Abstract
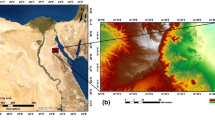
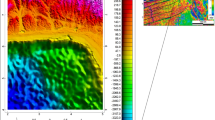
The study area is located at the east of Qattara Depression at the north of the Western Desert of Egypt. The study area contains Abu Gharadig basin, which is the most petroliferous basin in the Egyptian Western Desert. Only three exploratory wells are presented in the study area, showing a thick sediment section overlying basement rocks. Magnetic data have been frequently used in geophysical exploration. Aeromagnetic data are mainly utilized to estimate the depth to the magnetic basement as well as to delineate the possible structures of the study area. The depth to magnetic basement has been estimated using the analytical solution of exponential equations obtained from the Fourier transformation of magnetic data, assuming multi-prisms. The depths obtained from this technique vary from 0.70 to 2.91 km with an average depth of 2.08 km. Local phase filters have been mainly used as edges detector where the possible occurrences structures can be delineated. Hyperbolic tilt angle, second-order tilt angle, and normalized total horizontal derivative (TDX) provide the best results for delineating the possible structures, showing the possible contacts within the basement of the study area. The edge enhancement filters show that the study area has been affected by different structural trends taking E-W, NE-SW, NNE-SSW, N-S, and ENE-WSW directions.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu El-Ata ASA (1990) A comparative study of some aeromagnetic techniques for basement configuration in Qattara depression area, Western Desert, Egypt. M.E.R.C. Ain Shams Univ Earth Sci. Ser. 4:65–80
Abu El-Ata A.S.A., Abd El-Nabi S.H. (1987) The role of the structural activations and the stratigraphic manifestations in the origin of the Qattara Depression, Western Desert, Egypt, using gravity modelling; E.G.S. proc. of 5th ANN. Meet., Cairo, p. 90–110
Aydin I, Oksum E (2010) Exponential approach to estimate the curie-temperature depth. J Geophys Eng 7(2):113–125
Aydin I, Oksum E (2012) MATLAB code for estimating magnetic basement depth using prisms. Comput Geosci 46:183–188
Blakely TJ (1996) Potential field theory in gravity and magnetic applications, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 300–305
Cooper GRJ, Cowan DR (2006) Enhancing potential field data using filters based on the local phase. Comput Geosci 32:1585–1591
Fitzgerald D, Yassi N, Dart P (1997) A case study on geophysical gridding techniques: INTREPID perspective. Explor Geophys 28:204–208
Frizon de Lamotte D, Raulin C, Mouchot N, Daveau JCW, Blanpied C, Ringenbach JC (2011) The southernmost margin of the Tethys realm during the Mesozoic and Cenozoic: Initial geometry and timing of the inversion processes. Tectonics 30:TC3002. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010TC002691
Meshref WM, El-Sirafe AM (1988) Geophysical interpretation of the regional structural setting of Abu Gharadig Basin, Northern Western Desert of Egypt. E.G.S. Proc. of the 6th Ann. Meet. Cairo. P.115–123
Miller HG, Singh V (1994) Potential field tilt—a new concept for location of potential field sources. J Appl Geophys 32:213–217
Raulin C, Frizon de Lamotte D, Bouaziz S, Khomsi S, Mouchot N, Ruiz G, Guillocheau F (2011) Late Triassic–Early Jurassic block tilting along E–W faults, in southern Tunisia: new interpretation of the Tebaga of Medenine. J Afr Earth Sci 61(1):94–104
Saad MH (2008) Delineating the subsurface structural setting of the east Qattara Depression area, North Western Desert, Egypt, using aeromagnetic and gravity data, Egypt. J Petrol 17:117–131
Spiegel MR (1972) Theory and Problems of Complex Variables. McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York.
Verduzco B, Fairhead JD, Green CM, MacKenzie C (2004) New in-sights into magnetic derivatives for structural mapping. Lead Edge 23:116–119
Wijns C, Perez C, Kowalczyk P (2005) Theta map: edge detection in magnetic data. Geophysics 70:39–43
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank Mohamed H. Saad of Egyptian Petroleum Institute for providing me the aeromagnetic data. Also, special thanks go to the two anonymous reviewers for their comments which improve the original manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Geology of North Africa and Mediterranean Regions
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Garni, M.A. Aeromagnetic data interpretation of east Qattara Depression, Northwest Desert, Egypt. Arab J Geosci 11, 133 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3460-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3460-3