Abstract
Background
Adenotonsillectomy (AT) has been an effective treatment for sleep-disordered breathing (SDB) in children, and several studies described the risk of postoperative weight gain and obesity in children treated with AT. The present study aimed to evaluate behavioral improvements in children with SDB one year after adenotonsillectomy and to investigate an influence of postoperative weight gain on behaviors.
Methods
The study included 170 children aged 5–11 years who underwent adenotonsillectomy for SDB and 150 controls. Body mass index percentile was obtained for age and gender, and parental sleep-related breathing disorder (SRBD) questionnaire was used to assess the severity of SDB. Psychological assessment was performed pre- and post-adenotonsillectomy using standardized questionnaires including strength and difficulties questionnaire, children’s depression inventory and screen for child anxiety-related emotional disorder.
Results
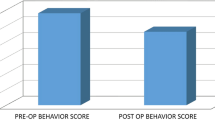
The mean age of 170 patients was 7.7 ± 1.5 years with 73 (42.9%) girls and 97 (57.1%) boys. The mean follow-up period were 15.4 ± 2.7 months. The patients had shown significant improvements in SDB scores as well as in questionnaire-based behavioral problems after adenotonsillectomy. The odds of a child being overweight were significantly increased after adenotonsillectomy. Less improvements in hyperactivity and conduct problems were observed in the patients with older ages, higher SRBD scores, and overweight/obesity at 1-year follow-up after adenotonsillectomy.
Conclusion
These data suggest that abnormal behavioral outcomes should be evaluated postoperatively, which potentially could be reduced with the early adenotonsillectomy and adequate postoperative weight control.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Owen GO, Canter RJ, Robinson A. Snoring, apnoea and ENT symptoms in the paediatric community. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1996;21:130–4.
O’Brien LM, Mervis CB, Holbrook CR, Bruner JL, Klaus CJ, Rutherford J, et al. Neurobehavioral implications of habitual snoring in children. Pediatrics. 2004;114:44–9.
Hulcrantz E, Lofstrand-Tidestrom B, Ahlquist-Rastad J. The epidemiology of sleep related breathing disorders in children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 1995;Suppl 32:S63–6.
Ferreira AM, Clemente V, Gozal D, Gomes A, Pissarra C, César H, et al. Snoring in Portuguese primary school children. Pediatrics. 2000;106:E46.
Marcus CL, Brooks LJ, Draper KA, Gozal D, Halbower AC, Jones J, et al. Diagnosis and management of childhood obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Pediatrics. 2012;130:e714–55.
Marcus CL, Moore RH, Rosen CL, Giordani B, Garetz SL, Taylor HG, et al. A randomized trial of adenotonsillectomy for childhood sleep apnea. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:2366–76.
Beebe DW. Neurobehavioral morbidity associated with disordered breathing during sleep in children: a comprehensive review. Sleep. 2006;29:1115–34.
Montgomery-Downs HE, Jones VF, Molfese VJ, Gozal D. Snoring in preschoolers: associations with sleepiness, ethnicity, and learning. Clin Pediatr. 2003;42:719–26.
Brockmann PE, Bertrand P, Pardo T, Cerda J, Reyes B, Holmgren NL. Prevalence of habitual snoring and associated neurocognitive consequences among Chilean school aged children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2012;76:1327–31.
Bhattacharyya N, Lin HW. Changes and consistencies in the epidemiology of pediatric adenotonsillar surgery, 1996–2006. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010;143:680–4.
Chervin RD, Ruzicka DL, Giordani BJ, Weatherly RA, Dillon JE, Hodges EK, et al. Sleep-disordered breathing, behavior, and cognition in children before and after adenotonsillectomy. Pediatrics. 2006;117:e769–78.
Friedman BC, Hendeles-Amitai A, Kozminsky E, Leiberman A, Friger M, et al. Adenotonsillectomy improves neurocognitive function in children with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep. 2003;26:999–1005.
Kohler MJ, Lushington K, van den Heuvel CJ, Martin J, Pamula Y, Kennedy D. Adenotonsillectomy and neurocognitive deficits in children with sleep disordered breathing. PLoS ONE. 2009;4:e7343.
Jeyakumar A, Fettman N, Armbrecht ES, Mitchell R. A systematic review of adenotonsillectomy as a risk factor for childhood obesity. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011;144:154–8.
Roemmich JN, Barkley JE, D’Andrea L, Nikova M, Rogol AD, Carskadon MA, et al. Increases in overweight after adenotonsillectomy in overweight children with obstructive sleep-disordered breathing are associated with decreases in motor activity and hyperactivity. Pediatrics. 2006;117:e200–8.
Levi J, Leoniak S, Schmidt R. Evaluating tonsillectomy as a risk factor for childhood obesity. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012;138:897–901.
Katz ES, Moore RH, Rosen CL, Mitchell RB, Amin R, Arens R, et al. Growth after adenotonsillectomy for obstructive sleep apnea: an RCT. Pediatrics. 2014;134:282–9.
