Abstract
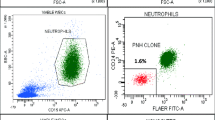
To study the utility and advantage of CD157 in the paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) screening along with its ability to replace CD24 and CD14. This was a confirmatory study to analyse the role and advantage of CD157 in a single tube five color combination to identify the PNH clones. A serial tenfold dilution experiments was carried out for sensitivity assessment. Reproducibility was checked in the intra-assay and inter-assay experiments. The results obtained with CD157 based assay were compared with the routinely used single tube six color CD24/CD14 based assay. CD157 showed a high degree of sensitivity at the level of 10−4. PNH positive clone sizes were precise with CVs of inter-assay and intra-assay precision analysis for polymorphs/monocytes ranging from 2.94 to 4.31/2.52 to 8.93, and 0.91 to 3.23/1.65 to 5.33%; respectively. The results were similar to those obtained from CD24/CD14 based assay (R2 > 0.993). There was no false positive or false negative result. CD157 was found better in delineating the type II clones. CD157 can be used as a common PNH leucocyte marker with high degree of sensitivity and precision. It can replace CD24 and CD14 from the currently used assays and thus bring down the cost of PNH screening.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nagarajan S, Brodsky RA, Young NS, Medof ME (1995) Genetic defects underlying paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria that arises out of aplastic anemia. Blood 86:4656–4661
Takahashi M, Takeda J, Hirose S, Hyman R, Inoue N, Miyata T et al (1993) Deficient biosynthesis of N-acetylglucosaminyl-phosphatidylinositol, the first intermediate of glycosyl phosphatidylinositol anchor biosynthesis, in cell lines established from patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. J Exp Med 177:517–521
Medof ME, Kinoshita T, Nussenzweig V (1984) Inhibition of complement activation on the surface of cells after incorporation of decay-accelerating factor (DAF) into their membranes. J Exp Med 160:1558–1578
Rollins SA, Sims PJ (1990) The complement-inhibitory activity of CD59 resides in its capacity to block incorporation of C9 into membrane C5b-9. J Immunol 144:3478–3483
Borowitz MJ, Craig FE, DiGiuseppe J, Illingworth AJ, Rosse W, Sutherland R et al (2010) Guidelines for the diagnosis and monitoring of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and related disorders by Flow cytometry. Cytom B 78B:211–230
Sutherland DR, Kuek N, Davidson J, Barth D, Chang H, Yeo E et al (2007) Diagnosing PNH with FLAER and multiparameter flow cytometry. Cytom B 72B:167–177
Brodsky RA, Mukhina GL, Nelson KL, Lawrence TS, Jones RJ, Buckley JT (1999) Resistance of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria cells to the glycosylphosphatidylinositol-binding toxin aerolysin. Blood 93:1749–1756
Hernandez-Campo PM, Almeida J, Sanchez ML, Malvezzi M, Orfao A (2006) Normal patterns of expression of glycosylphosphatidylinositolanchored proteins on different subsets of peripheral blood cells: aframe of reference for the diagnosis of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Cytom B 70B:71–81
Hernandez-Campo PM, Almeida J, Matarraz S, de Santiago M, Sánchez ML, Orfao A (2007) Quantitative analysis of the expression of glycosylphosphatidylinositol- anchored proteins during the maturation of different hematopoietic cell compartments of normal bone marrow. Cytom B 72:34–42
Brodsky RA, Mukhina GL, Li S, Nelson KL, Chiurazzi PL, Buckley JT et al (2000) Improved detection and characterization of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria using fluorescent aerolysin. Am J Clin Pathol 114:459–466
Sutherland DR, Acton E, Keeney M, Davis BH, Illingworth A (2014) Use of CD157 in FLAER based assay for high sensitivity PNH Granulocyte and PNH monocyte detection. Cytom B 86B:44–55
Marinov I, Kohutova M, Tkakova V, Pesek A, Cermak J, Cetkovsky P (2015) Clinical relevance of CD157 for rapid and cost effective simultaneous evaluation of PNH granulocyte and monocytes by low cytometry. Int J Lab Hematol 37:231–237
Rahman K, Gupta R, Yadav G, Husein N, Singh MK, Nityanand S (2017) Fluorescent Aerolysin (FLAER)-based paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) screening: a single center experience from India. Int. J Lab Hematol 39:261–271
Correia RP, Bento LC, Bortolucci ACP, Alexandre AM, Vaz ADC, Schimidel D, Pedro EdC, Perin F, Nozawa Mendes CEA, Barroso RdS, Bacal NS (2016) Technical advances in flow cytometry based diagnosis and monitoring of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Einstein 14(3):366–373
Galtseva IV, Fidarova ZT, Mikhailova EA, Borisov VI, Troitskaia VV, Parovichnikova EN, Savchenko VG (2014) A new approach of PNH clones detection. Blood 124:5149
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thanks Mr Kaushal Kumar, Technical staff, Flow cytometry Lab, SGPGI, Lucknow.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical Standards
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was taken from all the individuals participants included in this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahman, K., Gupta, R., Harankhedkar, S. et al. Utility of CD157 as a Common Leukocytes Marker for Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria Screening in a Single Tube Five Color Combination. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus 34, 304–309 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-017-0867-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-017-0867-z