Abstract
Background
Several clinical reports have been published on complications resulting from swallowing multiple magnetic foreign bodies. This study aimed to summarize the clinical experience of managing children who swallowed multiple magnetic foreign bodies.
Methods
We reviewed the clinical records of five children who swallowed multiple magnetic foreign bodies and were admitted to our hospital during June 2012 to June 2014. Details of the patients’ presentation, imaging studies, complications and treatment were recorded.
Results
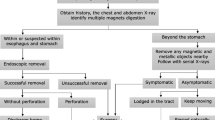
All five children suffered from gastrointestinal perforation and intestinal obstruction. The magnetic foreign bodies caused local bowel wall tissue ischemia necrosis and perforation as well as other complications associated with fistula formation. The magnets were finally removed by laparotomy surgery.
Conclusion
If magnetic foreign bodies cannot be removed by endoscopy, an operation is suggested as soon as possible to avoid serious complications.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Black RE, Johnson DG, Matlak ME. Bronchoscopic removal of aspirated foreign bodies in children. J Pediatr Surg 1994;29:682–684.
Cox S, Brown R, Millar A, Numanoglu A, Alexander A, Theron A. The risks of gastrointestinal injury due to ingested magnetic beads. S Afr Med J 2014;104:277–278.
Anselmi EH, San Román CG, Fontoba JEB, González LA, Dieguez EV, González JL, et al. Intestinal perforation caused by magnetic toys. J Pediatr Surg 2007;42:e13–e16.
Brown JC, Otjen JP, Drugas GT. Pediatric magnet ingestions: the dark side of the force. Am J Surg 2014;207:754–759; discussion 759.
Kim Y, Hong J, Moon SB. Ingestion of multiple magnets: the count does matter. J Pediatr Surg Case Rep 2014;2:130–132.
Mandhan P, Alsalihi M, Mammoo S, Ali MJ. Troubling toys: rare-Earth magnet ingestion in children causing bowel perforations. Case Rep Pediatr 2014;2014:908730.
Silverman JA, Brown JC, Willis MM, Ebel BE. Increase in pediatric magnet-related foreign bodies requiring emergency care. Ann Emerg Med 2013;62:604–608.
Tsai J, Shaul DB, Sydorak RM, Lau ST, Akmal Y, Rodriguez K. Ingestion of magnetic toys: report of serious complications requiring surgical intervention and a proposed management algorithm. Permanente J 2013;17:11–14.
Naji H, Isacson D, Svensson JF, Wester T. Bowel injuries caused by ingestion of multiple magnets in children: a growing hazard. Pediatr Surg Int 2012;28:367–374.
Robinson AJ, Bingham J, Thompson RL. Magnet induced perforated appendicitis and ileo-caecal fistula formation. Ulster Med J 2009;78:4.
Nui A, Hirama T, Katsuramaki T, Maeda T, Meguro M, Nagayama M, et al. An intestinal volvulus caused by multiple magnet ingestion: an unexpected risk in children. J Pediatr Surg 2005;40:e9–e11.
Pryor HI, Lange PA, Bader A, Gilbert J, Newman K. Multiple magnetic foreign body ingestion: a surgical problem. J Am Coll Surg 2007;205:182–186.
İlçe Z, Samsum H, Mammadov E, Celayir S. Intestinal volvulus and perforation caused by multiple magnet ingestion: report of a case. Surg Today 2007;37:50–52.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, YB., Gao, ZG., Xiong, QX. et al. Clinical experience in the treatment of children who swallowed multiple magnetic foreign bodies: A report of five cases. World J Pediatr 13, 274–277 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-016-0083-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-016-0083-1