Abstract
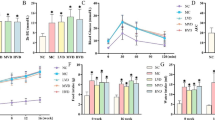
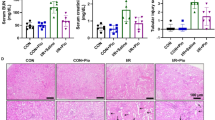
Empagliflozin, a SGLT-2 inhibitor, improves diabetic nephropathy through its pleiotropic anti-inflammatory effects. The present study aims to evaluate empagliflozin effects on renal and urinary levels of tubular epithelial cell injury markers in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Empagliflozin at 10 mg/kg (p.o.) was administered for 4 weeks, beginning 8 weeks after induction of diabetes. Renal function as well as markers of renal tubular epithelial cell injury were assessed in kidney tissue homogenates and urine. Empagliflozin was able to ameliorate diabetes induced elevations in serum cystatin C levels. It also alleviated renal KIM-1/NGAL levels and urinary albumin, α-GST, and RBP excretions. In addition to decreasing urinary levels of cell cycle arrest indices i.e. TIMP-2 and IGFBP7, empagliflozin mitigated acetylated NF-κB levels in renal tissues of diabetic rats. As a whole, these findings reveal empagliflozin capability in improving diabetic nephropathy via ameliorating indices of renal inflammation, injury, and cell cycle arrest on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SGLT-2:
-
Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2
- KIM-1:
-
Kidney injury molecule 1
- NGAL:
-
Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin
- KIM-1:
-
Kidney injury molecule-1
- α-GST:
-
Alpha-glutathione S-transferase
- RBP:
-
Retinol-binding protein
- TIMP-2:
-
Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2
- IGFBP7:
-
Insulin like growth factor binding protein 7
References
Nichols GA, Vupputuri S, Lau H. Medical care costs associated with progression of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Care. 2011;34(11):2374–8.
Forbes JM, Cooper ME. Mechanisms of diabetic complications. Physiol Rev. 2013;93(1):137–88.
Tervaert TWC, Mooyaart AL, Amann K, Cohen AH, Cook HT, Drachenberg CB, et al. Pathologic classification of diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;21(4):556–63.
Tang SC, Lai KN. The pathogenic role of the renal proximal tubular cell in diabetic nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012;27(8):3049–56.
Gæde P, Lund-Andersen H, Parving H-H, Pedersen O. Effect of a multifactorial intervention on mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(6):580–91.
Zoungas S, De Galan BE, Ninomiya T, Grobbee D, Hamet P, Heller S, et al. Combined effects of routine blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control on macrovascular and microvascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(11):2068–74.
Duckworth W, Abraira C, Moritz T, Reda D, Emanuele N, Reaven PD, et al. Glucose control and vascular complications in veterans with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(2):129–39.
Fried LF, Emanuele N, Zhang JH, Brophy M, Conner TA, Duckworth W, et al. Combined angiotensin inhibition for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(20):1892–903.
Fitchett D, Butler J, van de Borne P, Zinman B, Lachin JM, Wanner C, et al. Effects of empagliflozin on risk for cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalization across the spectrum of heart failure risk in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME® trial. Eur Heart J. 2017;39(5):363–70.
Škrtic M, Cherney DZ. Sodium–glucose cotransporter-2 inhibition and the potential for renal protection in diabetic nephropathy. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2015;24(1):96–103.
Gallo LA, Ward MS, Fotheringham AK, Zhuang A, Borg DJ, Flemming NB, et al. Once daily administration of the SGLT2 inhibitor, empagliflozin, attenuates markers of renal fibrosis without improving albuminuria in diabetic db/db mice. Sci Rep. 2016;6:26428.
Fioretto P, Zambon A, Rossato M, Busetto L, Vettor R. SGLT2 inhibitors and the diabetic kidney. Diabetes Care. 2016;39(Supplement 2):S165–71.
Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, von Eynatten M, Mattheus M, et al. Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(4):323–34.
Lameire N, Vanmassenhove J, Van Biesen W, Vanholder R. The cell cycle biomarkers: promising research, but do not oversell them. Clin Kidney J. 2016;9(3):353–8.
Tesauro M, Nisticò S, Noce A, Tarantino A, Marrone G, Costa A, et al. The possible role of glutathione-S-transferase activity in diabetic nephropathy. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2015;28(1):129–33.
Ojima A, Matsui T, Nishino Y, Nakamura N, Yamagishi S. Empagliflozin, an inhibitor of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 exerts anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic effects on experimental diabetic nephropathy partly by suppressing AGEs-receptor axis. Horm Metab Res. 2015;47(09):686–92.
Chen S, Chen H, Liu Q, Ma Q. Effect of simvastatin on the expression of nephrin, podocin, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in podocytes of diabetic rat. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(10):18225.
Randers E, Kristensen H, Erlandsen EJ, Danielsen S. Serum cystatin C as a marker of the renal function. Scand J Clin Lab Investig. 1998;58(7):585–92.
Ferenbach DA, Bonventre JV. Mechanisms of maladaptive repair after AKI leading to accelerated kidney ageing and CKD. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2015;11(5):264.
Kashani K, Kellum JA. Novel biomarkers indicating repair or progression after acute kidney injury. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2015;24(1):21–7.
Kellum JA. Diagnostic criteria for acute kidney injury: present and future. Crit Care Clin. 2015;31(4):621–32.
Watanabe J, Takiyama Y, Honjyo J, Makino Y, Fujita Y, Tateno M, et al. Role of IGFBP7 in diabetic nephropathy: TGF-β1 induces IGFBP7 via Smad2/4 in human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. PLoS ONE. 2016;11(3):e0150897.
Xu X, Xiao L, Xiao P, Yang S, Chen G, Liu F, et al. A glimpse of matrix metalloproteinases in diabetic nephropathy. Curr Med Chem. 2014;21(28):3244–60.
Tramonti G, Kanwar YS. Tubular biomarkers to assess progression of diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2011;79(10):1042–4.
Titan S, Vieira J, Dominguez W, Moreira S, Pereira A, Barros R, et al. Urinary MCP-1 and RBP: independent predictors of renal outcome in macroalbuminuric diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Complicat. 2012;26(6):546–53.
Gembardt F, Bartaun C, Jarzebska N, Mayoux E, Todorov VT, Hohenstein B, et al. The SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin ameliorates early features of diabetic nephropathy in BTBR ob/ob type 2 diabetic mice with and without hypertension. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014;307(3):F317–25.
Terami N, Ogawa D, Tachibana H, Hatanaka T, Wada J, Nakatsuka A, et al. Long-term treatment with the sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor, dapagliflozin, ameliorates glucose homeostasis and diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(6):e100777.
Panchapakesan U, Pegg K, Gross S, Komala MG, Mudaliar H, Forbes J, et al. Effects of SGLT2 inhibition in human kidney proximal tubular cells—renoprotection in diabetic nephropathy? PLoS ONE. 2013;8(2):e54442.
Acknowledgements
This investigation is a supported by grants from Student Research center and Biotechnology Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences; and Urology and Nephrology Research Center, Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None of the authors declare any conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashrafi Jigheh, Z., Ghorbani Haghjo, A., Argani, H. et al. Empagliflozin Attenuates Renal and Urinary Markers of Tubular Epithelial Cell Injury in Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Rats. Ind J Clin Biochem 35, 109–114 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-018-0790-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-018-0790-6