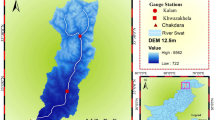
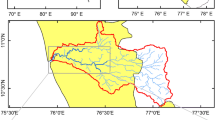
Abstract
Water discharge is the main parameter in hydraulic modeling for flood hazard assessment. However, the unavailability of data on discharge and observed river morphologies resulted in erroneous calculations and irregularities in flood inundation mapping. The objectives of this study are (i) to investigate uncertainties of hydraulic parameters (width, cross-sectional depth, and channel slope) used in discharge equation and (ii) to examine the influence of estimate discharge on water extent and flood depth with different boundary conditions on interferometric synthetic aperture radar (IFSAR) and modified IFSAR DEMs. Sensitivity analysis was conducted with the Monte Carlo simulation method to generate random data combinations. Bjerklie’s equation was used to calculate discharge based on the three variables, and Manning’s n was substituted into the Hydrologic Engineering Center River Analysis System (HEC-RAS) model. TerraSAR-X was used to distinguish existing flood water bodies and normal water extent. The uncertainty of the combined variables was assessed with the likelihood measures such as F-statistic, mean absolute error, root mean square error, and Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency which compares observed and predicted inundated area as well as flood water depth simulated using the HEC-RAS model.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah S, Ahmad Z (2007) Pesawah rugi RM27j banjir di Kedah. Utusan Online
Alaghmand S, Rozi A, Ismail A, Vosoogh B (2010) GIS-based river flood hazard mapping in urban area (a case study in Kayu Ara River basin, Malaysia). Int J Eng Technol 2:488–500
Ali M, Khan SJ, Aslam I, Khan Z (2011) Simulation of the impacts of land-use change on surface runoff of Lai Nullah Basin in Islamabad, Pakistan. Landsc Urban Plan 102:271–279
Al-sharif A, Pradhan B (2014) Monitoring and predicting land use change in Tripoli Metropolitan City using an integrated Markov chain and cellular automata models in GIS. Arab J Geosci 7(10):4291–4301
Bates PD, Marks KJ, Horritt MS (2003) Optimal use of high-resolution topographic data in flood inundation models. Hydrol Process 17:537–557
Berezowski T, Chorma'nski J, Batelaan O, Canters F, Van De Voorde T (2012) Impact of remotely sensed land-cover proportions on urban runoff prediction. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 16:54–65
Bhuyian NM, Kalyanapu AJ, Nardi F (2015) Approach to digital elevation model correction by improving channel conveyance. J Hydrol Eng 20:1–10
Birkinshaw SJ, Moore P, Kilsby CG, O’Donnell GM, Hardy AJ, Berry PAM (2014) Daily discharge estimation at ungauged river sites using remote sensing. Hydrol Process 28:1043–1054
Bjerklie DM (2007) Estimating the bankfull velocity and discharge for rivers using remotely sensed river morphology information. J Hydrol 341:144–155
Bjerklie DM, Lawrence Dingman S, Vorosmarty CJ, Bolster CH, Congalton RG (2003) Evaluating the potential for measuring river discharge from space. J Hydrol 278:17–38
Bjerklie DM, Moller D, Smith LC, Dingman SL (2005) Estimating discharge in rivers using remotely sensed hydraulic information. J Hydrol 309:191–209
Brandimarte L, Di Baldassarre G (2012) Uncertainty in design flood profiles derived by hydraulic modelling. Hydrol Res 43:753–761
Brunner GW (2010) HEC-RAS, river analysis system hydraulic reference manual. US Army Corps of Engineers, Washington
Cook A, Merwade V (2009) Effect of topographic data, geometric configuration and modeling approach on flood inundation mapping. J Hydrol 377:131–142
Dams J, Dujardin J, Reggers R, Bashir I, Canters F, Batelaan O (2013) Mapping impervious surface change from remote sensing for hydrological modeling. J Hydrol 485:84–95
