Abstract
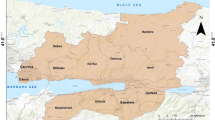
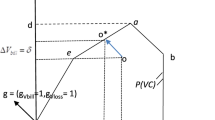
The high level of the non-revenue water (NRW: water not generating revenues) is a well-acknowledged problem water utilities are straggling with in areas facing water scarcity. High NRW values jeopardize the sustainability of water utilities, especially in cases, where these values exceed 50 % of the System Input Volume. WATERLOSS project developed a Decision Support System to help water utility managers design the most effective/efficient NRW reduction strategy. The project’s first step was to evaluate the performance of the water distribution systems selected as case studies. The paper presents the respective results of eight cases from Cyprus, Greece, Italy, France and Spain, based on a modified International Water Association Water Balance adapted to the water pricing practices met across the Mediterranean (high Fixed Charge included in the water tariffs). The results revealed that although almost all cases experience high NRW levels, the high Fixed Charge reduces the actual revenue losses, thus providing a perfect excuse to the managers of the local water utilities do almost nothing to address the actual extent of the NRW problem in their systems.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alegre H, Baptista J, Cabrera EJr, Cubillo F, Duarte P, Hirner W, Merkel W, Parena R (2006) Performance Indicators for Water Supply Services. 2nd Edition, IWAp., London, UK
Almandoz J, Cabrera E, Arregui F, Cobacho R (2005) Leakage assessment through water distribution network simulation. Water Resour Plan Manage 131:458–66
Arregui F, Cabrera E, Cobacho R, Garcia-Serra J (2006) Reducing apparent losses caused by meters inaccuracies. Water Pract Technol doi:10.2166/wpt.2006.0093
Criminisi A, Fontanazza CM, Freni G, Loggi GL (2009) Evaluation of the apparent losses caused by water meter under-registration in intermittent water supply. Water Sci Technol 60:2373–82
Farley M, Trow S (2003) Losses in water distribution networks: a practitioner’s guide to assessment, monitoring and control. IWA, London
Feldman M (2009), Aspects of energy efficiency in water supply systems. In: International conference on the waterloss, IWA, Cape Town, pp 26–30 April 2009
Fereol E (2005) How to measure and reduce water meter park inefficiency? In: International conference on the leakage, IWA, Halifax, September 2005
Georgiadis S, Kanellopoulou S (2008) Pressure management in the water supply network of Athens, Greece. In: International conference on the world water congress, IWA, Vienna
Kanakoudis V (2004) A troubleshooting manual for handling operational problems in water pipe networks. Water Supply Res Technol AQUA 53:109–24
Kanakoudis V, Tsitsifli S (2010) Water volume vs. revenues oriented water balance calculation for urban water networks: the “Minimum Charge Difference” component makes a difference. In: International conference on the waterloss, IWA, Sao Paolo
Kanakoudis V, Tsitsifli S (2013) Using the bimonthly wb of a non-fully monitored water distribution network with seasonal water demand peaks to define its actual nrw level: the case of Kos town Greece. Urban Water. doi:10.1080/1573062X.2013.806563
Kanakoudis V, Tsitsifli S, Samaras P, Zouboulis A (2013a) Assessing the performance of urban water networks performance assessment results across the EU Mediterranean area: the paradox of high NRW levels and absence of NRW reduction measures planning. Water Sci Technol: Water Supply 13(4):939–950
Kanakoudis V, Tsitsifli S, Samaras P, Zouboulis A (2013b) Urban water distribution networks performance assessment: comparing eight cases from Cyprus, Greece, Italy, France and Spain, located within the EU Mediterranean basin. IPWE. In: 6th International perspective on water resources & the environment conference, Izmir, Turkey
Karadirek I, Kara S, Yilmaz G, Muhammetoglu A, Muhammetoglu H (2010) Implementation of hydraulic modelling for water-loss reduction through pressure management. Water Resour Manag 26:2555–2568
Lambert A, Morrison J (1996) Recent developments in application of “bursts and background estimates” concepts for leakage management. Water Environ Manag 10:100–104
Lambert A, Brown T, Takizawa M, Weimer D (1999) Review of performance indicators for real losses from water supply systems. Water Supply Res Technol AQUA 48:227–237
Lambert A (2002) International report: water losses management and techniques. Water Supply, vol 2, pp 21–20
Liemberger R, Brothers K, Lambert A, McKenzie R, Rizzo A, Waldron T (2007) Water loss performance indicators. In: International Conference on the WaterLoss, IWA, Bucharest, vol 1, pp 148–160
Male J, Noss R, Moore I (1985) Identifying and reducing losses in water distribution systems. Noyes Publications, Park Ridge
McKenzie R, Seago C, Liemberger R (2007) Benchmarking of losses from potable water reticulation systems: results from IWA Task Team. In: International conference waterloss, IWA, Bucharest, Romania, vol 1, pp 161–75
Obradovic D (2000) Modeling of demand and losses in real-life water distribution systems. Urban Water 2:131–139
Rizzo A, Cilia J (2005) Quantifying meter under-registration caused by the ball valves of roof tanks (for indirect plumbing systems). In: International conference leakage, IWA, Halifax
Rizzo A, Bonello M, Galea St. John S (2007) Trials to quantify and reduce in-situ meter under-registration. In: International conference on waterloss, IWA, Bucharest, vol 3, pp 696–704
Tabesh M, Asadiyani Yekta AH, Burrows R (2009) An integrated model to evaluate losses in water distribution systems. Water Resour Manag 23:477–492
Thornton J (2002) Water Loss Control Man. McGraw Hill, New York
Tsitsifli S, Kanakoudis V (2009) Evaluating the performance of an urban water distribution network: tips and tricks for troubleshooting. In: 7th international conference EWRA water resources conservation & risk reduction under climatic instability, pp 419–426, Lemessos, Cyprus
Acknowledgments
This work is part of an ERDF Co-financed MED project (WATERLOSS-2G-MED09-445).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanakoudis, V., Tsitsifli, S., Samaras, P. et al. Water Pipe Networks Performance Assessment: Benchmarking Eight Cases Across the EU Mediterranean Basin. Water Qual Expo Health 7, 99–108 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-014-0113-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-014-0113-y