classification. (2007). Chinese Land Surveying and Planning Institute, Department of Land Management, Ministry of Land and Resources. Beijing: Standards Press of China.
Griffith, J. A., Martinko, E. A., & Price, K. P. (2000). Landscape structure analyses of Kansas in three scales. Landscape and Urban Planning, 52, 45–61.
Gustafson, E. J. (1998). Quantifying landscape spatial pattern: What is the state of the art? Ecosystems, 1(2), 143–156.
Han, D. L. (1999). The progress of research on oasis in China. Science Geography, 19(4), 313–319. (In Chinese).
Historical weather enquiries. (2016, 2017). The weather website (http://www.tianqi.com). Accessed 15 July 2018
Jia, B., Zhang, Z., Ci, L., Ren, Y., Pan, B., & Zhang, Z. (2004). Oasis land-use dynamics and its influence on the oasis environment in Xinjiang, China. Journal of Arid Environments, 56(1), 11–26.
Jiang, F., Cheng, Z., Mu, G., Hu, R., & Meng, Q. (2005). Magnification of flood disasters and its relation to regional precipitation and local human activities since the 1980s in Xinjiang, north-western China. Natural Hazards, 36(3), 307330.
Kolios, S., Stylios, C. D. (2013). Identification of land cover/land use changes in the greater area of the Preveza peninsula in Greece using Landsat satellite data. Applied Geography, 40(2), 150–160.
Lausch, A., Blaschke, T., Haase, D., Herzog, F., Syrbe, R. U., Tischendorf, L., et al. (2015). Understanding and quantifying landscape structure: A review on relevant process characteristics, data models and landscape metrics. Ecological Modelling, 295(1), 31–41.
Lausch, A., & Herzog, F. (2002). Applicability of landscape metrics for the monitoring of landscape change: Issues of scale, resolution and interpretability. Ecological Indicators, 2(1–2), 3–15.
Li, Y. L., Jiang, L. L., Bao, A. M., Chang, C., Bai, J., & Liu, H. L. (2015). Spatio-temporal change analysis of cultivated land in Manas drainage basin during 1962–2010. Transaction of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 31(4), 277–285. (In Chinese).
Li, Y. L., Qiao, M., Yang, X. L., Zhou, S. B., & Zeng, Y. J. (2008). Analysis on land use/cover change and landscape fragmentation in typical watershed of arid zone in the last 30 years: A case of Manas River watershed, Xinjiang. Journal of Desert Research, 28(6), 1500–1507.
Li, Z., Han, T., Jing, Z., Yang, H., & Jiao, K. (2003). A summary of 40-year observed variation facts of climate and Glacier No. 1 at headwater of Urumqi River, Tianshan, China. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 25(2), 117–123.
Liang, E. M., & Zhang, J. M. (2016). Analysis of ecological security of landscape pattern in Manas River watershed of Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 23(3), 170–175. (In Chinese).
Lin, N. F., Tang, J., & Han, F. X. (2001). Eco-environmental problems and effective utilization of water resources in the Kashi Plain, western Terim watershed, China. Hydrogeology Journal, 9(2), 202–207.
Lin, Y. P., Hong, N. M., Wu, P. J., Wu, C. F., & Verburg, P. H. (2007). Impacts of land use change scenarios on hydrology and land use patterns in the Wu-Tu watershed in Northern Taiwan. Landscape and Urban Planning, 80(1–2), 111–126.
Liu, H. L., Wang, L., Bao, A. M., & He, X. L. (2009). Analysis on snow and ice cover area in Manas River Watershed based on MODIS data. Journal of Shihezi University (Natural Science), 27(6), 770–773. (In Chinese).
Liu, S., Xie, Z., Wang, N., & Ye, B. (1999). Mass balance sensitivity to climate change: a case study of Glacier No. 1 at Urumqi Riverhead, Tianshan Mountains, China. Chinese Geographical Science, 9(2), 134–140.
Lonsdale, W. M. (1985). On the ordered development of plants: A critical analysis. Annals of Botany, 55(6), 903–907.
McGarigal, K., Cushman, S. A., Neel, M. C., & Ene, E. (2002). FRAGSTATS: Spatial pattern analysis program for categorical maps. Amherst, MA: Computer Software Program. University of Massachusetts.
McGarigal, K., & Marks, B. J., (1995). Spatial pattern analysis program for quantifying landscape structure. General Technical Report PNW-GTR-351. US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Pacific Northwest Research Station.
Mu, B., Mayer, A. L., He, R., & Tian, G. (2016). Land use dynamics and policy implications in central china: A case study of zhengzhou. Cities, 58, 39–49.
