Abstract
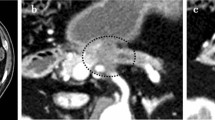
A 48-year-old man presented with epigastralgia and back pain. Radiological evaluation revealed a pancreatic tail tumor with contrast enhancement and an intratumoral fluid component involving the splenic artery and invading the left kidney. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy revealed an adenocarcinoma, and based on invasion of the left kidney, the patient was diagnosed with unresectable pancreatic cancer with suspected peritoneal dissemination. Radiological evaluation performed after the administration of eight courses of gemcitabine combined with nab-paclitaxel revealed stable disease without distant metastases or peritoneal dissemination. We planned to perform radical resection; however, the patient developed a pseudoaneurysm of the splenic artery preoperatively and initially underwent preoperative coil embolization, followed by radical resection (distal pancreatectomy with combined left nephrectomy and partial resection of the colon and stomach), 11 days after embolization. Histopathological examination of the resected specimen confirmed R0 resection, and the splenic artery pseudoaneurysm associated with pancreatic cancer was attributed to tumor invasion of this vessel. He showed satisfactory postoperative recovery and was discharged on the 24th day after surgery with administration of S-1 adjuvant chemotherapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hackert T, Sachsenmaier M, Hinz U, et al. Locally advanced pancreatic cancer: neoadjuvant therapy with folfirinox results in resectability in 60% of the patients. Ann Surg. 2016;26:457–63.
Satoi S, Yamaue H, Kato K, et al. Role of adjuvant surgery for patients with initially unresectable pancreatic cancer with a long-term favorable response to non-surgical anti-cancer treatments: results of a project study for pancreatic surgery by the Japanese Society of Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2013;20:590–600.
Heinrich S, Lang H. Neoadjuvant therapy of pancreatic cancer: definitions and benefits. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18:E1622.
Pasha SF, Gloviczki P, Stanson AW, et al. Splanchnic artery aneurysms. Mayo Clin Proc. 2007;82:472–9.
Sachdev-Ost U. Visceral artery aneurysms: review of current management options. Mt Sinai J Med. 2010;77:296–303.
Nanez L, Knowles M, Modrall JG, et al. Ruptured splenic artery aneurysms are exceedingly rare in pregnant women. J Vasc Surg. 2014;60:1520–3.
White AF, Baum S, Buranasiri S. Aneurysms secondary to pancreatitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1976;127:393–6.
Furukawa H, Fukushima N, Shimada K. Splenic artery aneurysm secondary to pancreatic carcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95:3659–60.
Toukouki A, Verbeeck N, Weber J, et al. Intragastric rupture of a splenic artery aneurysm associated with a pancreatic cancer. J Belg Soc Radiol. 2016;100:26.
Hoshimoto S, Aiura K, Shito M, et al. Successful resolution of a hemorrhagic pancreatic pseudocyst ruptured into the stomach complicating obstructive pancreatitis due to pancreatic cancer: a case report. World J Surg Oncol. 2016;14:46.
Miao YD, Ye B. Intragastric rupture of splenic artery aneurysms: Three case reports and literature review. Pak J Med Sci. 2013;29:656–9.
Loffroy R, Guiu B, Cercueil JP, et al. Transcatheter arterial embolization of splenic artery aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms: short- and long-term results. Ann Vasc Surg. 2008;22:618–26.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KF: collection of data and drafting of the article. HS: revision of the article. YS: collection of data. YN: collection of data. MS: collection of data. KY: revision of the article and final approval of the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Human/animal rights
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Jikei University School of Medicine.
Informed consent
This patient provided informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Furukawa, K., Shiba, H., Shirai, Y. et al. Splenic artery pseudoaneurysm following chemotherapy in a patient with pancreatic cancer: a case report. Clin J Gastroenterol 13, 969–972 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-020-01137-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-020-01137-0