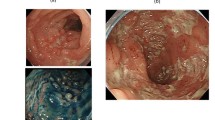
Abstract
Jaundice may be persistent in drug-induced liver injury associated with vanishing bile duct syndrome. However, recurrent jaundice is atypical, following bile flow restoration. Here, we report a 28-year-old man with prolonged, recurrent jaundice (more than 300 days) and combined immunodeficiency (CID) of B-cells, T-cells, and natural killer (NK) cells. Hypogammaglobulinemia was observed throughout his hospitalization, and peripheral blood flow cytometry detected a few B-cells (2% of CD19 + cells and 2% of CD20 + cells). We further detected the dysfunction of T-cells and NK cells. Based on these findings, CID was diagnosed. We presumed that hypogammaglobulinemia was related to the jaundice. After regular injections of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), the stool color gradually turned brown. However, the color returned to white as IgG levels decreased. The brown-to-white stool pattern was repeated with another IVIG administration, suggesting that the patient’s serum immunoglobulin levels were related to the jaundice. On follow-up, IVIG was performed every two to three weeks, and his total bilirubin improved gradually. Immunoglobulin replacement therapy could be one of the treatment choices for jaundice with CID.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonkovsky HL, Kleiner DE, Gu J, et al. Clinical presentations and outcomes of bile duct loss caused by drugs and herbal and dietary supplements. Hepatology. 2017;65:1267–77.
Yeh P, Lokan J, Anantharajah A, et al. Vanishing bile duct syndrome and immunodeficiency preceding the diagnosis of Hodgkin lymphoma. Int Med J. 2014;44:1240–4.
McCusker C, Upton J, Warrington R. Primary immunodeficiency. allergy asthma. Clin Immunol. 2018;14:61.
Bakhit M, McCarty TR, Park S, et al. Vanishing bile duct syndrome in Hodgkin’s lymphoma: a case report and literature review. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23:366–72.
Murakami J, Shimizu Y. Hepatic manifestations in hematological disorders. Int J Hepatol. 2013;2013:484903.
Oppenheimer AP, Koh C, McLaughlin M, et al. Vanishing bile duct syndrome in human immunodeficiency virus infected adults: a report of two cases. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19:115–21.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Shiro Watanabe, Isamu Hama and Hiroki Honda for their cooperation (Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Shinrakuen Hospital). We thank the Initiative on Rare and Undiagnosed Diseases (IRUD) for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CO, TU AK, KT, KH, and AT: analysis of data and drafting of the manuscript; ST: critical revision of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no current financial arrangement or affiliation with any organization that may have a direct influence on their work. Chiyumi Oda, Atsunori Tsuchiya, Atsushi Kimura, Kentaro Tominaga, Kazunao Hayashi, Takashi Ushiki, Hajime Umezu and Shuji Terai declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human rights
All procedures followed have been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Informed consent
The authors confirm that informed consent was obtained from the patient for the publication of his information and imaging. Informed consent was obtained from the patient for being included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oda, C., Tsuchiya, A., Kimura, A. et al. Immunoglobulin therapy for successful management of prolonged, recurrent jaundice in a young adult male with combined immunodeficiency. Clin J Gastroenterol 14, 1197–1201 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-021-01347-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-021-01347-0