Abstract
Background
Upregulated gene 4 (URG4) is a recently described oncogene that upregulates cell proliferation. Its overexpression has been identified in many malignancies, and it is thought to be related to tumour progression, angiogenesis, metastasis and the recurrence of many cancers. This is the first study to show its expression in breast cancer patients and its association with clinicopathological characteristics in these patients.
Methods
Fifty invasive ductal breast carcinoma cases and 25 control cases were included in the study. Tumourous tissues and control tissues were assessed molecularly for quantification of mRNA expression of URG4 and immunohistochemically for protein expression of URG4.
Results
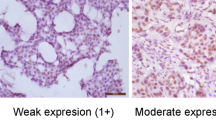
The mean ages of the patients and controls were 54.3 ± 11.3 and 38.9 ± 9.7 years, respectively. The expression levels of URG4 mRNA in tumour tissues were higher compared to control breast tissues (p = 0.023). An immunohistochemical assessment suggested that URG4 is strongly expressed in normal breast tissues and lower-grade (grades I and II) ductal carcinomas of the breast, but it is weakly expressed in high-grade (grade III) ductal breast carcinomas. Additionally, the immunohistochemical and molecular expression results of URG4 were relevant to most prognostic parameters (tumour size, oestrogen and progesterone receptor status, HER2 status and Ki67 proliferative index) for breast cancer. However, unlike the immunohistochemical studies, the molecular studies revealed that there was no significant difference in URG4 expression for different grades of tumour tissues.
Conclusion
The literature data suggest that URG4 overexpression is associated with poor prognosis in many types of cancer. Conversely, our results in breast cancer specimens indicate that URG4 overexpression in breast ductal carcinomas is significantly associated with good prognostic parameters. Nevertheless, these preliminary findings should be confirmed by further studies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tufan NL, Lian Z, Liu J, Pan J, Arbuthnot P, Kew M, et al. Hepatitis Bx antigen stimulates expression of a novel cellular gene, URG4, that promotes hepatocellular growth and survival. Neoplasia. 2002;4:355–68.
Li W, Zhou N. URG4 upregulation is associated with tumor growth and poor survival in epithelial ovarian cancer. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2012;286:209–15.
Song J, Xie H, Lian Z, Yang G, Du R, Zou X, et al. Enhanced cell survival of gastric cancer cells by a novel gene URG4. Neoplasia. 2006;8:995–1002.
Wu M, Chen J, Wang Y, Hu J, Liu C, Feng C, et al. URGCP/URG4 promotes apoptotic resistance in bladder cancer cells by activating NF-κB signalling. Oncotarget. 2015;6:30887–901.
Chen LC, Zhang HY, Qin ZY, Wang Y, Mao Y, Yao Y, et al. Serological identification of URGCP as a potential biomarker for glioma. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2014;20:301–7.
Cai J, Li R, Xu X, Zhang L, Wu S, Yang T, et al. URGCP promotes non-small cell lung cancer invasiveness by activating the NF-κB-MMP-9 pathway. Oncotarget. 2015;6:36489–504.
Dodurga Y, Eroğlu C, Seçme M, Elmas L, Avcı ÇB, Şatıroğlu-Tufan NL, et al. Anti-proliferative and anti-invasive effects of ferulic acid in TT medullary thyroid cancer cells interacting with URG4/URGCP. Tumour Biol. 2016;37:1933–40.
Dodurga Y, Gundogdu G, Koc T, Yonguç GN, Kucukatay V, Satıroğlu-Tufan NL, et al. Expression of URG4/URGCP, Cyclin D1, Bcl-2, and Bax genes in retinoic acid treated SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2013;17:346–9.
Dodurga Y, Avcı CB, Susluer SY, Satıroğlu Tufan NL, Gündüz C. The expression of URGCP gene in prostate cancer cell lines: correlation with rapamycin. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39:10173–7.
Dodurga Y, Oymak Y, Gündüz C, Satıroğlu-Tufan NL, Vergin C, Çetingül N, et al. Leukemogenesis as a new approach to investigate the correlation between up regulated gene 4/upregulator of cell proliferation (URG4/URGCP) and signal transduction genes in leukemia. Mol Biol Rep. 2013;40:3043–8.
Yu G, Meng Q, Zhang T, Zeng C, He B, Zhang S. URG4 expression is a novel prognostic factor for the progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and overall survival of patient. Onco Targets Ther. 2016;9:3059–65.
Hong L, Qing O, Ji Z, Chengqu Z, Ying C, Hao C, et al. Downregulation of miR-16 via URGCP pathway contributes to glioma growth. Sci Rep. 2017;7:13470.
Zhang L, Huang H, Zhang L, Hou T, Wu S, Huang Q, et al. URG4 overexpression is correlated with cervical cancer progression and poor prognosis in patients with early-stage cervical cancer. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:885.
Morgensztern D, McLeod HL. PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway as a target for cancer therapy. Anticancer Drugs. 2005;16:797–803.
Nahta R, Yu D, Hung MC, Hortobagyi GN, Esteva FJ. Mechanisms of disease: understanding resistance to HER2-targeted therapy in human breast cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2006;3:269–80.
Likhite VS, Stossi F, Kim K, Katzenellenbogen BS, Katzenellenbogen JA. Kinase-specific phosphorylation of the estrogen receptor changes receptor interactions with ligand, deoxyribonucleic acid, and coregulators associated with alterations in estrogen and tamoxifen activity. Mol Endocrinol. 2006;20:3120–32.
Lee ER, Kim JY, Kang YJ, Ahn JY, Kim JH, Kim BW, et al. Interplay between PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling pathways in DNA-damaging drug-induced apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1763:958–68.
Liang K, Lu Y, Li X, Zeng X, Glazer RI, Mills GB, et al. Differential roles of phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 and akt1 expression and phosphorylation in breast cancer cell resistance to Paclitaxel, Doxorubicin, and gemcitabine. Mol Pharmacol. 2006;70:1045–52.
Altomare DA, Testa JR. Perturbations of the AKT signaling pathway in human cancer. Oncogene. 2005;24:7455–64.
Knuefermann C, Lu Y, Liu B, Jin W, Liang K, Wu L, et al. HER2/PI-3K/Akt activation leads to a multidrug resistance in human breast adenocarcinoma cells. Oncogene. 2003;22:3205–12.
Ahmad S, Singh N, Glazer RI. Role of AKT1 in 17beta-estradiol- and insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I)-dependent proliferation and prevention of apoptosis in MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1999;58:425–30.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by Balıkesir University Coordinator of Scientific Research Projects. The authors would like to appreciate the help from Prof. Dr. Feray Koçkar and Dr. Esra Tokay, for their guidance on the processes in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Aslan, F., Avcıkurt, A.S. URG4 expression in invasive breast carcinoma and its relation to clinicopathological characteristics. Breast Cancer 26, 485–491 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-019-00947-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-019-00947-6