Di Baldassarre G, Schumann G, Bates PD (2009) A technique for the calibration of hydraulic models using uncertain satellite observations of flood extent. J Hydrol 367:276–282
Di Baldassarre G, Schumann G, Bates PD, Freer JE, Beven KJ (2010) Flood-plain mapping: a critical discussion of deterministic and probabilistic approaches. Hydrol Sci J 55:364–376
DID (2009) Ringkasan Laporan Banjir Tahunan Bagi Tahun 2009/2010. Malaysia
DID (2010a) Banjir Daerah Kubang Pasu/Pdg. Terap November 2010
DID (2010b) Ringkasan Laporan Banjir Tahunan Bagi Tahun 2010/2011. Malaysia
Dingman SL, Sharma KP (1997) Statistical development and validation of discharge equations for natural channels. J Hydrol 199:13–35
Eleuterio J (2012) Flood risk analysis: impact of uncertainty in Hazard modelling and vulnerability assessments. PhD thesis, University of Strasbourg
Getahun Y, Gebre S (2015) Flood hazard assessment and mapping of flood inundation area of the Awash River basin in Ethiopia using GIS and HEC-GeoRAS/HEC-RAS model. J Civ Environ Eng 5:1–12
Gianinetto M, Villa P, Lechi G (2006) Postflood damage evaluation using Landsat TM and ETM + data integrated with DEM. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 44:236–243
Grimaldi S, Li Y, Pauwels VRN, Walker JP (2016) Remote sensing-derived water extent and level to constrain hydraulic flood forecasting models: opportunities and challenges. Surv Geophys 37:977–1034
Hashim S, Mohd W, Wan N, Adnan NA (2016) Regional conference on science, technology and social sciences (RCSTSS 2014)
Hodgson ME, Jensen JR, Tullis JA, Riordan KD, Archer CM (2003) Synergistic use of Lidar and color aerial photography for mapping urban parcel imperviousness. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 69:973–980
Horritt MS (2006) A methodology for the validation of uncertain flood inundation models. J Hydrol 326:153–165
Huang B, Li H, Huang X (2010) A level set filter for speckle reduction in SAR images. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process 2010:1–14
Ibrahim NR, Jamal MH, Mohd Nasir KA, Md. Din MF, Ismail Z (2014) runoff modelling of Sungai Johor watershed. In: 13th Int Conf Urban Drain. Sarawak, Malaysia, pp 1–7
Jarret D, Asce M (1984) Hydraulics of high-gradient streams. J Hydraul Eng 110:1519–1539
Jung Y, Merwade V, Asce M (2012) Uncertainty quantification in flood inundation mapping using generalized likelihood uncertainty estimate and sensitivity analysis. J Hydrol Eng 17:507–520
Jung Y, Merwade V, Yeo K, Shin Y, Lee SO (2013) An approach using a 1D hydraulic model, Landsat imaging and generalized likelihood uncertainty estimation for an approximation of flood discharge. Water 5:1598–1621
Jung Y, Kim D, Kim D, Kim M, Lee SO (2014) Simplified flood inundation mapping based on flood elevation-discharge rating curves using satellite images in gauged watersheds. Water 6:1280–1299
Knebl MR, Yang ZL, Hutchison K, Maidment DR (2005) Regional scale flood modeling using NEXRAD rainfall, GIS, and HEC-HMS/ RAS: a case study for the San Antonio River basin summer 2002 storm event. J Environ Manag 75:325–336
Komi K, Neal J, Trigg MA, Diekkrüger B (2017) Modelling of flood hazard extent in data sparse areas: a case study of the Oti River basin, West Africa. J Hydrol Reg Stud 10:122–132
Lee JS (1983) Digital image smoothing and the sigma filter. Comput Vision, Graph Image Process 24:255–269
Li S, Sun D, Goldberg M, Stefanidis A (2013) Derivation of 30-m-resolution water maps from TERRA/MODIS and SRTM. Remote Sens Environ 134:417–430
Lin S, Jing C, Coles NA, Chaplot V, Moore NJ, Wu J (2013) Evaluating DEM source and resolution uncertainties in the soil and water assessment tool. Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 27:209–221
