Abstract
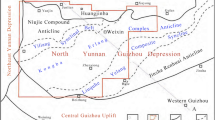
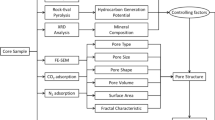
Knowledge of pore structure and adsorption capacity provides guidance for better studying the origin, hydrocarbon distribution, and productivity of shale gas reservoir. In this study, pore structure characteristics of six shale core plugs with different maturity from the Lower Silurian Longmaxi formation in south China were investigated using the Rock-eval analysis, X-ray diffraction, total organic carbon (TOC) content test, and scanning electron microscope (SEM) observation. To further investigate the influence of maturity, the adsorption behavior of gas shale was experimentally measured, with the maximal pressure being 20 MPa. Rock-eval analysis indicates that Ro is 0.67~1.34%. SEM results show that organic matter (OM) pores are abundant in high-maturity shale sample. The OM pores are mainly irregular to elliptical in shape, the size is 8~100 nm. The TOC content is 0.16~4.21% and shows a positive correlation with the BET surface area. A negative relationship exists between TOC content and average pore diameter, which indicates that abundant nanometer pores are related to the OM. A noticeable characteristic in the pore size distribution curve is that the content of micropores (pore width < 2 nm) increases with the increasing TOC content. Additionally, the thermal maturity results in significant difference in methane adsorption capacity. Maximal adsorption capacity of shale samples is also lineally correlated with TOC content, which increases with maturity. This study provides a quantitative understanding of how maturity affects pore structure and adsorption behavior of shale gas reservoir.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chalmers GRL, Bustin RM (2008) Lower Cretaceous gas shales in northeastern British Columbia, part 1: geological controls on methane sorption capacity. Bull Can Petrol Geol 56:1–21. https://doi.org/10.2113/gscpgbull.56.1.1
Gasparik M, Ghanizadeh A, Bertier P, Gensterblum Y, Bouw S, Krooss BM (2012) High-pressure methane sorption isotherms of black shales from the Netherlands. Energy Fuel 26:4995–5004. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef300405g
Gasparik M, Bertier P, Gensterblum Y, Ghanizadeh A, Krooss BM, Littke R (2014) Geological controls on the methane storage capacity in organic-rich shales. Int J Coal Geol 123:34–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2013.06.010
Jarvie DM, Hill RJ, Ruble TE, Pollastro RM (2007) Unconventional shale-gas systems: the Mississippian Barnett Shale of north-central Texas as one model for thermogenic shale-gas assessment[J]. AAPG Bull 91(4):475–499. https://doi.org/10.1306/12190606068
Jiang Z, Zhao L, Zhang D (2018) Study of adsorption behavior in shale reservoirs under high pressure[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science & Engineering 49:275–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2017.11.009
Li X, Wang Y, Zhang J, Guo M, Zhao P, Xu H, Yang J, Wang F (2016) Pore characteristics of shale gas reservoirs from the lower Paleozoic in the southern Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Geoscience 1(3):195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnggs.2016.07.002
Paylor A (2017) The social–economic impact of shale gas extraction: a global perspective. Third World Q 38(2):340–355. https://doi.org/10.1080/01436597.2016.1153420
Ross DJK, Bustin RM (2009) The importance of shale composition and pore structure upon gas storage potential of shale gas reservoirs. Mar Pet Geol 26:916–927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2008.06.004
Wang L, Fu Y, Li J, Sima L, Wu Q, Jin W, Wang T (2016) Mineral and pore structure characteristics of gas shale in Longmaxi formation: a case study of Jiaoshiba gas field in the southern Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Arab J Geosci 9(19):733. https://doi.org/10.1007/s125I7-016-2763-5
Yang F, Ning Z, Zhang R, Zhao H, Krooss BM (2015) Investigations on the methane sorption capacity of marine shales from Sichuan Basin, China. Int J Coal Geol 146:104–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2015.05.009
Yang F, Ning Z, Wang Q, Zhang R, Krooss BM (2016) Pore structure characteristics of lower Silurian shales in the southern Sichuan Basin, China: insights to pore development and gas storage mechanism. Int J Coal Geol 156:12–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2015.12.015
Yang F, Xie C, Ning Z, Krooss BM (2017) High-pressure methane sorption on dry and moisture-equilibrated shales[J]. Energy Fuel 31(1):482–492. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b02999
Zhao H, Ning Z, Zhao T, et al. (2015) Geological and petrophysical characterization of tight oil reservoirs: a case study from Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin in North China[C]//SPE Asia Pacific Unconventional Resources Conference and Exhibition. Society of Petroleum Engineers. https://doi.org/10.2118/177012-MS
Zhao T, Li X, Ning Z, Zhao H, Li M (2017a) Molecular simulation of methane adsorption on type II kerogen with the impact of water content[J]. J Pet Sci Eng 161:302–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2017.11.072
Zhao T, Li X, Zhao H, Li M (2017b) Molecular simulation of adsorption and thermodynamic properties on type II kerogen: influence of maturity and moisture content[J]. Fuel 190:198–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.11.027
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Geo-Resources-Earth-Environmental Sciences
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, T., Li, X., Ning, Z. et al. Pore structure and adsorption behavior of shale gas reservoir with influence of maturity: a case study of Lower Silurian Longmaxi formation in China. Arab J Geosci 11, 353 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3673-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3673-5