Abstract
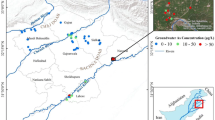
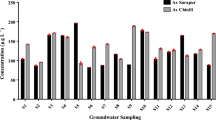
It has previously been reported that rice grown in regions of Bangladesh with low-arsenic (As) concentrations in irrigation water can have relatively high concentrations of As within their grains. This study aims to determine how widespread this issue is, and determine the seasonal variation in grain As in these regions. Levels of As were measured in shallow tube well (STW) water, soils, and rice grains collected during the Boro (dry) and Aman (wet) seasons from six Upazilas (sub-districts) of Bangladesh where As levels in groundwater were known to be low. In all the Upazilas, the As concentrations in STW water were <50 μg L−1. The As levels in soil samples collected from the Upazilas ranged between 0.2–4.0 mg kg−1 in the samples collected during the Boro season, and 0.4–5.7 mg kg−1 in the samples collected in the Aman season. Levels of As in both Boro and Aman rice grain varied widely: in Boro 0.02–0.45 mg kg−1, and in Aman 0.01–0.29 mg kg−1. Additionally, a household survey of dietary habits was also conducted in one Upazila by estimating As ingestion by 15 head female members. On average, the women consumed 3.1 L of water, 1.1 kg of cooked rice, and 42 g dry weight of curry per day. The total As ingestion rates ranged from 31.1–129.3 μg day−1 (mean 63.5 μg kg−1). These findings indicate that the major route of As ingestion in low groundwater-As areas of Bangladesh is rice, followed by curry and then water.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerman AH, Creed PA, Parks AN, Fricke MW, Schwegel CA, Creed JT, Heitkemper DT, Vela NP (2005) Comparison of a chemical and enzymatic extraction of arsenic from rice and an assessment of the arsenic absorption from contaminated water by cooked rice. Environ Sci Technol 39:5241–5246
Agusa TT, Kunito TB, Minh PTK, Trang H, Iwata PH, Tanabe S (2009) Relationship of urinary arsenic metabolites to intake estimates in resident of the Red River Delta, Vietnam. Environ Pollut 157:396–403
Alam MGM, Snow ET, Tanaka A (2003) Arsenic and heavy metal contamination of vegetables grown in Samta village, Bangladesh. Sci Total Environ 308:83–96
Arnold HL, Odam RB, James WD (1990) Disease of the skin. In: Clinical dermatology. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 121–122
Bae M, Watanabe C, Inaoka T, Sekiyama M, Sudo N, Bokul MH, Ohtsuka R (2002) Arsenic in cooked rice in Bangladesh. Lancet 360:1839–1840
BBS (Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics) (2008) Statistical yearbook of Bangladesh. Statistics Div, Ministry of Planning, Govt People’s Republic Bangladesh, pp 101–125
BGS and DPHE (Department of Public Health Engineering, Bangladesh) (2001) Arsenic contamination of groundwater in Bangladesh, vol 2: final report (Kinniburg DG, Smedley, PL eds.). BGS Technical Report WC/00/19. Keyworth, UK British Geological Survey
Bouman AM, Humphreys E, Tuong TP, Barker AT (2006) Rice and water. Adv Agron 92:187–237
Brammer H (1996) The geography of the soils of Bangladesh. University Press, Dhaka
Brammer H, Ravenscroft P (2009) Arsenic in groundwater: a threat to sustainable agriculture in South and South-east Asia. Environ Int 35:647–654
Brinkman R (1977) Surface-water gley soils in Bangladesh: genesis. Geoderma 17:199–206
Chakraborti D, Rahman MM, Das B, Murril M, Dey S, Mukherjee SC, Dhar RK, Biswas BK, Chowdhury UK, Roy S, Sorif S, Selim M, Rahman M, Quamruzzaman Q (2010) Status of groundwater arsenic contamination in Bangladesh: a 14-year study report. Water Res 44:5789–5802
