Abstract
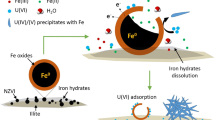
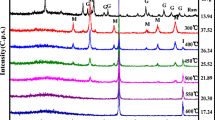
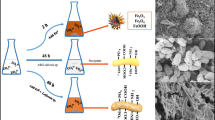
The nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) was synthesized by reduction of ferric chloride with sodium borohydride and characterized by SEM and XRD. The removal of U(VI) from aqueous solution by nZVI was investigated. The paper investigates the influence factors such as solution pH, initial U(VI) concentration, contact time and temperature on removal of U(VI) by nZVI with batch experiments and discusses the reduction kinetics characteristic. The results showed that U(VI) can be effectively removed from aqueous solution by nZVI, the reduction process followed the pseudo first-order kinetics. The apparent rate constant was proportional to nZVI concentration. The temperature had certain effect on removal of U(VI), the apparent rate constant increased with increase in temperature. The reaction activation energy E a was 28.5±0.435 kJ/mol, which was below the ordinary chemical reaction activation energy (60∼250 kJ/mol), so the reaction was easy to take place. The pH value had significant influence on the removal of U(VI), weakly acidic conditions were favorable to the removal of U(VI). For the fast reaction kinetics and high U(VI) removal capacity, nZVI has the potential to become an effective remedial agent for in situ remediation of uranium-contaminated soil and groundwater.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alidokht L, Khataee AR, Reyhanitabar A, Oustan S (2011) Reductive removal of Cr(VI) by starch-stabilized Fe0 nanoparticles in aqueous solution. Desalination 270:105–110
Chicgoua, Noubactep, Caré S, Crane R (2012) Nanoscale metallic iron for environmental remediation: prospects and limitations. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:1363–1382
DeepthiRani R, Sasidhar P (2012) Sorption of cesium on clay colloids: kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Aquat Geochem. doi:10.1007/s10498-012-9163-6
Dijie L, Qi Y, Haitao Sh (2009) Kinetics of removing nitrate by nanoscale zero-valent iron. Chin J Environ Eng 3(6):985–989
Du X, Boonchayaanant B, Wu WM et al. (2011) Reduction of uranium(VI) by soluble iron(II) conforms with thermodynamic predictions. Environ Sci Technol 45:4718–4725
Duygu Karabelli C, Talal A, Shah W et al. (2008) Batch removal of aqueous Cu2+ ions using nano particles of zero valent iron: a study of the capacity and mechanism of uptake. Ind Eng Chem Res 47:4758–4764
Fan M, Yuan P, Chen T et al. (2010) Synthesis, characterization and size control of zerovalent iron nanoparticles anchored on montmorillonite. Chin Sci Bull 55(11):1092–1099
Fangyan CH, Yubin TL, Wu X, Li M, Linlin L (2007) Study on reduction kinetics of Cr(VI) in water by nanoscale zero-valent iron. Chem World 3:144–147 (in Chinese)
Feng Y, Yi F (2011) Adsorptive property of rice husk for uranium. J At Energy Sci Technol 45:161–167
Fiedor JN, Bostick WD, Jarabek RJ et al. (1998) Understanding the mechanism of uranium removal from groundwater by zero-valent iron using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol 32(10):1466–1473
Hua M, Jian L, YueQiang, XiaoDong L et al. (2011) Characterization of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles prepared by transformation of α-FeOOH. Chin Sci Bull 56(22):2383–2388
Huang K, Zhu H (2012) Removal of Pb2+ from aqueous solution by adsorption on chemically modified muskmelon peel. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. doi:10.1007/s11356-012-1361-7
Hun Bok J, Jung, Boyanov MI, Konishi H et al. (2012) Redox behavior of uranium at the nanoporous aluminum oxide water interface: implications for uranium remediation. Environ Sci Technol 46:7301–7309
Jai YL, Sun YY, Sang C, Byung TO (2009) Removal of mixed contaminants by Fe0-based biobarrier in flow-through columns using recycled waste materials. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 11:214–221
Kaplan DI, Gilmore J (2004) Zero-valent iron removal rates of aqueous Cr(VI) measured under flow conditions. Water Air Soil Pollut 155:21–33