Mason DC, Garcia-Pintado J, Cloke HL, Dance SL (2015) The potential of flood forecasting using a variable-resolution global digital terrain model and flood extents from synthetic aperture radar images. Front Earth Sci 3:1–14
Merwade V, Cook A, Coonrod J (2008a) GIS techniques for creating river terrain models for hydrodynamic modeling and flood inundation mapping. Environ Model Softw 23:1300–1311
Merwade V, Olivera F, Arabi M, Edleman S (2008b) Uncertainty in flood inundation mapping: current issues and future directions. J Hydrol Eng 13:608–620
Miller JD, Kim H, Kjeldsen TR, Packman J, Grebby S, Dearden R (2014) Assessing the impact of urbanization on storm runoff in a peri-urban catchment using historical change in impervious cover. J Hydrol 515:59–70
Mohd W, Wan N, Abdullah MA, Hashim S (2014) Evaluation of vertical accuracy of digital elevation models generated from different sources : case study of Ampang and Hulu Langat. pp 1–17
Mokhtar ES, Pradhan B, Ghazali AH, Shafri HZM (2017) Comparative assessment of water surface level using different discharge prediction models. Nat Hazards 87(2):1125–1146
MStar 2010. Najib Umum Bantuan Ihsan Padi Akibat Banjir Dinaikkan RM876. Available from: http://www.mstar.com.my/berita/berita-semasa/2010/12/09/najib-umum-bantuan-ihsan-padi-akibat-banjir-dinaikkan-rm876/. Accessed 01 Nov 2015
National Research Council (2007) Elevation data for floodplain mapping. The National Academies Press, Washington, DC. https://doi.org/10.17226/11829
Nor Aizam A, Zulfadhli Ainul Hakim Z, Ernieza Suhana M, Zaharah MY (2014) Geospatial flood inundation modelling and estimation of Sungai Muda Kedah floodplain, Malaysia geospatial flood inundation modelling and estimation of. In: Int Conf – reflections Creat public Engagem Mak place [Internet]. Bandung, Indonesia, pp 1–9
Omer CR, Nelson EJ, Zundel AK (2003) Impact of varied data resolution on hydraulic modeling and floodplain delineation. J Am Water Resour Assoc 39:467–475
Pappenberger F, Beven K, Horritt M, Blazkova S (2005) Uncertainty in the calibration of effective roughness parameters in HEC-RAS using inundation and downstream level observations. J Hydrol 302:46–69
Pappenberger F, Matgen P, Beven KJ, Henry JB, Pfister L, Fraipont P (2006) Influence of uncertain boundary conditions and model structure on flood inundation predictions. Adv Water Resour 29:1430–1449
Pradhan B, Youssef M (2011) A 100-year maximum flood susceptibility mapping using integrated hydrological and hydrodynamic models: Kelantan River corridor, Malaysia. J Flood Risk Manag 4:189–202
Pradhan B, Hagemann U, Shafapour Tehrany M, Prechtel N (2014) An easy to use ArcMap based texture analysis program for extraction of flooded areas from TerraSAR-X satellite image. Comput Geosci 63:34–43
Pulvirenti L, Pierdicca N, Chini M, Guerriero L (2011) An algorithm for operational flood mapping from synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data using fuzzy logic. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 11:529–540
Said MZ, Abdul Gapor S, Samian MN, Abd Aziz AM (2013) Konflik di pusat pemindahan banjir: Kajian Kes di Daerah Padang. Malaysia J Soc Sp 9:61–69
Saksena S, Merwade V (2015) Incorporating the effect of DEM resolution and accuracy for improved flood inundation mapping. J Hydrol 530:180–194
Salimi S, Reza Ghanbarpour M, Solaimani K, Ahmadi MZ (2008) Floodplain mapping using hydraulic simulation model in GIS.pdf. J Appl Sci 8:660–665
Savage JTS, Bates P, Freer J, Neal J, Aronica G (2016) When does spatial resolution become spurious in probabilistic flood inundation predictions? Hydrol Process 30:2014–2032
