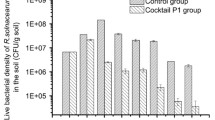
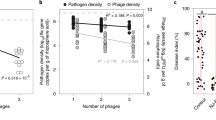
Abstract
This paper takes the phage of potato hospital as the research object. Firstly, the cause and infection way of the disease are analyzed in detail. Then, the viewpoint that the disease is closely related to soil ecology is put forward. Through the analysis of soil ecological environment and factors, and designed and completed the experiment of using the adaptive evolution of a high-temperature environment to screen the stable phages in the storage process. The experimental results show that the interaction of potato plant-related phage mixture in the different soil environments.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriaenssens E, Brister JR (2017) How to name and classify your phage: an informal guide. Viruses 9(4):70
Adriaenssens EM, Van VJ, Vandenheuvel D, Dunon V, Ceyssens PJ, De Proft M, Kropinski AM, Noben JP, Maes M, Lavigne R (2012) T4-related bacteriophage LIMEstone isolates for the control of soft rot on potato caused by ‘Dickeya solani’. PLoS One 7(3):e33227
Alič Š, Naglič T, Tušek-Žnidarič M, Ravnikar M, Rački N, Peterka M, Dreo T (2017) Newly isolated bacteriophages from the podoviridae, siphoviridae, and myoviridae families have variable effects on putative novel Dickeya spp. Front Microbiol 08:1870
Ando H, Lemire S, Pires DP, Lu TK (2015) Engineering modular viral scaffolds for targeted bacterial population editing. Cell Syst 1(3):187–196
Arora RK, Khurana SMP (2004) Major fungal and bacterial diseases of potato and their management. Dis Manag Fruit Veg 1:89–231
Bae JY, Wu J, Lee HJ, Jo EJ, Murugaiyan S, Chung E, Lee SW (2012) Biocontrol potential of a lytic bacteriophage PE204 against bacterial wilt of tomato. J Microbiol Biotechnol 22(12):1613–1620
Balogh B, Canteros BI, Stall RE, Jones JB (2008) Control of citrus canker and citrus bacterial spot with bacteriophages. Plant Dis 92(7):1048–1052
Helmberger MS, Tiemann LK, Grieshop MJ (2020) Towards an ecology of soil microplastics. Funct Ecol 34(3):550–560
Lee S, Lee J, Hwang AR, Kim YH, Min J (2020) A specific nonenal-binding peptide, p4 screened by phage display can remove trans-2-nonenal. Mol Biotechnol 62(5):273–279
Wang H, Zhong H, Bo G (2018) Existing forms and changes of nitrogen inside of horizontal subsurface constructed wetlands. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(1):771–781
Whitworth JL, Selstedt RA, Westra AAG, Nolte P, Duellman K, Yellareddygari SKR, Gudmestad NC (2019) Symptom expression of mainstream and specialty potato cultivars to bacterial ring rot (Clavibacter sepedonicus) and evaluation of in-field detection. Am J Potato Res 96(4):427–444
Zhang K, Lu H, Wan C, Tang D (2020) The spread and transmission of sweet potato virus disease (SPVD) and its effect on the gene expression profile in sweet potato. Plants 9(4):492
Funding
This work is support by Hebei Province Science and Technology Pillar Program: Greation of Potatos High-quality Germplasm Resources and New Breeding Technique (No. 16227508D).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Geological Modeling and Geospatial Data Analysis
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Wang, L., Chen, Y. et al. The interaction between potato pathogenic phage and soil microecology. Arab J Geosci 13, 874 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05910-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05910-w