Kumar A, Singhal RK, Rout S et al. (2013) Adsorption and kinetic behavior of uranium and thorium in seawater-sediment system. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 295:649–656
Liu X, Li G, Hu N et al. (2012) Adsorption characteristics of uranium on tea waste. CIESC J 63(10):3291–3296 (in Chinese)
Lovely DR, Philips EJP (1992) Bioremediation of uranium contamination with enzymatic uranium reduction. Environ Sci Technol 26:2228–2234
Mahramanlioglu M (2003) Adsorption of uranium on adsorbents produced from used tires. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 256(1):99–105
Malay KG, Gérrard Eddy JP, Touma BI, Pritam S (2012) Arsenic adsorption on goethite nanoparticles produced through hydrazine sulfate assisted synthesis method. Korean J Chem Eng 29(1):95–102
Manolis J, Mercouri M, Kanatzidis G (2012) Layered metal sulfides capture uranium from seawater. J Am Chem Soc 134:16441–16446
Marius G (2011) Hexavalent chromium reduction with zero-valent iron (ZVI) in aquatic systems. Water Air Soil Pollut 222:103–148
Mingming S, Qi W, Yuedong M (2012) Removal of \(\mathrm{UO}_{2}^{2+}\) from aqueous solution by plasma functionalized MWCNTs. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 293:899–906
Misra SK, Bhardwaj YK, Gandhi PM (2013) Feasibility of the recovery of uranium from alkaline waste by amidoximated grafted polypropylene polymer matrix. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 295:471–475
Mitsuo M, Yoji S, Koichi O, Yoshio W (2008) Uranium sorption onto natural sediments within a small stream in central Japan. Limnology 9:173–183
Nicole C, Mueller JB, Johannes B et al. (2012) Application of nanoscale zero valent iron (NZVI) for groundwater remediation in Europe. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 19:550–558
Noubactep C (2006) Effect of selected ligands on the U(VI) immobilization by zerovalent iron. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 267(1):13–19
Osama E, Keiko S, Shoichi T, Tsuyoshi H (2011) Kinetic model of arsenic sorption onto zero-valent iron (ZVI). Water Qual Expo Health 2:125–132
Phenrat T, Saleh N, Sirk K, Tilton RD, Lowry GV (2007) Aggregation and sediment at ion of aqueous nanoscale zero valent iron dispersions. Environ Sci Technol 41:284–290
Pshinko GN, Kobets SA, Bogolepov AA et al. (2010) Treatment of waters containing uranium with saponite clay. J Water Chem Technol 32(1):10–16
Rahmani AR, Samadi MT, Noroozi R (2011) Hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto synthetic nano size zero valent iron (nZVI). World Acad Sci, Eng Technol 50:80–83
Ritu S, Virendra M, Rana PS (2012a) Removal of Cr(VI) by nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) from soil contaminated with tannery wastes. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 88:210–214
Ritu S, Virendra M, Rana PS (2012b) Removal of hexavalent chromium from contaminated ground water using zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Environ Monit Assess 184(6):3643–3651
Rodrigues JI, Silva AC, deMelo Ferreira AC, daCosta AC (2009) Uranium biosorption under dynamic conditions: preliminary tests with Sargassum filipendula in real radioactive wastewater containing Ba, Cr, Fe, Mn, Pb, Ca and Mg. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 279(3):909–914
Saeed B, Lakzian A, Ahmadi SJ et al. (2010) Uranium removal from aqueous solutions by wood powder and wheat straw. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 283:289–296
Shih YH, Tai YT (2010) Reaction of decabrominate ddiphenylether by zero valent iron nanoparticles. Chemosphere 78:1200–1206
Shih YH, Chungyu H, Yuhfan S (2011) Reduction of hexachlorobenzene by nanoscale zero-valent iron: kinetics, pH effect, and degradation mechanism. Sep Purif Technol 76:268–274
ShiNi Zh, Guo-hua L, Zheng Fang Y (2012) Reduction of dinitrotoluene sulfonates in TNT red water using nanoscale zero valent iron particles. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. doi:10.1007/s11356-012-0 749-8