Schumann G, Matgen P, Cutler MEJ, Black A, Hoffmann L, Pfister L (2008) Comparison of remotely sensed water stages from LiDAR, topographic contours and SRTM. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 63:283–296
Sichangi AW, Wang L, Yang K, Chen D, Wang Z, Li X, Zhou J, Liu W, Kuria D (2016) Estimating continental river basin discharges using multiple remote sensing data sets. Remote Sens Environ 179:36–53
Sun W, Ishidaira H, Bastola S, Yu J (2015) Estimating daily time series of streamflow using hydrological model calibrated based on satellite observations of river water surface width: toward real world applications. Environ Res 139:36–45
Tarpanelli A, Barbetta S, Brocca L, Moramarco T (2013a) River discharge estimation by using altimetry data and simplified flood routing modeling. Remote Sens 5:4145–4162
Tarpanelli A, Brocca L, Melone F, Moramarco T (2013b) Hydraulic modelling calibration in small rivers by using coarse resolution synthetic aperture radar imagery. Hydrol Process 27:1321–1330
Thanapura P, Helder DL, Burckhard S, Warmath E, Neill MO, Galster D (2007) Mapping urban land cover using QuickBird NDVI and GIS spatial modeling for runoff coefficient determination. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 73:57–65
Tsubaki R, Fujita I (2010) Unstructured grid generation using LiDAR data for urban flood inundation modelling. Hydrol Process 24:1404–1420
Turner AB, Colby JD, Csontos RM, Batten M (2013) Flood modeling using a synthesis of multi-platform LiDAR data. Water 5:1533–1560
Wang W, Yang X, Yao T (2012) Evaluation of ASTER GDEM and SRTM and their suitability in hydraulic modelling of a glacial lake outburst flood in Southeast Tibet. Hydrol Process 26:213–225
Weng Q (2012) Remote sensing of impervious surfaces in the urban areas: requirements, methods, and trends. Remote Sens Environ 117:34–49
Wu F, Zhan J, Su H, Yan H, Ma E (2015) Scenario-based impact assessment of land use / cover and climate changes on watershed hydrology in Heihe River basin of Northwest China. Adv Meteorol 2015:1–11
Xie H, Lian Y (2013) Uncertainty-based evaluation and comparison of SWAT and HSPF applications to the Illinois River basin. J Hydrol 481:119–131
Yan K, Di Baldassarre G, Solomatine DP (2013) Exploring the potential of SRTM topographic data for flood inundation modelling under uncertainty. J Hydroinf 15:849–861
Zazo S, Molina JL, Rodríguez-Gonzálvez P (2015) Analysis of flood modeling through innovative geomatic methods. J Hydrol 524:522–537
Zhang S, Pan B (2014) An urban storm-inundation simulation method based on GIS. J Hydrol 517:260–268
Zhang Y, Zhang H, Lin H (2014) Improving the impervious surface estimation with combined use of optical and SAR remote sensing images. Remote Sens Environ 141:155–167
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Universiti Teknologi MARA Perlis, Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia, and Universiti Putra Malaysia. The authors wish to acknowledge the Malaysia Remote Sensing Agency, the Federal Department of Town and Country Planning Malaysia, the Department of Irrigation and Drainage and the Water Resources Engineering and Management Research Center, Universiti Teknologi MARA, Penang, Malaysia for providing satellite images, land use map, and hydraulic data and Qliner for analysis implementation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Global Sustainability through Geosciences and Civil Engineering
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mokhtar, E.S., Pradhan, B., Ghazali, A.H. et al. Assessing flood inundation mapping through estimated discharge using GIS and HEC-RAS model. Arab J Geosci 11, 682 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-4040-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-4040-2