Chowdhury UK, Rahman MM, Mondal BK, Paul K, Lodh D, Biswas BK, Basu GK, Chanda CR, Saha KC, Mukherjee SC, Roy S, Das R, Kaies I, Barua AK, Palit SK, Quamruzzaman Q, Chakraborti D (2001) Groundwater arsenic contamination and human suffering in West Bengal, India and Bangladesh. J Environ Sci 8:393–415
Das HK, Mitra AK, Sengupta PK, Hossaind A, Islame F, Rabbanif GH (2004) Arsenic concentrations in rice, vegetables, and fish in Bangladesh: a preliminary study. Environ Int 30:383–387
Daum D, Bogdan K, Schenk MK, Merkel D (2001) Influence of the field water management on accumulation of arsenic and cadmium in paddy rice. Dev Plant Soil Sci 92:290–291
Dittmar J, Voegelin A, Robert LC, Hug SI, Shah GC, Ali MA, Badruzzaman ABM, Kretzschmar R (2007) Spatial distribution and temporal variability of arsenic in irrigated rice fields in Bangladesh, I: paddy soil. Environ Sci Technol 41:5967–5972
Dittmar J, Voegelin A, Roberts LC, Hug SJ, Saha GC, Ali MA, Badruzzaman ABM, Kretzschmar R (2010) Arsenic accumulation in a paddy field in Bangladesh: seasonal dynamics and trends over a three-year monitoring period. Environ Sci Technol 44:2925–2931
Duxbury JM, Mayer AB, Lauren JG, Hassan N (2003) Food chain aspects of arsenic contamination in Bangladesh: effects on quality and productivity of rice. J Environ Sci Health 38:61–69
Farmer JG, Johnston LR (1990) Assessment of occupational exposure to inorganic arsenic based on urinary concentrations and speciation of arsenic. Br J Ind Med 47:342–348
Fazal MA, Kawachi T, Ichion E (2001) Extent and severity of ground water arsenic contamination in Bangladesh. Water Int 26:370–379
Heikens A (2006) Arsenic contamination of irrigation water, soils and crops in Bangladesh. Risk implications for sustainable agriculture and food safety in Asia. FAO, Bangkok. http://www.fao.org/docrep/009/ag105e00.htm
Huizing HGJ (1971) A reconnaissance study of the mineralogy of some seasonally flooded soils of East Pakistan sediments and soils. Geoderma 6:109–133
Islam MR, Islam S, Jahiruddin M, Islam MA (2004) Effects of irrigation water arsenic in the rice–rice cropping system. J Bio-Sci 4:542–546
Islam MR, Hoque ME, Jahiruddin M, Islam S (2005) Heavy metal contamination of vegetables grown in Chapai Nawabganj, Bangladesh and its implication to daily intake for human health. Bangladesh J Agric Environ 1:37–47
Karagas MR, Tosteson TD, Blum J, Klaue B, Weiss JE, Stannard V, Spate V, Morris JS (2000) Measurement of low levels of arsenic exposure: a comparison of water and toenail concentrations. Am J Epidemiol 152:84–90
Khan MA, Islam MR, Panaullah GM, Duxbury JM, Jahiruddin M, Loeppert RH (2009) Fate of irrigation-water arsenic in rice soils of Bangladesh. Plant Soil 322:263–277
Kile ML, Houseman EA, Rodrigues E, Smith TJ, Quamruzzaman Q, Rahman M, Mahiuddin G, Su L, Christiani DC (2005) Toenail arsenic concentrations, GSTT1 gene polymorphisms and arsenic exposure from drinking water. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 14:2419–2426
Kile ML, Houseman EA, Breton CV, Smith T, Quamruzzaman Q, Rahman M, Mohiuddin G, Christiani D (2007) Dietary arsenic exposure in Bangladesh. Environ Health Perspect 115:889–893
Laparra JM, Vélez D, Barberá R, Farré R, Montoro R (2005) Bioavailability of inorganic arsenic in cooked rice: practical aspects for human health risk assessments. J Agric Food Chem 53:8829–8833
Lonaid N, Bors G, Popa I (1961) Beitagezurkenntnis des normalenarsengehaltes von nageln and des Gehaltes in den Faillen von Arsenpolyneuritis. Dtsch Z Gesamte Gerichtl Med 52:90–94