ShuMei G, Xiao Dong W, Liang Q, Si L (2007) Preparation of nano zero-valent iron particles by modified liquid phase reduction method. J Nanjing Univ Nat Sci 43(4):349–355
Singh A, Catalano JG, Ulrich KU, Giammar DE (2012) Molecular-scale structure of uranium(VI) immobilized with goethite and phosphate. Environ Sci Technol 46:6594–6603
Su-Wen Ch, BoLong G, YuLong W et al. (2012) Study on sorption of U(VI) onto ordered mesoporous silicas. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. doi:10.1007/s10967-012-1998-1
Sun YB, Wang Q, Yang ST, Sheng GD, Guo ZQ (2011) Characterization of nano-iron oxyhydroxides and their application in \(\mathrm{UO}_{2}^{2+}\) removal from aqueous solutions. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 290:643–648
Sung PH, Davis JA, Kai S, Hayes KF (2012) Uranium(VI) reduction by iron(II) monosulfide mackinawite. Environ Sci Technol 46:3369–3376
Talal A, Achintya B (2012) Aqueous phosphate removal using nanoscale zero-valent iron. J Nanopart Res 14:900
Tiziana M, Miguel GG, Cesar M (2003) Experimental and modeling study of the uranium(VI) sorption on goethite. J Colloid Interface Sci 260:291–301
Xia L, Tan K, Wang X, Zhen W (2010) Adsorption behavior of uranium and mechanism analysis on banyan leaves. J At Energy Sci Technol 44(3):278–284 (in Chinese)
Xiao-qin L, Derick GB, Weixian Zh (2007) Stabilization of biosolids with nanoscale zero-valent iron(nZVI). J Nanopart Res 9:233–243
Xiaobao ZH, Hongfang L, Qingwe D et al. (2011) Research on the removal of ReO-4 by zero valent nano iron. Environ Pollut Protect 33(5):7–10 (in Chinese)
Xiaofeng L, Jiansheng L, Wen Zh, Yaoyao et al. (2012) Synthesis of nanoscale zero-valent iron/ordered mesoporous carbon for adsorption and synergistic reduction of nitrobenzene. Chemosphere 87:655–660
Xiaoliang W, Guowen P, Yan Y et al. (2012) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 291:825–830
Xiaoqin L, Weixian Zh (2007) Sequestration of metal cations with zero valent iron nanoparticles: a study with high resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (HR-XPS). J Phys Chem 111:6939–6946
Xin Zh, Shen L, XiaoQiao L, Zuliang Ch (2010) Removal of Pb(II) from water using synthesized kaolin supported nanoscale zero-valentiron. J Chem Eng 163:243–248
Yan Sen, Zhang B, Zheng YB, Yang J, Liu C, Deng B (2010) Uranium(VI) removal by nanoscale zerovalent iron in anoxic batch systems. Environ Sci Technol 44:7783–7789
Yan S (2010) Uranium(VI) reduction by nanoscale zero-valent iron under anoxic conditions: kinetics and mechanism. China University of Geosciences for the Doctor Degree of Sciences (in Chinese)
Yan W, Herzing AA, Kiely CJ et al. (2010) Nanoscalezero-valentiron (nZVI): aspects of the core-shell structure and reactions with inorganic species in water. J Contam Hydrol 118:96–104
Zhang C, Zhou W, Xi N (2009) Immobilization of U(VI) in solution by zero-valent iron. Uranium Mining Metall 28(3):155–158
Zhengxian Ch, Ying Ch, Zuliang Ch et al. (2012) Kaolin-supported nanoscalezero-valent iron for removing cationic dye–crystal violet in aqueous solution. J Nanopart Res 14:899
Zou W, Zhao L, Zhu L (2013) Adsorption of uranium(VI) by grapefruit peel in a fixed-bed column: experiments and prediction of breakthrough curves. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 295:717–727
Acknowledgements
This work was financed by the Natural Science Foundation of China (11205030, 41201500), State Key Laboratory Breeding Base of Nuclear Resources and Environment, East China Institute of Technology (101111) and Fundamental Science on Radioactive Geology and Exploration Technology Laboratory, East China Institute of Technology (2011RGET06, REGT1220). The authors thank the anonymous reviewers for their comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Zhang, M., Liu, Y. et al. Removal of U(VI) in Aqueous Solution by Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron(nZVI). Water Qual Expo Health 5, 31–40 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-013-0084-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-013-0084-4