Abstract
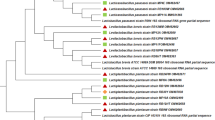
Water vending machines provide an alternative source of clean and safe drinking water to the consumers. However, the quality of drinking water may alter due to contamination from lack of hygienic practices and maintenance of the machines. Hence, this study was conducted to determine the microbiological quality of water from vending machines and associated contact surfaces. Seventeen water samples and 85 swab samples (nozzles, drip trays, coin slots, buttons and doors) from 3 locations in Kelantan were collected. Polymerase chain reaction amplification and 16S ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) sequencing were carried out and sequences obtained were compared against the sequences available in the National Centre for Biotechnology Information database using the basic local alignment search tool programme. Coliform counts were observed in 94.12 % of water samples, 76.47 % of nozzles and 82.35 % of drip tray swabs. Furthermore, results of 16S rRNA sequence analysis indicated that two gram-negative isolates were identified as Escherichia coli U 5/41 (Accession no. NR_024570.1) and E. coli O157:H7 EDL933 (Accession no. CP008957.1) with similarity value of 100 %, respectively. The results from this study further improve our understanding of the potential microorganisms in drinking water. Regular maintenance and cleaning of water vending machines are important to reduce bacterial growth and the presence of waterborne pathogens.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali SS, Anwar Z, Zaman J, Khattak K, Islamic I (2012) Microbial analysis of drinking water and water distribution system in new urban Peshawar. Curr Res J Biol Sci 4:731–737
Andreoli SP, Trachtman H, Acheson DWK, Siegler RL, Obrig TG (2002) Hemolytic uremic syndrome: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and therapy. Pediatr Nephrol 17:293–298
APHA (American Public Health Association) (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. APHA, Washington, D.C
Beloin C, Roux A, Ghigo J-M (2008) Escherichia coli biofilms. Curr Top Microbiol 322:249–289
Bloomfield SF, Exner M, Signorelli C, Nath KJ, Scott EA (2012) The chain of infection transmission in the home and everyday life settings and the role of hygiene in reducing the risk of infection. Int Sci Forum Home Hygiene. http://www.ifh-homehygiene.org/sites/default/files/publications/IFHinfectiontransmissionreviewFINAL.pdf. Accessed 7 Sept 2015
Chaidez C, Rusin P, Naranjo J, Gerba CP (2010) Microbiological quality of water vending machines. Int J Environ Heal Res 9:197–206
Du S, Knorr V (2004) Drinking-water quality and issues associated with water vending machines in the city of Los Angeles. J Environ Health 66:25–30
Elalfy SM (2007) Bacteriological quality of drinking water dispensed from street’s mains supplied, stand floor water coolers. Eleventh International Water Technology Conference 995–1004
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) (2011) Water treatment manual: Disinfection. https://www.epa.ie/pubs/advice/drinkingwater/Disinfection2_web.pdf. Accessed 29 Mar 2014
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) (2012) Edition of the drinking water standards and health advisors. Office of Water U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC 5–12
Hertin KJ (2011) A comparative study of indicator bacteria present in ice and soda from Las Vegas food establishments. B. Sc. Thesis. University of Nevada, Las Vegas, U.S
IBWA (2015) International Bottled Water Association. http://www.bottledwater.org/. Accessed 14 Jan 2015
Ladner DA (2009) Effects of bloom-forming algae on fouling integrated membrane systems in seawater desalination. Ph. D. Thesis. University of Illinois, U.S
Lakshmanan C, Schaffner D (2006) Understanding and controlling microbiological contamination of beverage dispensed in university food service operations. Food Prot Trends 26:27–31
Mako SL, Harrison MA, Sharma V, Kong F (2014) Microbiological quality of ice made and bagged on-premises in retail stores and in self-service vending machines in comparison to manufactured produced ice in Georgia, University of Georgia 15–55
Momba MNB (2012) Assessment of groundwater quality in the rural areas of the North West Province, South Africa. Sci Res Essays 7:903–914
Parsek MR, Singh PK (2003) Bacterial biofilms: an emerging link to disease pathogenesis. Annu Rev Microbiol 57:677–701
Peacock E, Jacob VW, Fallone SM (2001) Escherichia coli O157:H7: Etiology, clinical features, complications and treatment. Nephr Nurs J 28:547–555
Prasai T, Lekhak B, Joshi DR, Baral MP (2007) Microbiological analysis of drinking water of Kathmandu Valley. J Sci World 5:112–114
Price JH, Murnan J, Moore B (2006) Soft drink vending machines in schools: a clear and present danger. Am J Health Edu 37:306–314
Public Health England (n.d.) Bacteria collection: Escherichia coli. http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/bacteria/detail.jsp?collection=nctc&refId=NCTC%209001. Accessed 08 Jan 2016
Pupo GM, Karaolis DKR, Lan RT, Reeves PR (1997) Evolutionary relationships among pathogenic and nonpathogenic Escherichia coli strains inferred from multilocus enzyme electrophoresis and mdh sequence. Infect Immun 65:2685–2692
Ramadan A, Alatawi A, Susilowati A, Hailu HW (2015) Biochemical and molecular characterization of food contaminating bacteria isolates from food stall vegetables. Br Microbiol Res J 5:406–410
Rim AH, Azza AH, Wafaa MK (2009) Assessment of the quality of water from some public coolers in Alexandria, Egypt. J Egypt Public Health Assoc 84:198–217
Robertson P (1987) The modern drinks vending machine—A link in the food poisoning chain? Environ Health 94:281–285
Sabat G, Rose P, Hickey WJ, Harkin JM, Sabat G, Rose P, Hickey WJ (2000) Selective and sensitive method for PCR amplification of Escherichia coli 16S rRNA genes in soil. App Environ Microb 66:844–849
Shar AH, Kazi YF, Zardari M, Soomro IH (2008) Enumeration of total and fecal coliform bacteria in drinking water of Khairpur Sindh. Pak J Med Resour 47:28–36
State L, Omezuruike OI, Damilola AO, Adeola OT (2008) Microbiological and physicochemical analysis of different water samples used for domestic purposes in Abekouta and Ojota, Lagos State, Nigeria. Afr J Biotechnol 7:617–621
Tobin RS, Smith DK, Lindsay JA (1981) Effects of activated carbon and bacteriostatic filters on microbiological quality of drinking water. App Environ Microb 41:646–651
WHO (World Health Organization) (2004) Guidelines for drinking water quality. World Health Organization, Geneva
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, E.Y., Arifullah, M. & Soon, J.M. Identification of Escherichia coli Strains from Water Vending Machines of Kelantan, Malaysia Using 16S rRNA Gene Sequence Analysis. Expo Health 8, 211–216 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0194-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0194-x