Lu Y, Adomako EE, Solaiman ARM, Islam MR, Deacon C, Williams PN, Rahman GKMM, Meharg AA (2009) Baseline soil is a major factor in arsenic accumulation in Bengal Delta paddy rice. Environ Sci Technol 43:1724–1729
Ma JF, Yamaji N, Mitani N, Xu XY, Su YH, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ (2008) Transporters of arsenite in rice and their role in arsenic accumulation in rice grain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:9931–9935
Meharg AA, Rahman MM (2003) Arsenic contamination of Bangladesh paddy field soils: implications for rice contribution to arsenic consumption. Environ Sci Technol 37:229–234
Meharg AA, Williams PN, Adomako E, Lawgali YY, Deacon C, Villada A, Cambell RCJ, Sun G, Zhu YG, Feldman J, Raab A, Zhao JF, Islam MR, Hossain S, Yanai J (2009) Geographical variation in total and inorganic arsenic content of polished (white) rice. Environ Sci Technol 43:1612–1627
Mestrot A, Uroic MK, Plantevin T, Islam MR, Krupp E, Feldmann J, Meharg AA (2009) Quantitative and qualitative trapping of arsines deployed to assess loss of volatile arsenic from paddy soil. Environ Sci Technol 43:8270–8275
Mondal D, Polya DA (2008) Rice is a major exposure route for arsenic in Chakdaha block, Nadia district, West Bengal, India: a probabilistic risk assessment. Appl Geochem 23:2987–2998
Mondal D, Banerjee M, Kundu M, Banerjee N, Bhattacharya U, Giri AK, Ganguli B, Roy S, Polya DA (2010) Comparison of drinking water, raw rice and cooking of rice as arsenic exposure routes in three contrasting areas of West Bengal, India. Environ Geochem Health 32:463–477
Norton GJ, Islam MR, Deacon CM, Zhao FJ, Stroud JL, McGrath SP, Islam S, Jahiruddin M, Feldmann J, Price AH, Meharg AA (2009a) Identification of low inorganic and total grain arsenic rice cultivars from Bangladesh. Environ Sci Technol 43:6070–6075
Norton GJ, Duan G, Dasgupta T, Islam MR, Lei M, Zhu Y, Deacon CM, Moran AC, Islam S, Zhao FJ, Stroud JL, McGrath SP, Feldmann J, Price AH, Meharg AA (2009b) Environmental and genetic control of arsenic accumulation and speciation in rice grain: comparing a range of common cultivars crown in contaminated sites across Bangladesh, China, and India. Environ Sci Technol 43:8381–8386
Norton GJ, Pinson SRM, Alexander J, Mckay S, Hansen H, Duan GL, Islam RM, Islam S, Stroud JL, Zhao FJ, Mcgrath SP, Zhu YG, Lahner B, Yakubova E, Guerinot ML, Tarpley L, Eizenga GC, Salt DE, Meharg AA, Price AH (2012) Variation in grain arsenic assessed in a diverse panel of rice (Oryza sativa) grown in multiple sites. New Phytol 193:650–664
Ohno K, Yanase T, Matsuo Y, Kimura T, Rahman MH, Magara Y, Matsui Y (2007) Arsenic intake via water and food by a population living in an arsenic-affected area of Bangladesh. Sci Total Environ 381:68–76
Ohno K, Matsuo Y, Kimura T, Yanase T, Rahman MH, Magara Y, Matsushita T, Matsui Y (2009) Effect of rice cooking water to the daily arsenic intake in Bangladesh: results of field surveys and rice cooking experiments. Water Sci Technol 50:195–201
Raab A, Baskaran C, Feldmann J, Meharg AA (2009) Cooking rice in a high water to rice ratio reduces inorganic As content. J Environ Monit 11:41–44
Rahman MA, Hasegawa H, Rahman MA, Rahman MM, Miah MA (2006) Influence of cooking method on arsenic retention in cooked rice related to dietary exposure. Sci Total Environ 370:51–60
Rahman MM, Owen G, Naidu R (2009) Arsenic levels in rice grain and assessment of daily dietary intake of arsenic from rice in arsenic contaminated regions of Bangladesh: implication to ground water irrigation. Environ Geochem Health 31:179–187
Rahman MM, Asaduzzaman M, Naidu R (2011) Arsenic exposure from rice and water sources in the Noakhali district of Bangladesh. Water Qual Expo Health 3:1–10