National Earth System Science Data Sharing Infrastructure (2003). National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China (http://www.geodata.cn). Accessed 13 July 2018
Notice concerning the annual task of returning farmland to forest and grassland in 2016(western China [2016] no.1138), (2016). National Development and Reform Commission.
Riitters, K. H., O’Neill, R. V., Hunsaker, C. T., Wickham, J. D., Yankee, D. H., Timmins, S. P., et al. (1995). A factor analysis of landscape pattern and structure metrics. Landscape Ecology, 10, 23–40.
Rutledge, D. (2003). Landscape indices as measures of the effects of fragmentation: can pattern reflect process? Doc Science Internal Series, 98, 1–24.
Schindler, S., Poirazidis, K., & Wrbka, T. (2008). Towards a core set of landscape metrics for biodiversity assessments: A case study from Dadia National Park, Greece. Ecology Indicators, 8, 502–514.
Smith, M. S. (2008). The ‘desert syndrome’: Causally-linked factors that characterise outback Australia. Rangeland Journal, 30(1), 3–14.
Sun, C., Zhao, L., Wei, Z., & Zheng, D. (2014). Water resource utilization efficiency and spatial spillover effects in China. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 24(5), 771–788.
Uuemaa, E., Mander, Ü., & Marja, R. (2013). Trends in the use of landscape spatial metrics as landscape indicators: A review. Ecological Indicators, 28(5), 100–106.
Vitousek, P. M. (1994). Beyond global warming: Ecology and global change. Ecology, 75(7), 1861–1876.
Wang, T. (2009). Review and prospect of research on oasification and desertification in arid regions. Journal of Desert Research, 29(1), 1–9. (In Chinese).
Wrbka, T., Schindler, S., Pollheimer, M., Schmitzberger, I., & Peterseil, J. (2008). Impact of the Austrian agri-environmental scheme on diversity of landscapes, plants and birds. Community Ecology, 9(2), 217–227.
Xiao, C., Liu, S., Zhao, L., et al. (2007). Observed changes of cryosphere in China over the second half of the 20th century: an overview. Annals of Glaciology, 46(1), 382–390.
Xie, Y. C., Gong, J., Sun, P., & Gou, X. H. (2014). Oasis dynamics change and its influence on landscape pattern on Jinta oasis in arid China from 1963a to 2010a: Integration of multi-source satellite images. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 33, 181–191.
Xinjiang Statistical Yearbook (1989–2015). (2015). Xinjiang Statistic Bureau.
Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region Forestry. (2011). Administrative measures on the conversion of “Grain to Green” in Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region.
Yang, W. H., Zhang, J. M., Li, S. X., Xu, L. P., & Wang, L. (2015). Study on the characteristics of land effects in Manas River basin. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 22(3), 73–78. (In Chinese).
Yu, P., Xu, H., Liu, S., Qiao, M., Zhang, Q., An, H., et al. (2011). Spatial distribution pattern changes of oasis soil types in Manasi River watershed, arid north-western China. Catena, 87(2), 253–259.
Zhang, H. F., Ouyang, Z. Y., Zheng, H., & Xu, W. H. (2009). Landscape pattern change and its ecological effect in the Manas River basin of Xinjiang, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 6, 1408–1414. (In Chinese).
Zhang, L. Q., & Wang, H. Z. (2006). Planning an ecological network of Xiamen Island (China) using landscape metrics and network analysis. Landscape and Urban Planning, 78(4), 449–456.
Zhang, Q., Xu, H., Fu, J., Yu, P., & Zhang, P. (2012). Spatial analysis of land use and land cover changes in recent 30 years in Manas River watershed. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 12, 906–916.
Zhao, K., Li, X., Zhou, X., Dodson, J., & Ji, M. (2013). Impact of agriculture on an oasis landscape during the late Holocene: Palynological evidence from the Xintala site in Xinjiang, NW China. Quaternary International, 311, 81–86.
Zhou, S., Huang, Y., Yu, B., & Wang, G. (2015). Effects of human activities on the eco-environment in the middle Heihe River watershed based on an extended environmental Kuznets curve model. Ecological Engineering, 76, 14–26.
Acknowledgements
This material was funded by a Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps (XPCC) Scientific and Technological Project (Grant No. 2015AD018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Li, Y., Wang, S. et al. Oasis Landscape Pattern Dynamics in Manas River Watershed Based on Remote Sensing and Spatial Metrics. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 47, 153–163 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-018-0881-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-018-0881-0