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Flegal KM. Prevalence of childhood and adult obesity in the United States, 2011–2012. JAMA. 2014;311:806–14.
Silvestri JM, Weese-Mayer DE, Bass MT, Kenny AS, Hauptman SA, Pearsall SM. Polysomnography in obese children with a history of sleep-associated breathing disorders. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1993;16:124–9.
Chay OM, Goh A, Abisheganaden J, Tang J, Lim WH, Chan YH, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in obese Singapore children. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2000;29:284–90.
Lee CH, Kim YJ, Lee SB, Yoo CK, Kim HM. Psychological screening for the children with habitual snoring. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2014;78:2145–50.
Fujioka M, Young LW, Girdany BR. Radiographic evaluation of adenoidal size in children: adenoidal-nasopharyngeal ratio. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1979;133:401–4.
Brodsky L, Moore L, Stanievich JF. A comparison of tonsillar size and oropharyngeal dimensions in children with obstructive adenotonsillar hypertrophy. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 1987;13:149–56.
Moon JS, Lee SY, Nam CM, Choi JM, Choe BK, Seo JW, et al. 2007 Korean National Growth Charts: review of developmental process and an outlook. Kor J Pediatr. 2008;51:1–25 (in Korean).
Iber C, Ancoli-Israel S, Chesson AL, Quan SF. The AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events: rules, terminology and technical specifications. Westchester: American Academy of Sleep Medicine; 2007.
Chervin RD, Hedger K, Dillon JE, Pituch KJ. Pediatric sleep questionnaire (PSQ): validity and reliability of scales for sleep-disordered breathing, snoring, sleepiness, and behavioral problems. Sleep Med. 2000;1:21–32.
Goodman R. The strengths and difficulties questionnaire: a research note. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 1997;38:581–6.
Ahn JS, Jun SK, Han JK, Noh KS, Goodman R. The development of a Korean version of the strength and difficulties questionnaire. J Kor Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2003;42:141–7 (in Korean).
Kovacs M. University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine. The children’s depression inventory. A self-rated depression scale for school-aged youngsters. Unpublished manuscript, 1983.
Cho SC, Lee YS. Development of the Korean form of the Kovacs’ children’s depression inventory. J Kor Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 1990;29:943–56 (in Korean).
Birmaher B, Khetarpal S, Brent D, Cully M, Balach L, Kaufman J, et al. The screen for child anxiety related emotional disorders (SCARED): scale construction and psychometric characteristics. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1997;36:545–53.
Kim MJ. A validation study of the SCARED: for the elementary school upper grades and middle school students. Sookmyung Women’s University, 2010.
Halbower AC, Degaonkar M, Barker PB, Earley CJ, Marcus CL, Smith PL, et al. Childhood obstructive sleep apnea associates with neuropsychological deficits and neuronal brain injury. PLoS Med. 2006;3:e301.
Sharafkhaneh A, Giray N, Richardson P, Young T, Hirshkowitz M. Association of psychiatric disorders and sleep apnea in a large cohort. Sleep. 2005;28:1405–11.
Bass JL, Corwin M, Gozal D, Moore C, Nishida H, Parker S, et al. The effect of chronic or intermittent hypoxia on cognition in childhood: a review of the evidence. Pediatrics. 2004;114:805–16.
Chervin RD, Ruzicka DL, Archbold KH, Dillon JE. Snoring predicts hyperactivity four years later. Sleep. 2005;28:885–90.
Mitchell RB, Boss EF. Pediatric obstructive sleep apnea in obese and normal-weight children: impact of adenotonsillectomy on quality-of-life and behavior. Dev Neuropsychol. 2009;34:650–61.
Rudnick EF, Mitchell RB. Behavior and obstructive sleep apnea in children: is obesity a factor? Laryngoscope. 2007;117:1463–6.
Griffiths LJ, Dezateux C, Hill A. Is obesity associated with emotional and behavioural problems in children? Findings from the Millennium Cohort Study. Int J Pediatr Obes. 2011;6:e423–32.
Datar A, Sturm R, Magnabosco JL. Childhood overweight and academic performance: national study of kindergartners and first-graders. Obes Res. 2004;12:58–68.
Beebe DW, Ris MD, Kramer ME, Long E, Amin R. The association between sleep disordered breathing, academic grades, and cognitive and behavioral functioning among overweight subjects during middle to late childhood. Sleep. 2010;33:1447–56.
O’Brien LM, Ivanenko A, Crabtree VM, Holbrook CR, Bruner JL, Klaus CJ, et al. Sleep disturbances in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Pediatr Res. 2003;54:237–43.
Funding
No funding was secured for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KJY designed and performed the study, and analyzed the data. KHM designed and performed the study, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. LCH analyzed the data. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the hospital ethics committee.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.Y., Lee, C.H. & Kim, HM. Behavioral consequences of children with sleep-disordered breathing after adenotonsillectomy. World J Pediatr 14, 57–65 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-017-0108-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-017-0108-4