Ravenscroft P, Burgess WG, Ahmed KM, Burren M, Perrin J (2005) Arsenic in groundwater of the Bengal Basin, Bangladesh: distribution, field relations, and hydrogelogical setting. Hydrogeol J 13:727–751
Roychowdhury T, Tokunaga H, Ando M (2003) Survey of arsenic and other heavy metals in food composites and drinking water and estimation of dietary intake by the villagers from an arsenic affected area of West Bengal, India. Sci Total Environ 308:15–35
Schoof RA, Yost LJ, Eickhoff EA, Crecelius DW, Cragin DW, Meacher DM, Mengel DB (1999) A market basket survey of inorganic arsenic in food. Food Chem Toxicol 37:839–846
Sengupta MK, Hossain MA, Mukherjee A, Ahamed S, Das B, Nayak B, Pal A, Chakraborti D (2006) Arsenic burden of cooked rice: traditional and modern methods. Food Chem Toxicol 44:1823–1829
Shraim A, Cui X, Li S, Ng JC, Wang J, Jin Y, Liu Y, Guo L, Li D, Wang S, Zhang R, Hirano S (2003) Arsenic speciation in the urine and hair of individuals exposed to airborne arsenic through coal-burning in Guizhou, PR China. Toxicol Lett 137:35–48
Signes A, Mitra K, Burlo F, Carbonell-Barrachina AA (2008) Effect of cooking method and rice type on arsenic concentration in cooked rice and the estimation of arsenic dietary intake in a rural village in West Bengal, India. Food Addit Contam 25:1345–1352
Stroud JL, Norton GJ, Islam MR, Dasgupta T, White RP, Price AH, Meharg AA, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ (2011) The dynamics of arsenic in four paddy fields in the Bengal Delta. Environ Pollut 159:947–953
Sun G, Williams PN, Zhu Y, Deacon C, Carey A, Raab A, Feldmann J, Meharg AA (2009) Survey of arsenic and its speciation in rice products such as breakfast cereals, rice crackers and Japanese rice condiments. Environ Int 35:473–475
Talukder ASMHM, Meisner CA, Sarkar MAR, Islam MS (2011) Effect of water management, tillage options and phosphorus status on arsenic uptake in rice. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:834–839
Uphoff N, Kassam A (2011) Paddy and water management with the system of rice intensification (SRI). Paddy Water Environ 9(1)
Watanabe C (2001) Environmental arsenic exposure in Bangladesh: water versus extra-water intake of arsenic. Environ Sci 8:458–466
Watanabe C, Kawat A, Dudo N, Sekiyama M, Inaoka T, Bae M, Ohtsuka R (2004) Water intake in an asian population living in arsenic contaminated water. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 198:272–282
Williams PN, Price AH, Raab A, Hossain SA, Feldmann J, Meharg AA (2005) Variation in arsenic speciation and concentration in paddy rice related to dietary exposure. Environ Sci Technol 39:5531–5540
Williams PN, Islam MR, Adomako EE, Raab A, Hossain SA, Zhu YG, Meharg AA (2006) Increase in rice grain arsenic for regions of Bangladesh irrigating paddies with elevated arsenic in groundwaters. Environ Sci Technol 40:4903–4908
Williams PN, Vilada A, Deacon C, Raab A, Figuerola J, Green AJ, Feldmann J, Meharg AA (2007) Greatly enhanced arsenic shoot assimilation in rice leads to elevated grain levels compared to wheat and barley. Environ Sci Technol 41:6854–6859
Xu XY, McGrath SP, Meharg AA, Zhao FJ (2008) Growing rice aerobically markedly decreases arsenic accumulation. Environ Sci Technol 42:5574–5579
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Islam, M.R., Brammer, H., Mustafizur Rahman, G.K.M. et al. Arsenic in Rice Grown in Low-Arsenic Environments in Bangladesh. Water Qual Expo Health 4, 197–208 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-012-0079-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-012-0079-6